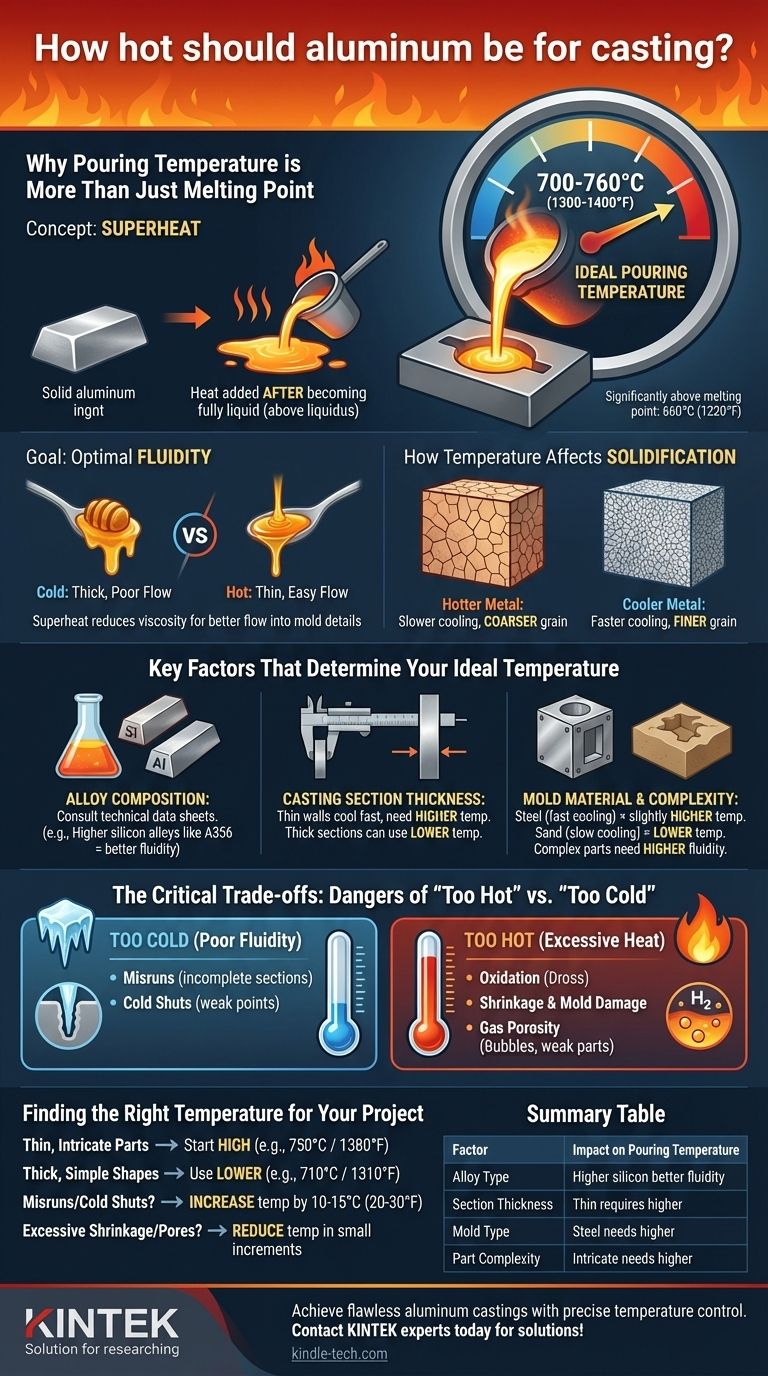
For most common aluminum alloys, the ideal pouring temperature for casting is typically between 700-760°C (1300-1400°F). This range is significantly above aluminum's melting point of 660°C (1220°F) and serves as a critical starting point. The precise temperature you need depends directly on your specific alloy, the thickness of your part, and the complexity of your mold.
The core principle is not simply to melt the aluminum, but to achieve the optimal fluidity to fill the mold completely without introducing defects caused by excessive heat. Finding this balance is the key to a successful casting.
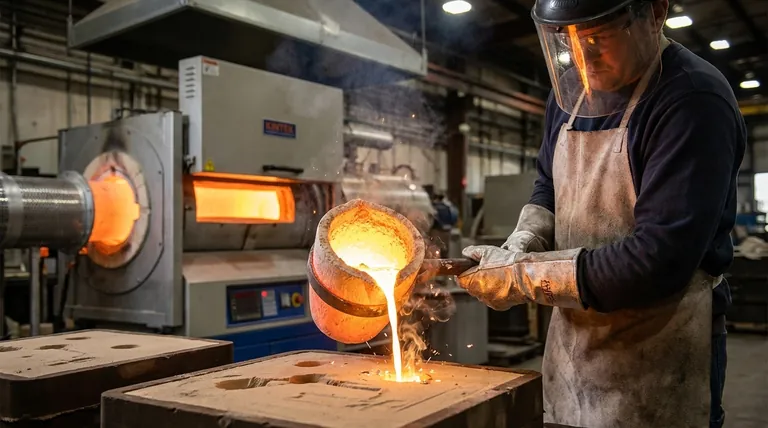

Why Pouring Temperature is More Than Just Melting Point
Simply reaching the melting point is not enough. To create a sound casting, you must add additional heat, a concept known as superheat. This ensures the metal remains fully liquid long enough to travel through the mold and fill every detail.
Understanding Superheat
Superheat is the amount of heat added to a metal after it has become fully liquid (i.e., above its liquidus temperature).
This extra thermal energy acts as a buffer. It compensates for the heat that the molten metal loses to the cooler mold walls as it flows.
The Goal: Optimal Fluidity
Think of fluidity like the viscosity of honey. When cold, honey is thick and flows poorly. When warmed, it becomes thin and flows easily.
Superheat does the same for molten aluminum. A higher temperature reduces its viscosity, allowing it to flow more freely into thin sections and intricate details of the mold cavity.
How Temperature Affects Solidification
The pouring temperature directly influences how the aluminum cools and solidifies, which determines the final grain structure of the part.
Hotter metal cools more slowly, resulting in a larger, coarser grain structure. Cooler metal that solidifies quickly tends to have a finer, stronger grain structure.
Key Factors That Determine Your Ideal Temperature
The 700-760°C (1300-1400°F) range is a general guideline. You must adjust your target temperature based on three primary variables.
Alloy Composition
Different aluminum alloys have different melting ranges and fluidity characteristics. For example, alloys with higher silicon content (like A356) are designed for casting and have excellent fluidity.
Always consult the technical data sheet for your specific alloy to find its recommended pouring temperature range.
Casting Section Thickness
This is one of the most important factors. Thin-walled parts have a very high surface-area-to-volume ratio, causing them to cool extremely fast.
To compensate, you must use a higher pouring temperature to ensure the metal fills the entire section before it solidifies prematurely. Thick sections can be poured at lower temperatures.
Mold Material and Complexity
The type of mold you use dictates how quickly heat is extracted from the metal. A permanent steel mold pulls heat out much faster than a sand mold.
Therefore, you may need a slightly higher pouring temperature for a permanent mold to achieve the same result as in a sand mold. Similarly, more complex parts with fine details require higher fluidity and thus a higher temperature.
The Critical Trade-offs: Dangers of "Too Hot" vs. "Too Cold"
Deviating from the optimal temperature window in either direction will introduce predictable defects into your final casting.
The Problem with Pouring Too Cold
If the metal is not hot enough, its fluidity will be poor. This leads to defects where the metal freezes before it can completely fill the mold cavity.
Common issues include misruns (incomplete sections) and cold shuts (when two streams of metal meet but are too cool to fuse together properly), creating a critical weak point.
The Problem with Pouring Too Hot
Pouring with excessive heat is a common mistake that creates severe, often invisible, problems.
Overheating the aluminum leads to increased oxidation (dross formation), greater shrinkage, and can damage the mold. Most importantly, it dramatically increases the risk of gas porosity.
The Role of Hydrogen Porosity
Molten aluminum readily absorbs hydrogen from the atmosphere, and its capacity to hold this gas increases with temperature.
As the superheated metal cools in the mold, its ability to hold the dissolved hydrogen plummets. The gas comes out of solution and forms tiny bubbles, creating gas porosity that gets trapped in the final part, severely reducing its strength and integrity.
Finding the Right Temperature for Your Project
Use the properties of your casting to determine your starting point within the standard range.
- If you are casting thin, intricate parts: Start at the higher end of the recommended range (e.g., 750°C / 1380°F) to maximize fluidity and ensure complete mold filling.
- If you are casting thick, simple shapes: Use a lower temperature (e.g., 710°C / 1310°F) to minimize shrinkage, reduce the risk of gas porosity, and promote a finer grain structure.
- If your parts show misruns or cold shuts: Your pouring temperature is almost certainly too low. Increase it in small increments of 10-15°C (20-30°F).
- If you see excessive shrinkage or find fine pores on machined surfaces: Your pouring temperature is likely too high. Reduce it in small increments to minimize gas absorption and thermal contraction.
Systematically controlling your pouring temperature is the most critical step toward producing sound, high-quality aluminum castings.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Pouring Temperature |
|---|---|
| Alloy Type | Higher silicon alloys (e.g., A356) have better fluidity; consult data sheets. |
| Section Thickness | Thin sections require higher temperatures; thick sections can use lower temperatures. |
| Mold Type | Steel molds (fast cooling) need higher temps; sand molds (slow cooling) need lower temps. |
| Part Complexity | Intricate parts with fine details require higher temperatures for complete fill. |
Achieve flawless aluminum castings with precise temperature control.
At KINTEK, we understand that the right pouring temperature is critical for producing strong, defect-free parts. Our specialized lab equipment, including high-temperature furnaces and precise temperature controllers, is designed to help you maintain the optimal 700-760°C range for superior fluidity and grain structure.
Whether you are working with thin-walled intricate parts or thick, simple shapes, KINTEK provides the reliable tools you need to avoid common defects like misruns, cold shuts, and gas porosity.
Ready to optimize your casting process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's aluminum casting needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a pyrolysis furnace? Transform Waste into Valuable Products with Thermal Decomposition
- Is aluminum brazing as strong as welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Joining Method
- Why are high-purity argon and vacuum necessary for 14Cr ODS steel? Essential Protection for Mechanical Alloying
- What is the heating rate during heat treatment? Master the Key to Material Integrity
- How does furnace cooling occur in the heat treatment process? A Guide to Controlled Slow Cooling
- How are vacuum removal systems utilized during the synthesis of titanium alloy modification molecules? | KINTEK
- What is the function of a high-temperature heat treatment furnace in graphite and copper composite pre-treatment?
- What environments does a high-vacuum furnace provide for h-BN synthesis? Master High-Purity Nanopowder Production



















