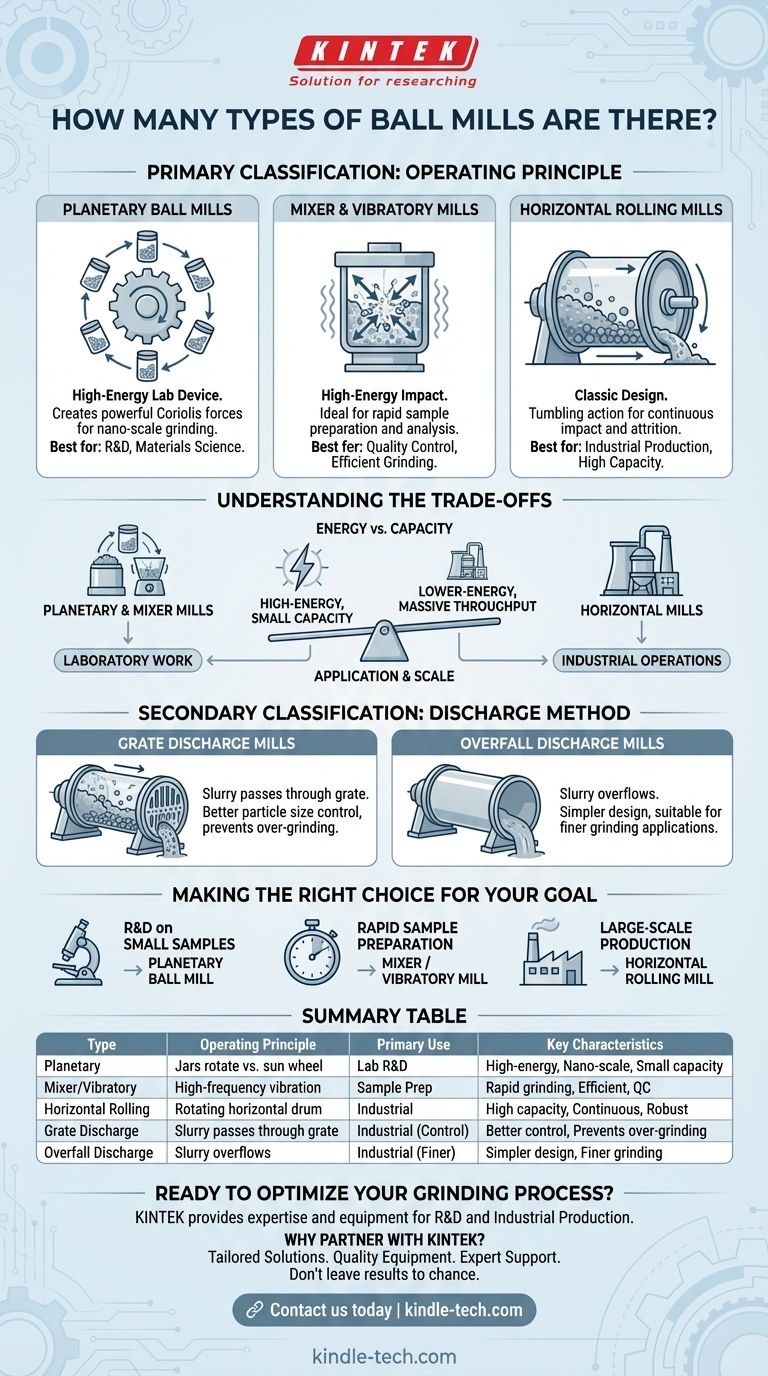
In short, ball mills are primarily categorized by their mechanical operating principle. While there is no single, fixed number, the most common types are planetary, mixer/vibratory, and horizontal rolling mills. A secondary classification, often used for industrial-scale mills, is based on how they discharge the processed material.
The "type" of ball mill is not just a label; it defines the machine's core mechanical action. This action dictates the mill's energy input, capacity, and ultimate suitability for a specific task, from high-precision lab research to large-scale industrial production.

The Primary Classification: Operating Principle
The most fundamental way to differentiate ball mills is by how they generate the grinding force. This mechanical action is the single biggest factor determining a mill's performance and application.
Planetary Ball Mills
Planetary mills are high-energy devices primarily used in laboratory settings.
They feature one large "sun" wheel on which several smaller grinding jars are mounted. As the sun wheel turns in one direction, the individual jars rotate on their own axes in the opposite direction, creating powerful Coriolis forces for extremely fine grinding.
Mixer and Vibratory Mills
These mills also generate high-energy impacts, making them ideal for rapid and efficient sample preparation.
Instead of rotating, the grinding jar is subjected to high-frequency vibrations or oscillations. The grinding media inside collide intensely, pulverizing the sample material quickly.
Horizontal Rolling Mills
This is the classic design most people imagine when thinking of a ball mill, especially for industrial applications.
A large cylindrical drum rotates on a horizontal axis, causing the grinding media and material inside to tumble. The grinding action occurs from the continuous impact and attrition as the media fall from the top of the drum to the bottom.
A Secondary Classification: Discharge Method
For larger, continuous-feed horizontal mills, the mechanism for removing the ground material provides another way to classify them.
Grate Discharge Mills
These mills have a grate, or a slotted plate, at the discharge end.
The grate holds back the larger grinding media while allowing the finely ground slurry to pass through. This design offers better control over the final particle size and prevents over-grinding.
Overfall Discharge Mills
This is a simpler design where the discharge opening is slightly smaller than the feed opening.
As new material is fed into the mill, the ground material slurry builds up and simply overflows out of the discharge end. This method is often used for finer grinding applications where lower throughput is acceptable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a ball mill type involves balancing energy, capacity, and the final goal of the grinding process. There is no single "best" type, only the most appropriate tool for the job.
Energy vs. Capacity
Planetary and mixer mills are high-energy systems. They achieve very fine particle sizes quickly but are limited to small capacities, typically measured in milliliters or a few liters.
Horizontal rolling mills are lower-energy-intensity systems. The grinding is less aggressive, but they can be built to enormous sizes to handle massive throughput required for industrial production.
Application and Scale
The high energy and precision of planetary and mixer mills make them indispensable for laboratory work, such as research and development, materials science, and quality control.
The high capacity and robust nature of horizontal rolling mills make them the standard for industrial operations like mineral processing, cement production, and large-scale chemical manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's scale and desired particle size will determine the correct type of ball mill.
- If your primary focus is research and development on small samples: A planetary ball mill offers the highest energy input for achieving nano-scale particle sizes.
- If your primary focus is rapid sample preparation for analysis: A mixer or vibratory mill provides the speed and efficiency needed for quality control labs.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: A horizontal rolling mill, specified as either a grate or overfall discharge type, is the only practical solution for high-capacity needs.
Ultimately, understanding these core classifications empowers you to select the precise technology that aligns with your specific operational requirements.
Summary Table:
| Type | Operating Principle | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planetary Ball Mill | Jars rotate opposite to sun wheel | Laboratory R&D | High-energy, nano-scale grinding, small capacity |
| Mixer/Vibratory Mill | High-frequency vibration/oscillation | Sample Preparation | Rapid grinding, efficient, ideal for quality control |
| Horizontal Rolling Mill | Cylindrical drum rotates horizontally | Industrial Production | High capacity, continuous operation, robust design |
| Grate Discharge | Slurry passes through a grate | Industrial (Control) | Prevents over-grinding, better particle size control |
| Overfall Discharge | Slurry overflows from discharge end | Industrial (Finer Grinding) | Simpler design, suitable for finer grinding applications |
Ready to Optimize Your Grinding Process?
Choosing the right ball mill is critical for achieving your desired particle size and throughput. Whether you're conducting precise R&D in a lab or managing large-scale industrial production, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Tailored Solutions: We help you select the perfect mill—from high-energy planetary mills for nano-scale research to robust horizontal mills for industrial capacity.
- Quality Equipment: KINTEK specializes in reliable lab equipment and consumables, ensuring consistent performance and durability.
- Expert Support: Our team provides guidance on setup, operation, and maintenance to maximize your mill's efficiency.
Don't leave your grinding results to chance. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory or production workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the grinding mechanism of ball mill? Master Impact & Attrition for Perfect Particle Size
- Are roller mills more energy efficient? The truth about particle size and performance.
- What can a ball mill produce? Achieve Fine Powders and Slurries for Your Materials
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- Why is high-precision mixing and grinding equipment necessary for fluorine doping in anti-perovskite materials?
- Why must plant-based coagulant raw materials be processed into ultra-fine powder? Enhance Reactivity & Performance
- How does a vibration mixing mill optimize composite cathode preparation? Achieve Superior Interface Density
- What is the maximum feed size for a hammer mill? It's a System-Dependent Variable, Not a Fixed Number



















