For watches, PVD coating is an exceptionally effective and popular choice for adding durability and color. It provides a hard, corrosion-resistant finish that significantly enhances both the aesthetic and the longevity of the timepiece. This technology, which bonds a thin film of material to the watch case at a molecular level, offers a robust layer of protection against daily wear and environmental factors.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) dramatically improves a watch's scratch resistance and prevents corrosion, offering a durable finish in various colors. However, it is a surface coating, not solid metal, meaning a deep enough gouge can still penetrate the layer and reveal the base material underneath.
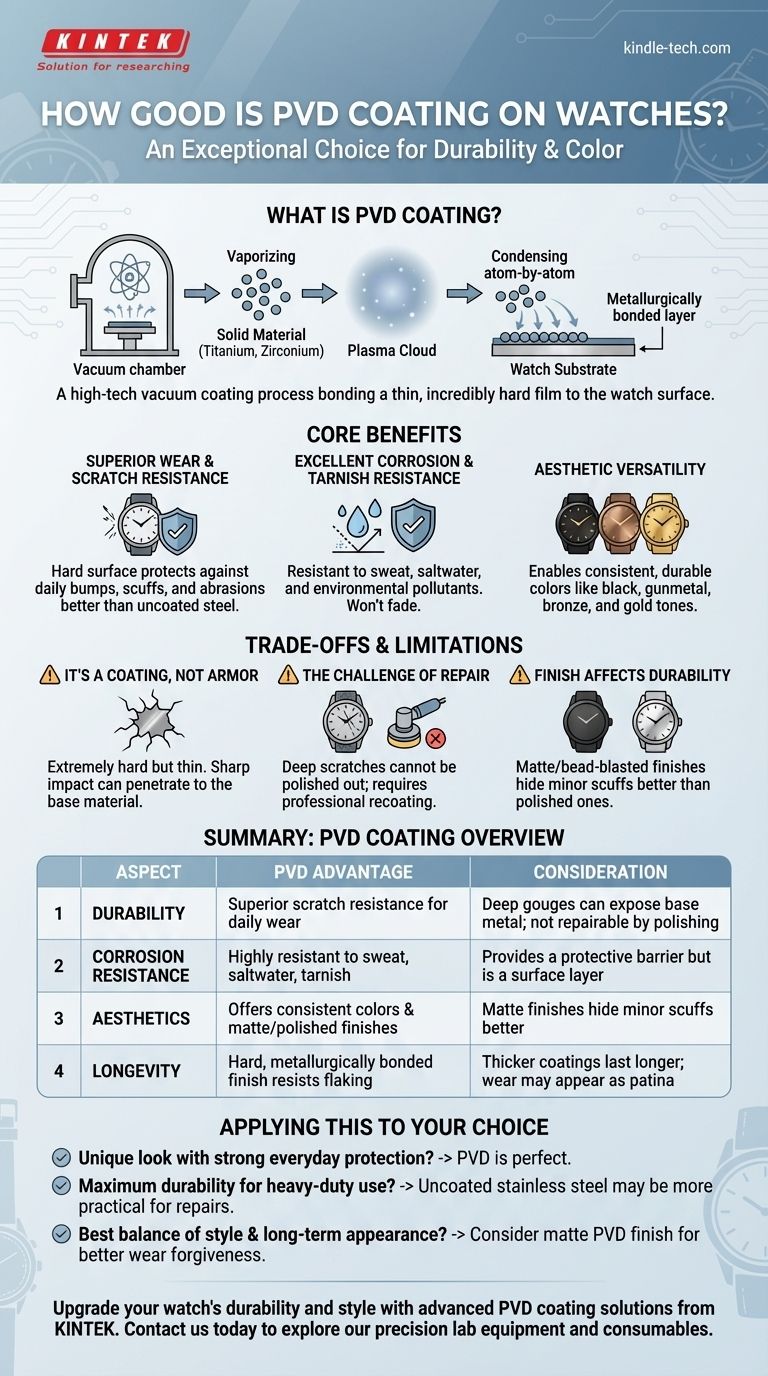
What Exactly is PVD Coating?
The Science in Simple Terms
Physical Vapor Deposition is a high-tech vacuum coating process. In simple terms, a solid material (like titanium or zirconium nitride) is vaporized into a plasma inside a vacuum chamber. The watch components, or 'substrates', are then introduced, and the vaporized material condenses onto them, one atom at a time.
This process forms a new, incredibly thin, but extremely hard and durable surface that is metallurgically bonded to the base metal of the watch.
The Result: A Fused, Resilient Surface
Unlike painting or electroplating, which just lays a coating on top, PVD integrates the coating with the substrate. This creates a finish that is not prone to flaking or chipping. The primary goal is to increase wear and oxidation resistance, making the surface of the watch significantly harder than raw stainless steel.
The Core Benefits of a PVD-Coated Watch
Superior Wear and Scratch Resistance
The primary advantage of PVD is its hardness. This treatment protects a watch from the minor bumps, scuffs, and abrasions of everyday life far better than an uncoated steel or gold-plated watch would.
Excellent Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
PVD coatings provide an inert barrier that is highly resistant to sweat, saltwater, and environmental pollutants. The finish will not tarnish or fade, and testing has shown it can withstand over 1,200 hours of neutral salt spray, meeting rigorous industry standards for corrosion protection.
Aesthetic Versatility
PVD is the technology behind the popular black, gunmetal, bronze, and even gold-toned watches. It allows manufacturers to achieve consistent, durable colors that would be impossible with the base metal alone, dramatically expanding design possibilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
It's a Coating, Not Indestructible Armor
This is the most critical point to understand. While PVD is extremely hard, it is still a thin layer. A sufficiently sharp or forceful impact—such as scraping the watch against a brick wall or dropping it on concrete—can cut through the PVD layer and expose the silver-colored steel beneath.
The Challenge of Repair
Unlike a standard stainless steel watch that can have scratches polished out, a deep scratch on a PVD watch cannot be repaired. Polishing would simply remove the coating around the scratch. The only true fix is to have the entire part professionally recoated, which is often not practical or cost-effective.
Finish Affects Visual Durability
Thicker PVD coatings are more durable, but the visual finish also plays a role. A matte or bead-blasted PVD finish tends to hide minor scuffs better than a highly polished, shiny PVD finish. Over many years, wear may appear as a slight "patina" on edges, which some find appealing.
How to Apply This to Your Choice
A PVD-coated watch is an excellent option for most people, but your specific needs should guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is a unique look with strong everyday protection: PVD is a perfect choice, offering robust defense against the scuffs and scratches of daily life.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for heavy-duty use: Understand that a deep gouge is permanent. For a true "beater" watch, uncoated stainless steel may be more practical, as its deeper scratches can be polished and refinished over time.
- If you want the best balance of PVD style and long-term appearance: Consider a watch with a matte PVD finish, as it will be more forgiving of minor wear and tear than a polished version.
Armed with this understanding, you can confidently choose a PVD-coated watch that aligns perfectly with your lifestyle and aesthetic goals.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Coating Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Superior scratch resistance for daily wear | Deep gouges can expose base metal; not repairable by polishing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly resistant to sweat, saltwater, and tarnish | Provides a protective barrier but is a surface layer |
| Aesthetics | Offers consistent colors (black, bronze, gold) and matte/polished finishes | Matte finishes hide minor scuffs better than polished ones |
| Longevity | Hard, metallurgically bonded finish resists flaking and chipping | Thicker coatings last longer; wear may appear as a patina over time |
Upgrade your watch’s durability and style with advanced PVD coating solutions from KINTEK. Whether you're a watch manufacturer seeking to enhance product longevity or a lab testing materials for wear resistance, KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables to support your coating development and quality control. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can help you achieve superior, durable finishes for your timepieces!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















