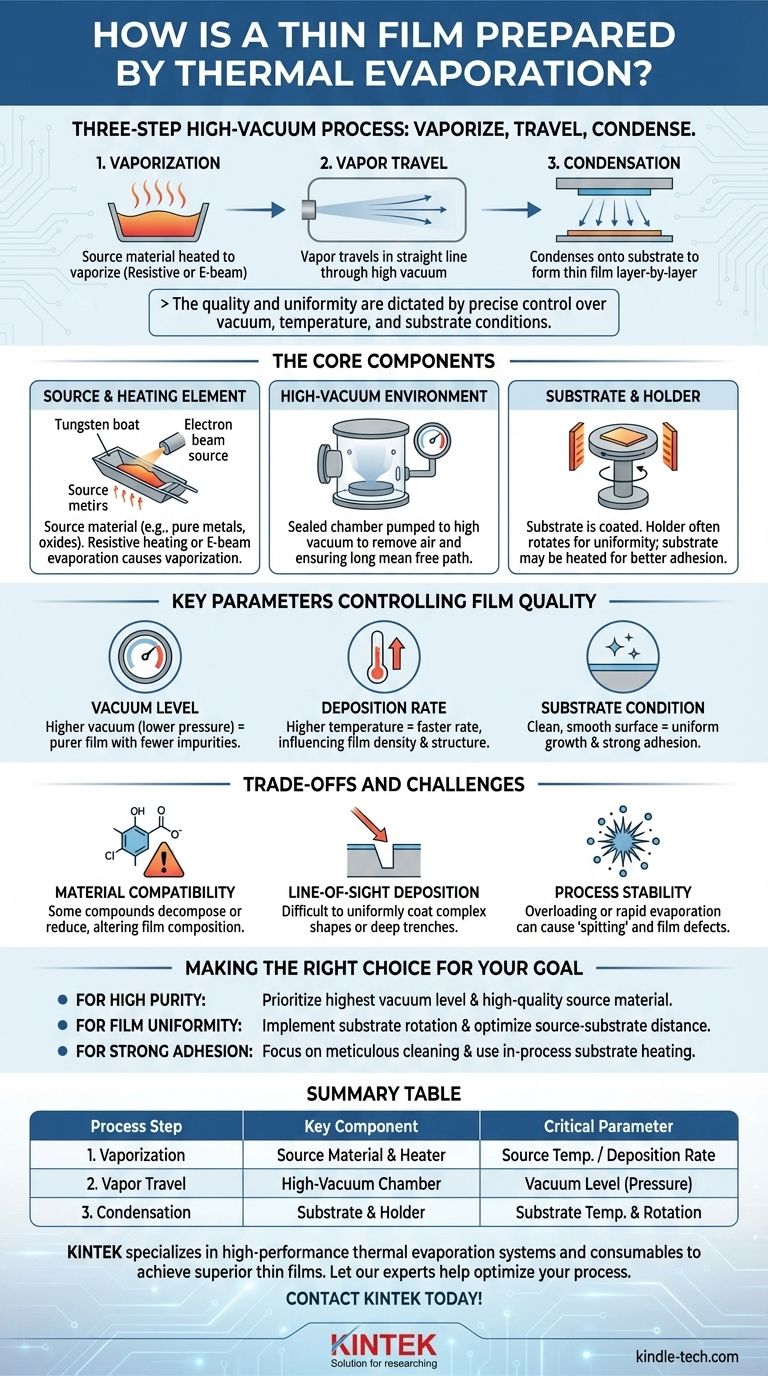
In essence, thermal evaporation prepares a thin film using a three-step process inside a high-vacuum chamber. First, a source material is heated using a resistive element or an electron beam until it vaporizes. Second, these vaporized atoms or molecules travel in a straight line through the vacuum. Finally, they land on a cooler surface, known as the substrate, where they condense and build up layer-by-layer to form a solid, thin film.
The core principle of thermal evaporation is phase change under vacuum. It is a fundamentally simple, line-of-sight deposition technique where the quality and uniformity of the final film are dictated by precise control over vacuum, temperature, and substrate conditions.
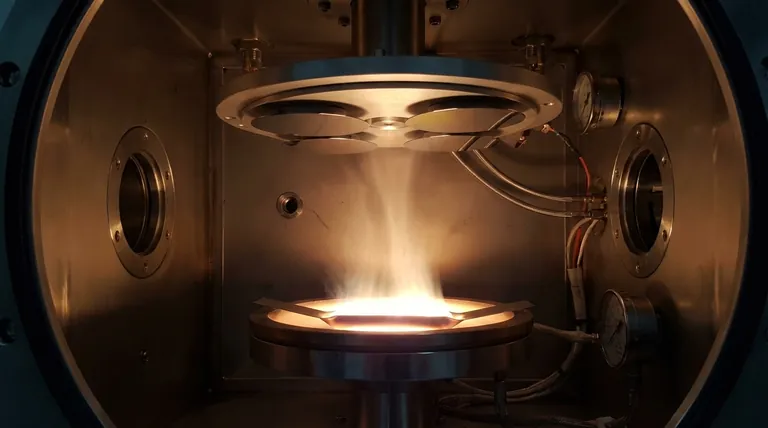
The Core Components of the Evaporation Process
To understand how a film is prepared, we must first understand the essential components of the system and the role each one plays.
The Source Material and Heating Element
The process begins with the material you intend to deposit, known as the source material. This can range from pure metals and non-metals to specific oxides and nitrides.
This material is placed in a container, often a tungsten "boat," or crucible. Resistive heating involves passing a high electrical current through the boat, causing it to heat up and vaporize the source material.
Alternatively, e-beam evaporation uses a high-energy electron beam focused directly onto the source material, causing localized vaporization.
The High-Vacuum Environment
The entire process occurs within a sealed chamber pumped down to a high vacuum. This vacuum is critical for two reasons.
First, it removes air and other gas molecules that could react with the hot vapor, ensuring the purity of the deposited film.
Second, it allows the vaporized material to travel from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles. This unimpeded, straight-line travel is known as a long mean free path.
The Substrate and Holder
The substrate is the surface onto which the thin film is deposited. It is positioned above the source material on a holder or stage.
To ensure the film has an even thickness across the entire surface, the holder is often rotated during deposition.
The substrate may also be heated. This can improve the film's adhesion and influence its final crystalline structure.
Key Parameters Controlling Film Quality
The success of a deposition is not automatic. It depends on carefully managing several key process parameters that directly impact the final film's characteristics.
Vacuum Level
The quality of the vacuum is paramount. A higher degree of vacuum (lower pressure) directly translates to a purer film with fewer trapped impurities from residual gases in the chamber.
Deposition Rate
The rate at which the film grows is controlled by the temperature of the source material. A higher temperature leads to a faster evaporation rate and, consequently, a faster deposition rate. This rate can influence the film's density and structure.
Substrate Condition
The state of the substrate is just as important as the deposition process itself. A rough or unclean substrate surface can lead to non-uniform film growth and poor adhesion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While effective, thermal evaporation is not without its limitations and operational challenges that require careful management.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for thermal evaporation. Some compounds can decompose or reduce when heated, meaning the deposited film will not have the same chemical composition as the source material.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because vapor travels in straight lines, thermal evaporation is a line-of-sight process. This makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes or the sides of deep trenches.
Process Stability
There is a constant balance between maximizing the deposition rate and maintaining stability. Overloading a heating boat or evaporating too quickly can cause particle fracturing or "spitting," where small clumps of solid material are ejected onto the substrate, creating defects in the film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The applications for thermal evaporation are broad, from conductive layers in OLED displays and solar cells to bonding layers for semiconductor wafers. To achieve success, you must tailor the process to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is high purity: Prioritize achieving the highest possible vacuum level and ensuring your source material is of high quality.
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: Implement controlled substrate rotation and optimize the distance between the source and the substrate.
- If your primary focus is strong adhesion: Focus on meticulous substrate cleaning and consider using in-process substrate heating.
By mastering these fundamental principles, you can effectively leverage thermal evaporation to create high-quality thin films for a wide range of advanced applications.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Component | Critical Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vaporization | Source Material & Heater (Boat or E-beam) | Source Temperature / Deposition Rate |
| 2. Vapor Travel | High-Vacuum Chamber | Vacuum Level (Pressure) |
| 3. Condensation | Substrate & Holder | Substrate Temperature & Rotation |
Ready to achieve superior thin films for your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems and consumables. Our solutions are designed to help you master vacuum deposition, ensuring high purity, excellent uniformity, and strong adhesion for your specific application—from OLEDs and solar cells to semiconductor bonding.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's thin-film needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum evaporation plating method? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the uses of thermal evaporation? Essential for Electronics, Optics & Decorative Finishes
- What is the temperature of e-beam evaporation? Mastering the Two-Zone Thermal Process for Precision Films
- What is the difference between sputtering and evaporation deposition? A Guide to Choosing the Right PVD Method
- What is the process of vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision Coatings
- How is physical vapor deposition performed using an electron beam evaporator? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Films
- Which parameter effect on thin film formation in thermal evaporation? Master the Key Variables for Superior Films



















