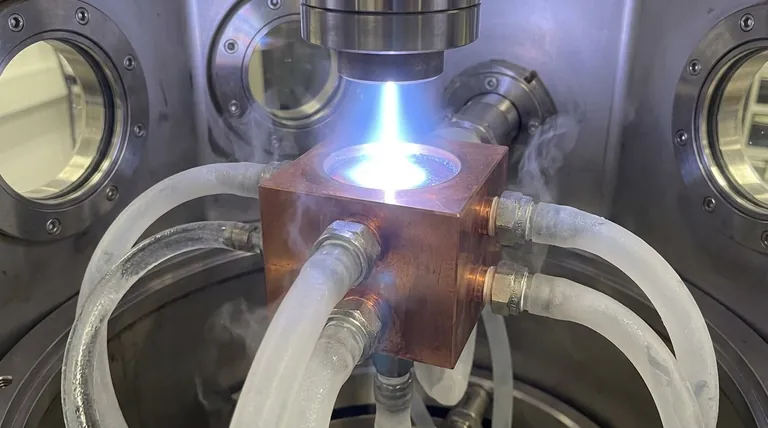
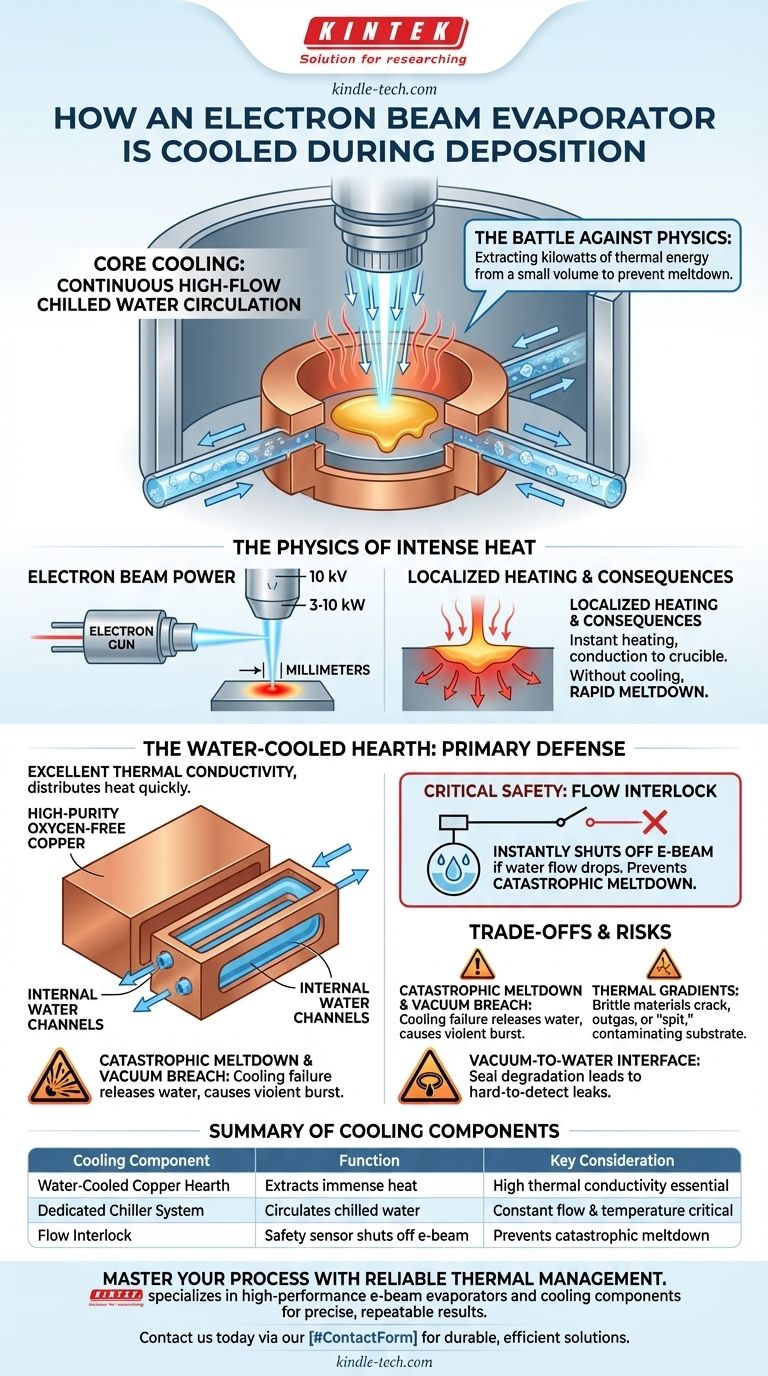
At its core, an electron beam evaporator is actively cooled by a continuous, high-flow circulation of chilled water. This water runs through dedicated channels built directly into the copper crucible hearth, which holds the material being evaporated. This aggressive cooling is not an auxiliary feature but a fundamental requirement to manage the immense, localized heat generated by the high-energy electron beam.
The central principle to grasp is that e-beam cooling is a battle against physics. The system must continuously extract kilowatts of thermal energy from a very small volume to prevent the evaporator itself from melting and to maintain the stability of the entire deposition process.

The Physics of Intense Heat Generation
To understand the cooling system, you must first appreciate the thermal challenge it solves. An electron beam is an incredibly efficient method for delivering a massive amount of energy to a precise location.
The Power of the Electron Beam
The electron gun accelerates a beam of electrons with high voltage, typically around 10 kilovolts (kV). This beam carries significant power, often in the range of 3 to 10 kilowatts (kW), and focuses it onto a spot only a few millimeters in diameter on the source material.
Localized Heating and Its Consequences
This concentration of power instantly heats the target material past its melting and boiling points, creating the vapor for deposition. However, this intense energy also conducts directly into the structure holding the material—the crucible. Without active cooling, this heat would rapidly melt the crucible itself, destroying the evaporator.
The Core Cooling Mechanism: The Water-Cooled Hearth
The primary defense against this thermal load is the design of the crucible hearth. It is an elegant piece of thermal engineering designed for one purpose: maximum heat extraction.
The Role of the Copper Block
The crucible hearth is machined from a large block of high-purity, oxygen-free copper. Copper is chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity, which allows it to quickly pull heat away from the small evaporation spot and distribute it throughout the block.
Internal Water Channels
This copper block is not solid. It contains a network of internal, sealed channels. A dedicated chiller system continuously pumps cold water—often a deionized water and glycol mixture—at a high flow rate through these channels.
The Chiller and Flow Interlock
The chiller acts as the heart of the cooling system, supplying a constant source of refrigerated water. Critically, the e-beam power supply is connected to a flow interlock. If the water flow drops below a safe level, this sensor instantly shuts off the high voltage to the electron gun, preventing a catastrophic meltdown.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While essential, this aggressive cooling strategy introduces its own set of operational challenges and risks that every operator must understand.
Risk of Catastrophic Meltdown
The most significant risk is cooling failure. If the water flow stops for even a few seconds while the beam is on, the electron beam will melt through the source material and then through the copper crucible itself. This releases water directly into the high-vacuum chamber, causing a violent pressure burst and contaminating the entire system.
Thermal Gradients and Material Integrity
The extreme temperature difference between the molten pool and the water-cooled crucible walls creates immense thermal stress. For brittle materials like dielectrics (e.g., silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide), this can cause the source material to crack, outgas violently, or "spit", launching small particles that contaminate the substrate.
The Vacuum-to-Water Interface
An e-beam evaporator requires robust seals (typically elastomeric O-rings) between the copper hearth and the vacuum chamber feedthroughs that supply the water. Any degradation or failure of these seals can lead to a slow water leak into the vacuum system, which can be difficult to detect and ruins process consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Proper thermal management is not just about preventing failure; it is about ensuring a stable and repeatable deposition. Your operational focus will determine where you place your attention.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Ensure the chiller temperature and water flow rate are constant, as fluctuations will directly impact the evaporation rate and film thickness.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Implement a strict maintenance schedule for the chiller and regularly inspect all water lines and seals for any signs of leaks or degradation.
- If you are depositing brittle dielectric materials: Use a controlled power ramp and a wide beam sweep pattern to pre-heat the source material slowly, reducing thermal shock and the risk of spitting.
By mastering the principles of thermal management, you gain direct control over the quality, reliability, and safety of your deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Component | Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Water-Cooled Copper Hearth | Extracts immense heat from the electron beam impact point. | High thermal conductivity is essential to prevent melting. |
| Dedicated Chiller System | Circulates chilled water (often a deionized water/glycol mix) through the hearth. | Constant flow and temperature are critical for process stability. |
| Flow Interlock | Safety sensor that shuts off the electron beam if water flow is interrupted. | Prevents catastrophic meltdown and water release into the vacuum chamber. |
Master your deposition process with reliable thermal management. The quality and safety of your e-beam evaporation depend on robust cooling systems. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including electron beam evaporators and the critical cooling components that ensure their stable operation. Our expertise helps laboratories achieve precise, repeatable results while minimizing downtime and risks. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs with durable, efficient solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















