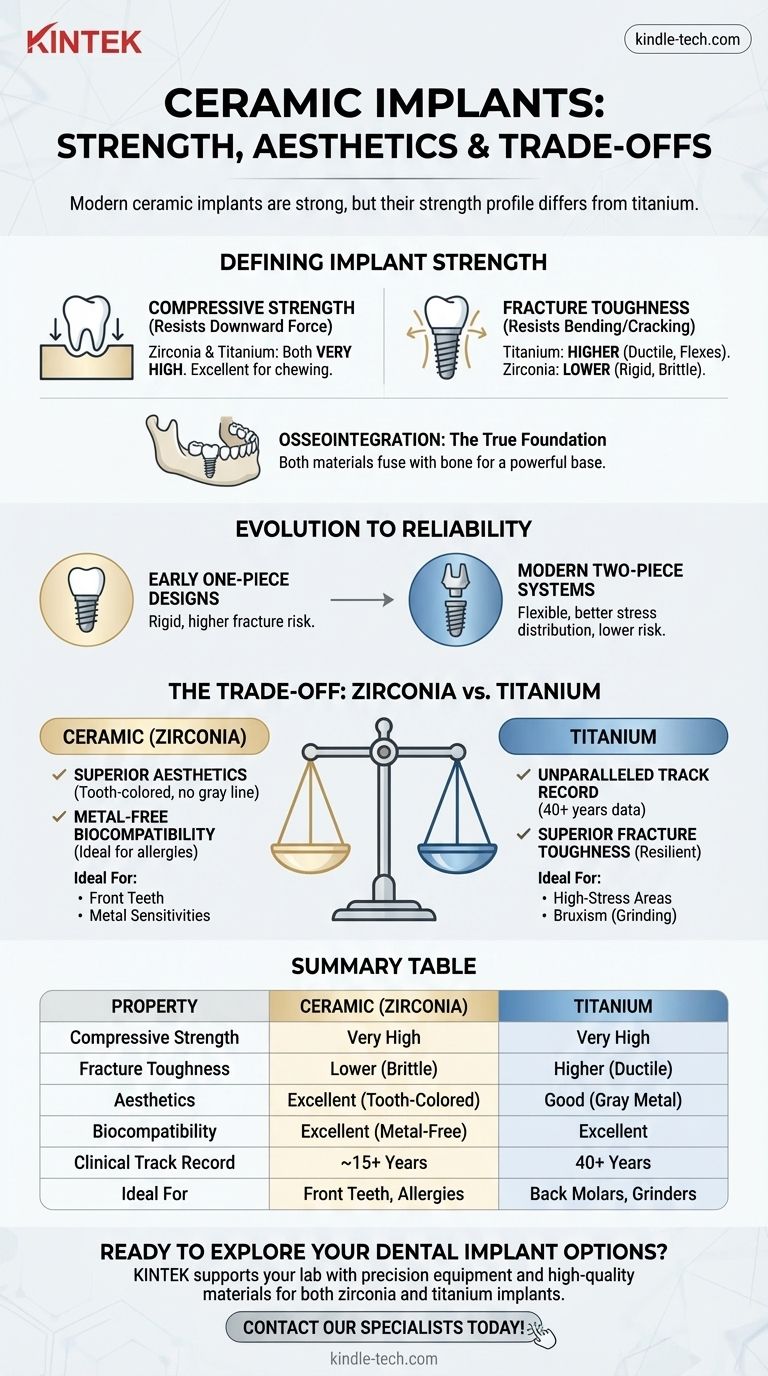
In short, modern ceramic implants are very strong and are approved by the FDA as a safe and effective long-term solution for tooth replacement. Made from a high-performance ceramic called zirconia, they possess immense compressive strength, easily withstanding the normal forces of chewing. However, their strength profile is different from that of traditional titanium implants, presenting a unique set of considerations.
The decision between a ceramic (zirconia) and titanium implant is not a matter of "strong versus weak." It is a calculated choice based on prioritizing superior aesthetics and metal-free biocompatibility (ceramic) against the unparalleled long-term clinical data and fracture toughness of the industry standard (titanium).
What Defines Implant "Strength"?
An implant's success is not determined by a single strength metric. It's a combination of material properties and its biological interaction with your body.
Compressive Strength vs. Fracture Toughness
The most important distinction is how the materials handle force.
-
Compressive strength is the ability to resist forces that push down on the implant, like chewing. Zirconia has exceptional compressive strength, comparable to or even exceeding that of titanium alloys.
-
Fracture toughness (or ductility) is the ability to resist cracking or breaking when subjected to bending or twisting forces. This is where titanium, as a metal, has a natural advantage. It can flex slightly under stress, whereas ceramics are more rigid and can be more brittle.
The Material: Zirconia
Ceramic implants are not like porcelain dishes. They are milled from solid blocks of zirconia, an extremely hard and durable bioceramic. Its inherent white, tooth-like color is its most significant advantage over the gray-colored titanium.
Osseointegration: The True Foundation of Strength
The real strength of any implant comes from osseointegration—the process where your jawbone fuses directly to the implant surface. Both zirconia and titanium are highly biocompatible and achieve excellent, stable osseointegration, creating a powerful foundation for the replacement tooth.
The Evolution from Early Issues to Modern Reliability
Concerns about ceramic strength often stem from outdated information about first-generation products. Modern ceramic implants have been significantly redesigned to maximize durability.
Early One-Piece Designs
The first ceramic implants were often "one-piece" designs, where the implant and the abutment (the post that holds the crown) were a single, solid unit. This rigidity sometimes concentrated stress, leading to a higher potential for fracture, especially if placed at a slight angle.
The Shift to Two-Piece Systems
Today, most leading ceramic implant systems are two-piece, just like their titanium counterparts. A separate zirconia implant is placed in the bone, and a separate abutment is attached later. This design offers several key advantages:
- Greater flexibility for the surgeon to achieve the perfect angle.
- Better stress distribution, significantly reducing fracture risk.
- A surgical process that is nearly identical to the time-tested titanium protocol.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ceramic vs. Titanium
Objectively, neither material is "better" in all situations. The right choice depends on balancing the following factors.
Aesthetics: The Primary Advantage of Ceramic
This is the clearest benefit of zirconia. Its white color prevents the dark gray line that can sometimes appear at the gumline with titanium implants, particularly in patients with thin gum tissue. For front teeth, this can be a decisive factor.
Biocompatibility and Tissue Response
Both materials are extremely biocompatible with minimal risk of rejection or allergic reaction. Some studies suggest zirconia may accumulate slightly less plaque and bacteria than titanium, potentially leading to healthier gum tissue over the long term, though titanium's track record with gum health is also excellent.
Fracture Risk: The Primary Concern
This is the core of the trade-off. While the fracture risk for a modern, well-placed two-piece zirconia implant is very low (studies show survival rates over 95%), it is not zero. The risk of a titanium implant itself fracturing is virtually non-existent. The ductile nature of the metal makes it uniquely resilient.
Clinical Track Record and Cost
Titanium has been the gold standard for over 40 years, with a vast body of data proving its safety and longevity. Zirconia has a strong track record of over 15 years, but it is simply newer. Ceramic implant procedures are also typically more expensive due to material and manufacturing costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Situation
The decision must be made in consultation with your dental surgeon, but you can guide the conversation based on your priorities.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics in the smile zone: A ceramic implant is an outstanding choice that eliminates any risk of a gray shadow at the gumline.
- If your primary focus is minimizing all long-term risk: Titanium's decades of clinical data and superior fracture toughness make it the most predictable and proven option.
- If you have a known or suspected metal allergy or sensitivity: A ceramic implant is the definitive metal-free solution, providing complete peace of mind.
- If you are a heavy grinder (bruxism) or need an implant for a back molar: Discuss the biting forces with your surgeon; the exceptional fracture resistance of titanium may be the more conservative recommendation.
Ultimately, the best implant is one placed by a skilled clinician who can match the right material to your specific anatomical and functional needs.
Summary Table:
| Property | Ceramic (Zirconia) Implants | Titanium Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Very High | Very High |
| Fracture Toughness | Lower (Brittle) | Higher (Ductile) |
| Aesthetics | Excellent (Tooth-Colored) | Good (Gray Metal) |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent (Metal-Free) | Excellent |
| Clinical Track Record | ~15+ Years | 40+ Years |
| Ideal For | Front Teeth, Metal Allergies | High-Stress Areas, Bruxism |
Ready to Explore Your Dental Implant Options?
Choosing the right implant material is a critical step toward a healthy, confident smile. Whether you prioritize the aesthetic appeal of metal-free ceramic or the proven durability of titanium, KINTEK is here to support your dental laboratory with precision equipment and consumables.
We provide:
- High-quality materials for crafting durable zirconia and titanium implants.
- Advanced lab equipment for precise fabrication and testing.
- Expert solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of dental professionals and their patients.
Let us help you deliver the best possible outcomes for your patients. Contact our specialists today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your dental lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What are the two methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of a metal? Barrier vs. Sacrificial Protection Explained
- What function do alumina ceramic plates serve as supports in the preparation of molecular sieve membranes?
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection










