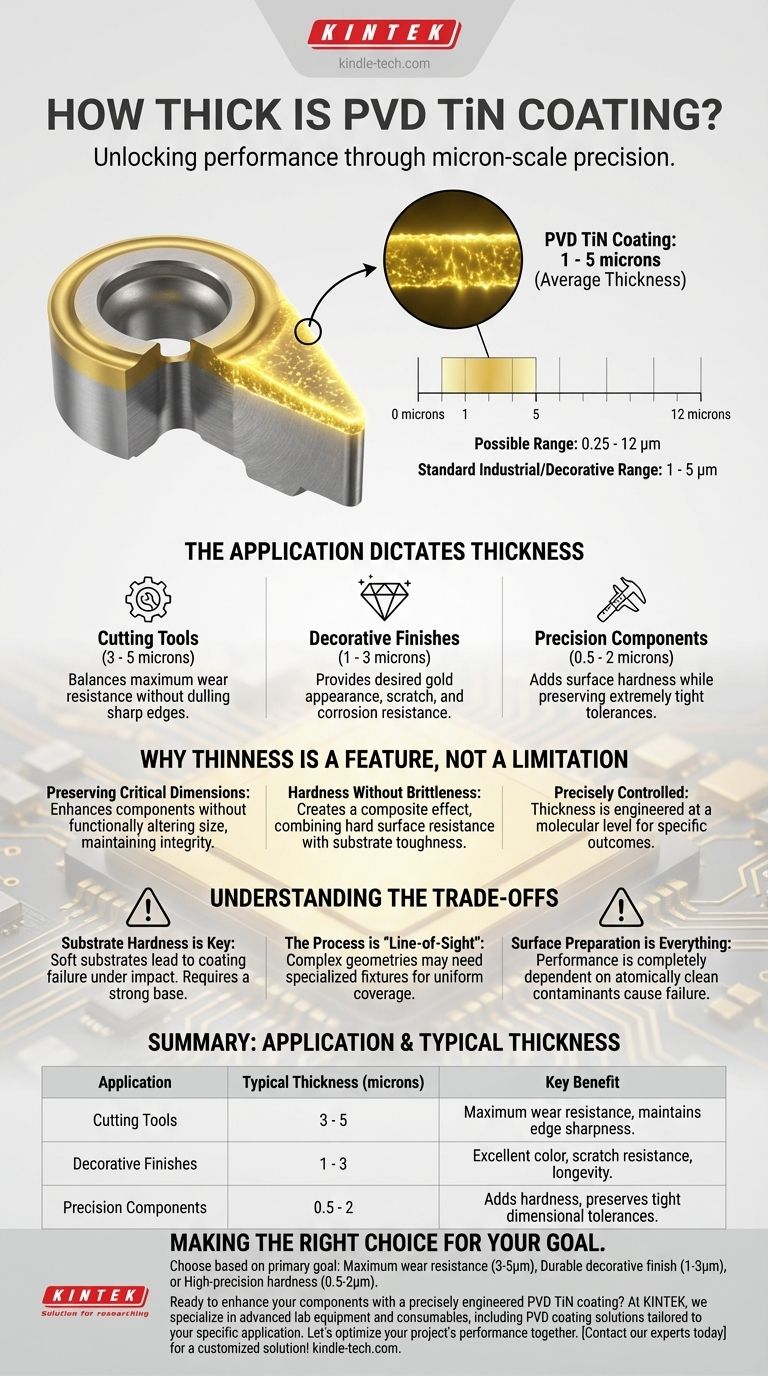
On average, a PVD TiN coating is between 1 and 5 microns thick. While the possible range extends from as thin as 0.25 microns to as thick as 12 microns, the vast majority of industrial and decorative applications fall within that narrow 1-to-5-micron window. This seemingly insignificant layer is responsible for dramatic improvements in surface hardness, wear resistance, and durability.
The core principle to understand is that the extreme thinness of a PVD coating is a deliberate feature, not a limitation. This micro-scale layer enhances a component's surface properties without altering its fundamental dimensions, geometry, or the mechanical properties of the base material.

Why PVD TiN Coatings Are So Thin
The thickness of a PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating is not arbitrary; it is precisely controlled to achieve specific outcomes. The process itself, which occurs in a vacuum at a molecular level, is designed to produce these ultra-thin, high-density films.
The Application Dictates the Thickness
The ideal thickness is a direct function of the part's intended use. A thicker coating is not always better and can even be detrimental.
- Cutting Tools: Often require a thickness of 3 to 5 microns. This provides a superb balance of wear resistance while being thin enough to maintain the sharpness of the cutting edge. A thicker coating could dull the edge.
- Decorative Finishes: For items like jewelry or architectural hardware, a thinner layer of 1 to 3 microns is typically sufficient to provide the desired gold appearance and resistance to scratches and corrosion.
- Precision Components: Parts with extremely tight tolerances may use coatings as thin as 0.5 microns to gain surface hardness without affecting dimensional accuracy.
Preserving Critical Dimensions
One of the primary advantages of PVD is its ability to enhance a part without functionally changing its size.
For a precision-machined part, adding even a small amount of material can ruin its tolerances. A coating of just a few microns is often negligible and can be easily accounted for in the design phase, preserving the component's integrity.
Hardness Without Brittleness
The TiN coating itself is a very hard ceramic material. By applying it as a thin film, you add this hard, wear-resistant surface to a tougher, more ductile base material.
This creates a composite effect: the surface resists abrasion and friction, while the underlying substrate provides the structural strength to handle impacts and loads.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the thin-film nature of PVD coatings introduces specific considerations that are critical for success.
Substrate Hardness is Key
A PVD coating is like a thin layer of ice over softer ground. If the underlying substrate material is too soft, a sharp impact can deform the substrate, causing the hard coating to crack because it lacks support. The hardness of the base material is a crucial factor in the overall durability of the coated part.
The Process is "Line-of-Sight"
Physical Vapor Deposition works by bombarding a surface with coating material in a vacuum chamber. This process is generally "line-of-sight," meaning surfaces that are hidden or in deep, narrow cavities may not receive a uniform coating. Complex geometries require specialized fixtures and rotation to ensure even coverage.
Surface Preparation is Everything
The incredible adhesion of PVD coatings is only possible on an atomically clean surface. Any contamination, such as oils or microscopic dust, will create a point of failure. The performance of the thin coating is therefore completely dependent on the quality of the pre-treatment and cleaning process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specified thickness of a PVD TiN coating should be a deliberate engineering decision based on the primary goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance for tooling: A thickness in the 3-5 micron range offers the best durability without compromising the sharpness of cutting edges.
- If your primary focus is a durable, decorative finish: A 1-3 micron coating provides excellent color, scratch resistance, and longevity for consumer or architectural products.
- If your primary focus is adding hardness to high-precision parts: Specify a thinner coating of 0.5-2 microns to ensure critical dimensional tolerances are maintained.
Ultimately, the power of PVD TiN lies not in its bulk, but in the dense, precisely controlled, and molecularly-bonded structure of its thin film.
Summary Table:
| Application | Typical Thickness (microns) | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Tools | 3 - 5 | Maximum wear resistance without dulling edges |
| Decorative Finishes | 1 - 3 | Excellent color and scratch resistance |
| Precision Components | 0.5 - 2 | Adds hardness while preserving tight tolerances |
Ready to enhance your components with a precisely engineered PVD TiN coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including PVD coating solutions tailored to your specific application—whether for cutting tools, decorative finishes, or precision parts. Our expertise ensures your components gain superior surface hardness, wear resistance, and durability without compromising dimensional accuracy.
Let’s optimize your project’s performance together. Contact our experts today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials

















