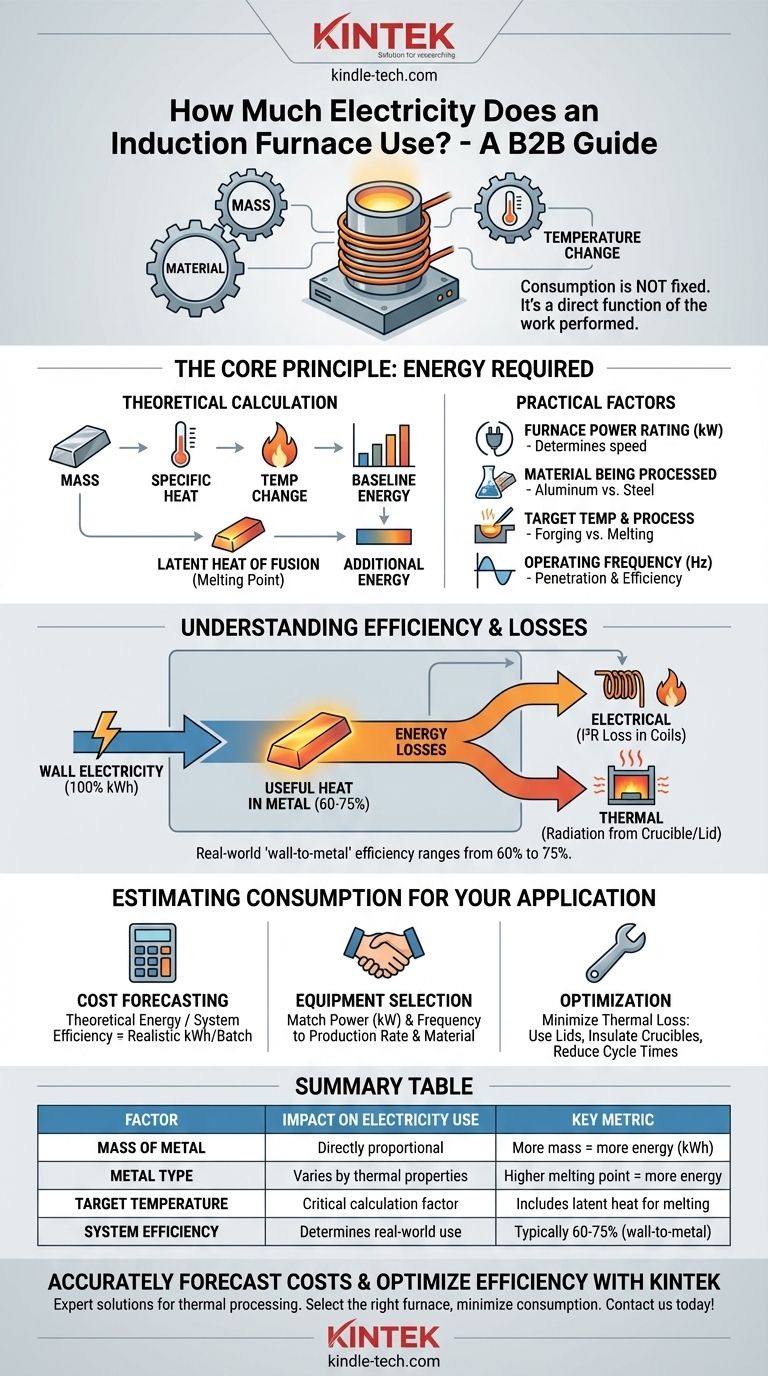
At its core, the electricity consumption of an induction furnace is not a single, fixed number. It is a variable figure that depends entirely on the mass of the metal being heated, the type of metal, the target temperature, and the overall efficiency of the furnace system. A small furnace heating aluminum to its melting point will use drastically less energy than a large furnace melting tons of steel.
Instead of a fixed kilowatt-hour rating, view an induction furnace's consumption as a direct function of the work it needs to perform. Understanding the key variables—mass, material, and temperature change—is the only way to accurately estimate its power usage and operational cost.

The Core Principle: Energy Required for a Task
An induction furnace's job is to transfer energy into a metal to raise its temperature. The amount of energy required is governed by fundamental physics, not by the furnace itself.
The Fundamental Calculation
The theoretical minimum energy needed to heat a metal is calculated based on its properties. The key factors are the mass of the material, its specific heat capacity (the energy needed to raise 1 kg by 1°C), and the desired temperature change.
For simply heating metal without melting, the baseline energy is determined before any furnace inefficiencies are considered.
The Added Energy of Melting
If the goal is to melt the metal, a significant amount of additional energy is required. This is known as the latent heat of fusion. This is the energy needed to break the metallic bonds and change the material from a solid to a liquid at its melting point, even without any further temperature increase.
Key Factors That Determine Power Consumption
The theoretical energy requirement is just the starting point. Real-world electricity usage is determined by several practical factors related to the furnace and the process.
Furnace Power Rating (kW)
The power rating of the furnace, measured in kilowatts (kW), determines how quickly it can deliver energy. A 1,000 kW furnace will consume more electricity per hour than a 100 kW furnace, but it will also complete the heating task much faster.
Material Being Processed
Different metals have vastly different thermal properties. For example, melting one ton of aluminum requires significantly less energy than melting one ton of steel because steel has a much higher melting point and different specific heat.
Target Temperature and Process
The end goal dictates the total energy input. Heating steel for forging (e.g., to 1200°C) requires less energy than melting it completely (e.g., to 1650°C), as melting involves the additional latent heat of fusion.
Operating Frequency
Induction furnaces operate across a range of frequencies (typically 150 Hz to 8000 Hz). The chosen frequency affects how the electromagnetic field couples with the metal. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper for large melts, while higher frequencies are better for surface heating or small parts, impacting the overall efficiency of energy transfer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency and Heat Loss
The electricity you are billed for is always higher than the theoretical energy absorbed by the metal. This difference is due to system inefficiencies and heat loss.
Electrical Efficiency
Not all the electricity drawn by the induction coil is converted into useful heat in the metal. Some energy is lost as heat within the copper coil itself due to electrical resistance. This is known as I²R loss. Modern power supplies are highly efficient, but some loss is unavoidable.
Thermal Efficiency
This is the largest source of energy loss. The hot metal and the crucible constantly radiate heat into the surrounding environment. Factors like the quality of the furnace's insulation, whether a lid is used, and the total time the metal spends at high temperature directly impact how much energy is wasted.
Overall System Efficiency
Combining electrical and thermal losses, the "wall-to-metal" efficiency of an induction furnace typically ranges from 60% to 75%. This means for every 100 kWh of electricity you purchase, only 60-75 kWh is actually used to heat and melt the metal.
Estimating Consumption for Your Application
To move from theory to a practical estimate, you must consider your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is cost forecasting: Calculate the theoretical energy needed (mass x specific heat x temp change + latent heat) and then divide by the expected system efficiency (e.g., 0.70) to find the realistic kWh consumption per batch.
- If your primary focus is selecting new equipment: Match the furnace's power rating (kW) and frequency to your required production rate and the specific metal you will be processing.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing furnace: Concentrate on minimizing thermal loss. Use well-insulated crucibles, ensure lids are always in place during heating, and optimize cycle times to reduce the amount of time the furnace spends holding metal at temperature.
By moving from the simple question of "how much" to a deeper understanding of "why," you can accurately forecast costs and optimize your entire heating process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Electricity Use | Key Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Mass of Metal | Directly proportional | More mass = more energy (kWh) |
| Metal Type | Varies by thermal properties | Higher melting point = more energy |
| Target Temperature | Critical for energy calculation | Includes latent heat of fusion for melting |
| System Efficiency | Determines real-world consumption | Typically 60-75% (wall-to-metal) |
Accurately forecast your induction furnace energy costs and optimize your lab's efficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your laboratory's thermal processing needs. Our team can help you select the right furnace and optimize your process to minimize electricity consumption. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















