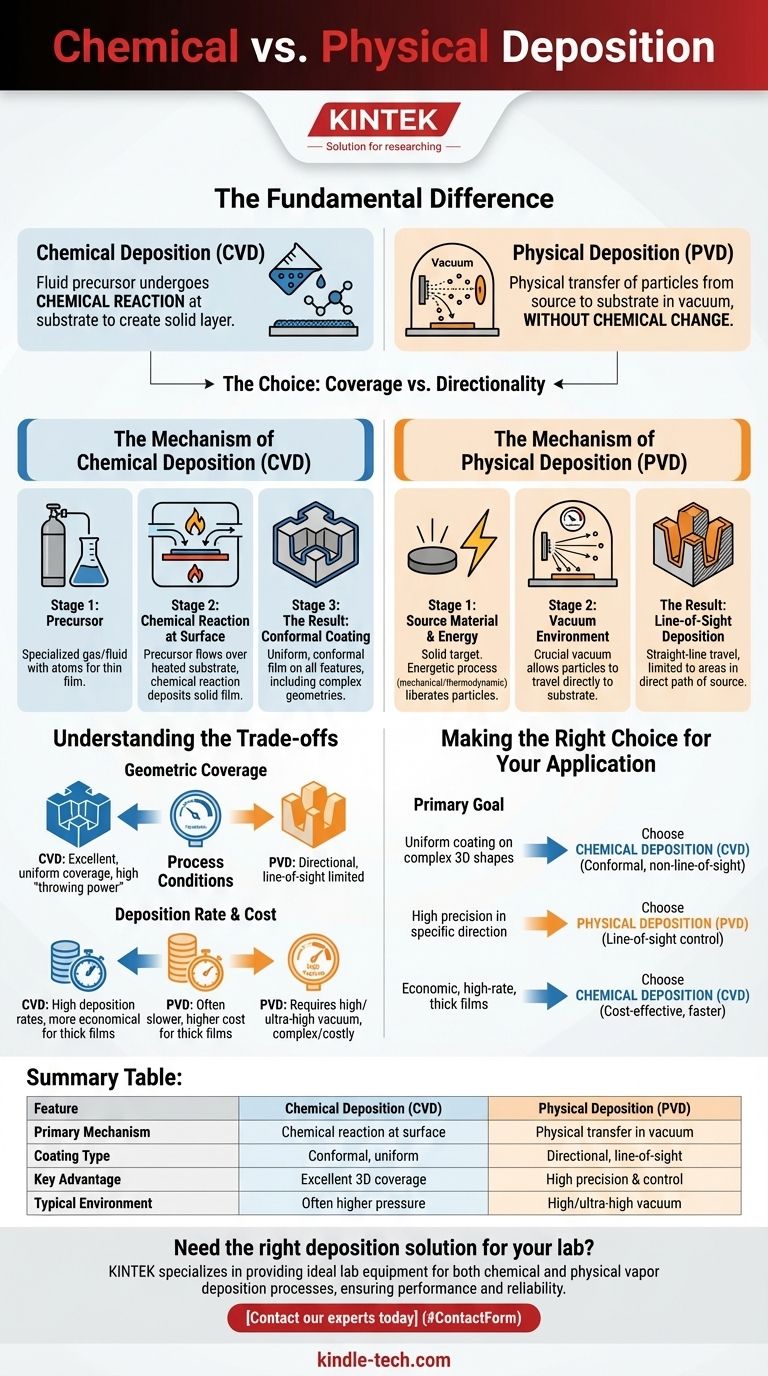
The fundamental difference between chemical and physical deposition lies in how the material arrives and forms on a surface. Chemical deposition involves a fluid precursor that undergoes a chemical reaction at the substrate to create a solid layer. In contrast, physical deposition uses mechanical or thermodynamic force in a vacuum to transfer particles from a source to the substrate without a chemical change.
The choice between chemical and physical deposition is ultimately a choice between coverage and directionality. Chemical methods excel at creating uniform, conformal coatings on complex shapes, while physical methods offer precise, line-of-sight deposition.
The Mechanism of Chemical Deposition
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most common form of chemical deposition. Its process is defined by a reaction that builds the new layer atom by atom.
The Role of the Precursor
The process begins with a precursor material, typically a specialized gas or fluid. This precursor contains the atoms that will eventually form the thin film.
The Chemical Reaction at the Surface
This precursor is introduced into a chamber where it flows over the target object, known as the substrate. Energy (like heat) triggers a chemical reaction on the substrate's surface, breaking down the precursor and depositing a solid film.
The Result: Conformal Coating
Because the deposition is driven by a chemical reaction that can occur on any available surface, the resulting film is highly conformal. It uniformly coats all features, including holes, recesses, and complex 3D geometries, without being limited by the direction of the source.
The Mechanism of Physical Deposition
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) covers a range of techniques that physically move material from a source to a target.
The Source Material and Energy
The process starts with a solid source material, or "target." An energetic process—such as mechanical, electromechanical, or thermodynamic force—is used to liberate atoms or molecules from this source.
The Vacuum Environment
This entire process occurs within a vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it allows the freed particles to travel directly to the substrate without colliding with other gas molecules in the air.
The Result: Line-of-Sight Deposition
The particles travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate, creating a line-of-sight deposition. Any area not in the direct path of the source, such as the sides of a deep trench, will receive little or no coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The distinct mechanisms of CVD and PVD create clear advantages and disadvantages for different applications.
Geometric Coverage
CVD has a high "throwing power," allowing it to produce uniform films on intricate shapes. PVD is directional, which is a limitation for complex geometries but an advantage for applications requiring precise, patterned coatings.
Process Conditions
PVD almost always requires a high or ultra-high vacuum to function, which can add complexity and cost. CVD processes can often be run at higher pressures and do not typically require the same level of vacuum.
Deposition Rate and Cost
For creating thick coatings, CVD is often more economical. It can achieve high deposition rates and is generally better suited for large-scale production where uniformity over complex parts is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D shapes uniformly: Chemical deposition is the superior choice due to its non-line-of-sight, conformal nature.
- If your primary focus is depositing a material with high precision in a specific direction: Physical deposition provides the line-of-sight control necessary for these applications.
- If your primary focus is economic, high-rate production of thick films: Chemical deposition often offers a more cost-effective solution without requiring an ultra-high vacuum.
Understanding this core distinction between chemical reaction and physical transfer is the key to selecting the optimal process for your specific material and geometric needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Deposition (CVD) | Physical Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Chemical reaction at substrate surface | Physical transfer in a vacuum |
| Coating Type | Conformal, uniform on complex shapes | Directional, line-of-sight |
| Key Advantage | Excellent coverage of 3D geometries | High precision and control |
| Typical Environment | Often higher pressure | Requires high/ultra-high vacuum |
Need the right deposition solution for your lab's specific materials and geometries?
KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment for both chemical and physical vapor deposition processes. Whether you require uniform coatings on complex 3D parts or precise, directional thin films, our expertise ensures you get the performance and reliability your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin-film deposition needs with precision equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















