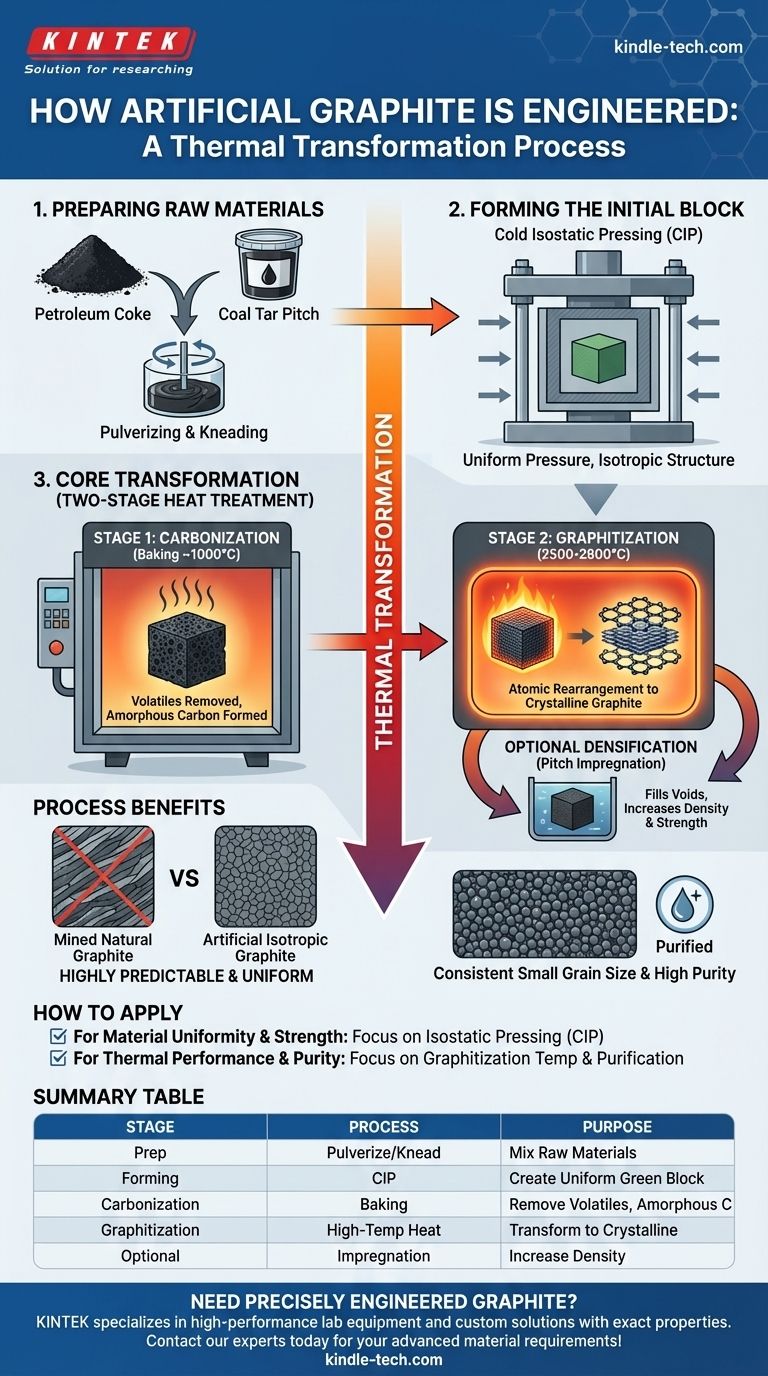
In short, artificial graphite is not mined but engineered. It is manufactured by taking carbon-rich raw materials like petroleum coke and coal tar pitch, pressing them into a desired shape, and then subjecting them to an intense, multi-stage heat treatment process that transforms the amorphous carbon into a pure, crystalline graphite structure.
The critical insight is that manufacturing artificial graphite is a process of thermal transformation. It converts disorganized carbon atoms into the highly ordered, layered lattice of graphite through extreme heat, typically between 2500-2800 °C.

The Manufacturing Blueprint: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The production of high-quality artificial graphite, particularly isostatic graphite, is a precise and controlled process. Each stage is designed to build specific properties into the final material.
H3: Preparing the Raw Materials
The process begins with carefully selected raw materials, primarily petroleum coke (a solid carbon byproduct of oil refining) and coal tar pitch (a binder).
The coke is first calcined (heated) to remove impurities and then pulverized into a fine powder. This powder is mixed and kneaded with the heated pitch, which acts as a binder, creating a uniform, paste-like mixture.
H3: Forming the Initial Block
This raw mixture is then formed into a solid block, often called a "green" block. A key method for high-performance graphite is Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP).
In this technique, the material is placed in a flexible mold and subjected to extremely high pressure from all directions using a liquid medium. This ensures the block has a highly uniform density and an isotropic structure, meaning its properties are the same in all directions.
The Core Transformation: From Carbon to Graphite
Once the block is formed, it undergoes a two-stage heat treatment that fundamentally alters its atomic structure.
H3: Stage 1: Carbonization (Baking)
The formed block is slowly heated in an oxygen-free environment. This initial baking process, known as carbonization, removes volatile compounds from the pitch binder.
The result is a hard, brittle, and porous block of amorphous carbon.
H3: Stage 2: Graphitization (The Final Conversion)
This is the most critical and energy-intensive step. The carbonized block is heated in a specialized furnace to extremely high temperatures, typically between 2500 °C and 2800 °C.
At these temperatures, the disorganized carbon atoms have enough energy to rearrange themselves into the ordered, hexagonal, and layered crystalline structure of graphite.
H3: Optional Densification
For applications requiring maximum density and minimal porosity, the block may undergo pitch impregnation after the initial carbonization.
The porous carbon block is saturated with liquid pitch and then re-baked. This fills the internal voids and significantly increases the final material's density and strength.
Understanding the Process Benefits
This multi-step manufacturing process is complex, but it provides precise control over the final material's properties, which is impossible with mined natural graphite.
H3: Achieving Isotropic Uniformity
The use of isostatic pressing is crucial. It eliminates the directional grain flow found in other forming methods, resulting in a graphite that is highly predictable and behaves uniformly regardless of orientation.
H3: Controlling Grain Size and Purity
By selecting specific coke powders and controlling the process parameters, manufacturers can produce graphite with very small and consistent grain sizes.
Furthermore, the extremely high temperatures of the graphitization stage also serve to vaporize and remove most impurities, leading to a final product of very high purity.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the manufacturing stages helps in selecting the right material for a specific technical application.
- If your primary focus is material uniformity and strength: The use of isostatic pressing is the most important factor, as it dictates the isotropic nature of the final block.
- If your primary focus is thermal performance and chemical purity: The graphitization temperature and optional purification steps are the critical determinants of the material's final quality.
Ultimately, the artificial manufacturing process allows graphite to be engineered as a predictable and high-performance industrial material.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Prep | Pulverizing & Kneading | Mix petroleum coke with coal tar pitch binder |
| Forming | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Create uniform, isotropic 'green' block |
| Carbonization | Baking (~1000°C) | Remove volatiles, form amorphous carbon |
| Graphitization | High-Temp Heating (2500-2800°C) | Transform carbon into crystalline graphite |
| Optional Step | Pitch Impregnation | Increase density and strength |
Need precisely engineered graphite for your lab or industrial application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including custom graphite solutions. Our expertise ensures you get materials with the exact properties you need—whether it's isotropic uniformity, high purity, or specific thermal performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's advanced material requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the melting point of graphite and why? Unlocking Extreme Heat Resistance
- Why is graphite the best conductor of heat? Understanding Its Directional Thermal Superiority
- What is the process of isostatic graphite manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Material Uniformity and Performance
- What are the properties of the graphite material? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Heat
- What is the temperature of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry? Mastering the Multi-Stage Heating Program
- Does graphite conduct electricity when melted? Discover the Secrets of Liquid Carbon Conductivity
- What is the role of an industrial graphitization furnace in SiC/MoSi2 coatings? Enhance Substrate Protection
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon



















