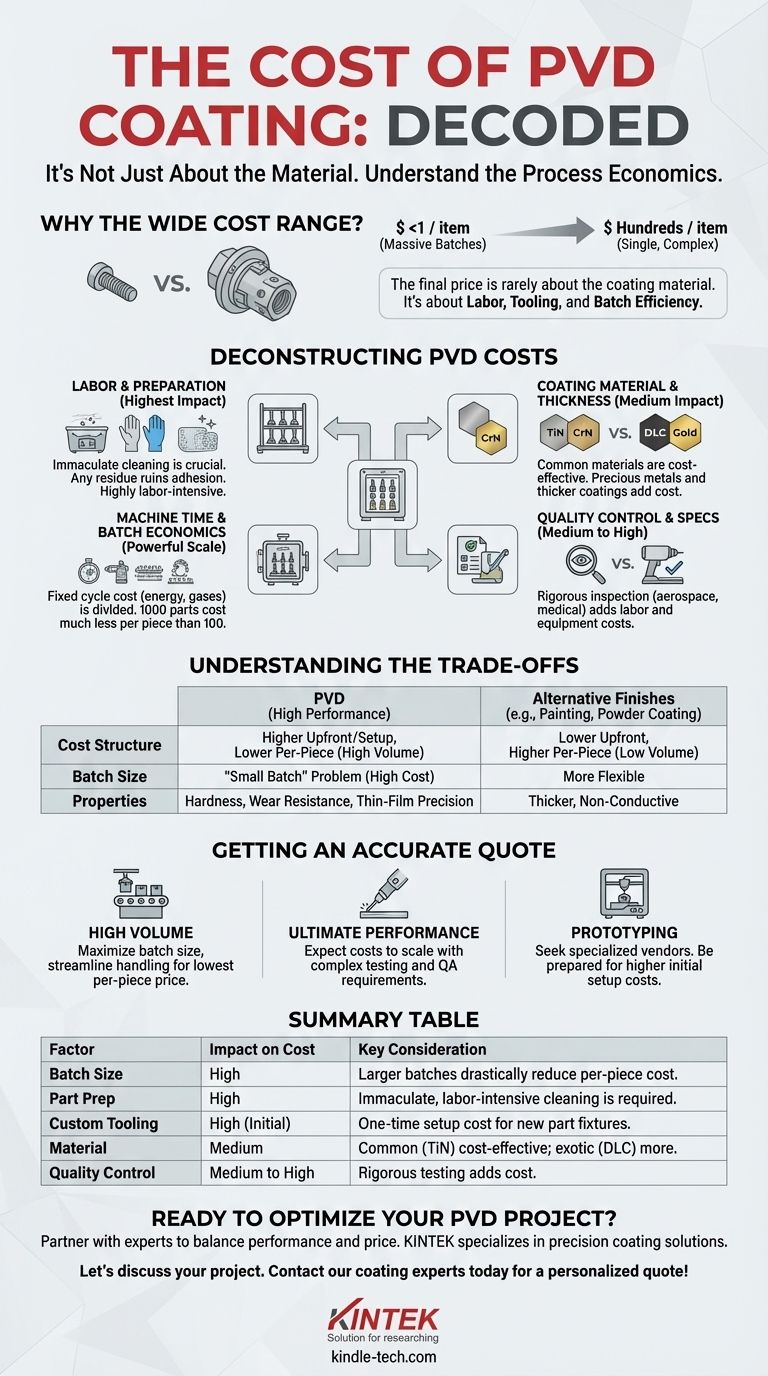
The cost of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is highly variable, ranging from less than a dollar per item for massive batches of small parts to hundreds of dollars for large, complex, single components. This wide range exists because the price is determined less by the coating material and more by the logistics of the industrial process, including part preparation, tooling, and batch size.
The final price of PVD coating is rarely about the coating material itself. It's a function of process economics: labor-intensive preparation, custom tooling, and the efficiency of the batch size you can run in the vacuum chamber.

Deconstructing PVD Coating Costs
To understand a PVD quote, you must understand how a coating facility calculates its price. The cost is an assembly of several key factors, each contributing significantly to the final number.
The Role of Labor and Preparation
This is often the largest and most underestimated cost component. PVD is a line-of-sight process performed in a high-vacuum environment, meaning parts must be immaculately clean before entering the chamber.
Any oil, residue, or even a fingerprint can ruin the coating adhesion for the entire batch. This requires multi-stage ultrasonic cleaning, de-ionized water rinses, and careful handling, all of which are labor-intensive.
Custom Tooling and Fixturing
Parts cannot simply be placed on a tray. They must be held on custom-designed racks or fixtures that secure them and orient them correctly for the coating source.
Developing and fabricating these fixtures is a non-recurring engineering (NRE) cost. For a first-time run of a new part, this setup charge can be significant. For high-volume repeat jobs, this cost is amortized and becomes negligible.
Machine Time and Batch Economics
A PVD coating chamber is an expensive piece of capital equipment. Running a cycle has a fixed cost, regardless of how many parts are inside. This includes energy, inert gases, target material consumption, and machine operator time.
This creates a powerful economy of scale. The cost to coat 1,000 small screws in one batch is dramatically lower per piece than coating just 100 of them, as the fixed cycle cost is divided across more parts.
Coating Material and Thickness
While not the primary driver, the material choice does matter. Common, functional coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN) are very cost-effective.
More advanced or complex materials, like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) or coatings containing precious metals like gold or platinum, will increase the cost due to raw material price and more complex deposition parameters. Thicker coatings also require longer cycle times, increasing the cost.
Quality Control and Specifications
The required level of quality assurance directly impacts the price. A simple decorative coating on a consumer product may only require a visual inspection.
In contrast, a PVD coating for an aerospace component or medical implant requires rigorous post-process inspection. This can include adhesion tests, thickness verification with X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and surface hardness measurements, all of which add labor and equipment costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PVD offers exceptional performance, but it's essential to recognize the economic trade-offs compared to other finishing methods like painting, powder coating, or electroplating.
The "Small Batch" Problem
PVD is often not economical for one-off parts or very small prototype runs. The high fixed costs of setup, cleaning, and running a machine cycle mean a batch of 5 pieces can cost nearly as much as a batch of 100.
High Upfront Costs for New Parts
The NRE cost for custom fixturing can be a barrier to entry. If you are only coating a small number of unique parts, this tooling charge can make the per-piece price seem prohibitively high.
Cost vs. Alternative Finishes
PVD is almost always more expensive upfront than powder coating or painting. However, those methods provide a thick, non-conductive layer that lacks the hardness, wear resistance, and thin-film precision of PVD. You are paying for a significant leap in physical properties and durability.
Getting an Accurate Quote for Your Project
To determine if PVD is right for your application and budget, you must engage with a coating provider with the right information. Your goal will dictate your cost sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Your path to a low per-piece price is maximizing your batch size and streamlining part handling to reduce labor.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and precision: Be prepared for costs to scale with the complexity of your quality assurance, testing, and documentation requirements.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or small runs: Seek a vendor specializing in small batches or be prepared for high initial setup and per-piece costs.
By understanding these cost drivers, you can approach a coating vendor not with a simple question of price, but with the right information to build a partnership for a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Size | High | Larger batches drastically reduce the per-piece cost. |
| Part Preparation | High | Immaculate, labor-intensive cleaning is required. |
| Custom Tooling | High (Initial) | One-time setup cost for new part fixtures. |
| Coating Material | Medium | Common coatings (TiN) are cost-effective; exotic materials (DLC, gold) cost more. |
| Quality Control | Medium to High | Rigorous testing (adhesion, thickness) adds cost. |
Ready to Optimize Your PVD Coating Project?
Understanding the cost drivers is the first step. The next is partnering with an expert who can help you navigate these factors to achieve the best balance of performance and price for your specific application.
KINTEK specializes in precision coating solutions and laboratory equipment. Whether you are scaling up a high-volume production line or developing a prototype requiring the utmost precision, our expertise ensures you get a durable, high-performance finish that meets your specifications and budget.
Let's discuss your project. Provide us with your part details, target batch size, and performance requirements, and we will provide a tailored solution that delivers exceptional value.
Contact our coating experts today for a personalized quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















