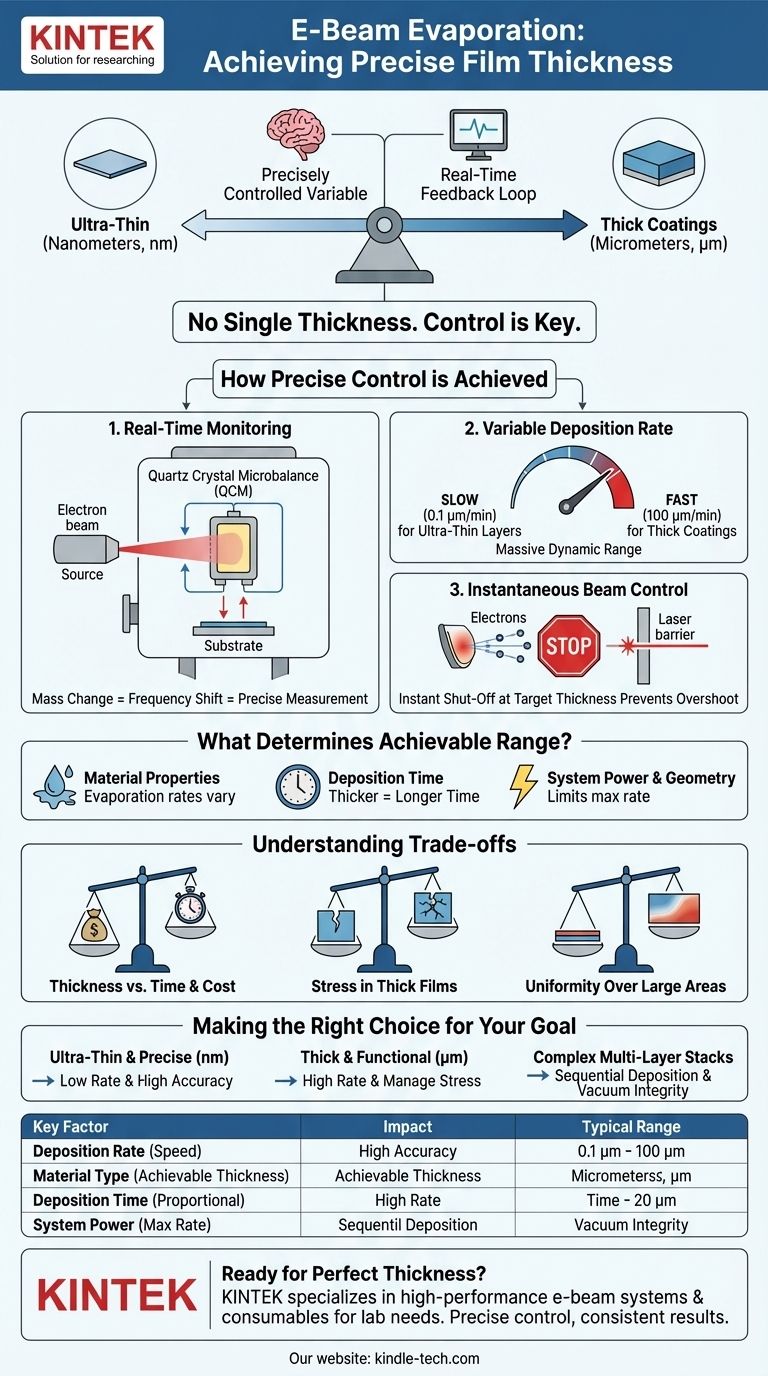
There is no single thickness for a film created by electron-beam evaporation; rather, the thickness is a precisely controlled variable tailored to the specific application. The process is defined by its vast range, capable of producing films from just a few nanometers to well over 100 micrometers. This control is achieved by using a quartz crystal monitor to measure film growth in real-time and shutting off the electron beam the instant the desired thickness is reached.
The core principle of e-beam evaporation is not about achieving a fixed thickness, but about having precise, real-time control over the deposition process. This allows for an exceptionally wide range of film thicknesses, limited primarily by the material being used and the time allocated for the procedure.

How E-Beam Evaporation Achieves Precise Thickness Control
The defining characteristic of modern e-beam evaporation is its feedback-driven control system. This system allows operators to target and achieve a specific film thickness with high repeatability.
The Role of Real-Time Monitoring
The entire process is governed by a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) positioned inside the vacuum chamber. As evaporated material coats the crystal, its resonant frequency changes.
This frequency shift is directly proportional to the mass added to the crystal, allowing for an extremely precise, real-time measurement of the film's growing thickness.
The Impact of Deposition Rate
E-beam systems offer a massive dynamic range of deposition rates, typically from 0.1 to 100 micrometers per minute (μm/min).
For extremely thin and precise layers, a very slow rate is used. For thick, protective coatings, the system can be run at its maximum rate to reduce process time.
Instantaneous Beam Control
Once the QCM indicates that the target thickness has been reached, the system instantly shuts off the electron beam. This immediate stop is critical for preventing overshoot and ensuring the final film thickness is accurate to the nanometer scale.
What Determines the Achievable Thickness Range?
While theoretically versatile, the practical limits on film thickness are influenced by several factors, including the material properties and the system's configuration.
Material Evaporation Characteristics
Every material has a unique evaporation rate based on its melting point and the power applied by the electron beam. High-temperature materials like tungsten or metal oxides may deposit slower than materials like aluminum or gold.
Deposition Time
The most straightforward factor is time. A thicker film simply requires a longer deposition time. A 100 µm film deposited at 10 µm/min will take 10 minutes, whereas a 10 nanometer film at 0.1 µm/min will take only 6 seconds.
System Power and Geometry
The maximum power of the electron gun and the distance between the source and the substrate (the "throw distance") influence the maximum achievable deposition rate, and therefore how quickly a very thick film can be produced.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a target thickness involves balancing competing factors. The versatility of e-beam evaporation comes with engineering and physical considerations that are important to understand.
Thickness vs. Time and Cost
Extremely thick films (hundreds of micrometers) can take a significant amount of time to deposit. This increases operational costs and reduces the throughput of the system.
Stress in Thick Films
As a film becomes thicker, internal stresses can build up. This can lead to poor adhesion, cracking, or delamination of the film from the substrate, setting a practical upper limit for many material combinations.
Uniformity Over Large Areas
While the QCM provides a precise point measurement, achieving perfect thickness uniformity across a large substrate becomes more challenging with thicker films. The deposition plume has a natural distribution that must be managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements will determine the optimal approach to film thickness with e-beam evaporation.
- If your primary focus is ultra-thin, precise layers (nanometers): Leverage the system's low deposition rates and the high accuracy of the real-time quartz crystal monitor.
- If your primary focus is thick, functional coatings (micrometers): Utilize the high deposition rates to minimize process time, but be mindful of managing internal film stress.
- If your primary focus is complex multi-layer stacks: Capitalize on the ability to deposit different materials in sequence, with precise thickness control over each individual layer without breaking vacuum.
Ultimately, electron-beam evaporation provides you with the control to create the exact film thickness your design requires.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Thickness | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Rate | Controls speed of film growth | 0.1 - 100 μm/min |
| Material Type | Affects achievable thickness | Varies by melting point |
| Deposition Time | Directly proportional to thickness | Seconds to hours |
| System Power | Limits maximum deposition rate | Depends on e-gun power |
Ready to deposit the perfect film thickness for your application? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance e-beam evaporation systems and consumables for laboratory needs. Our solutions offer the precise control and reliability you need to achieve consistent results, from ultra-thin layers to thick coatings. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your deposition process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently



















