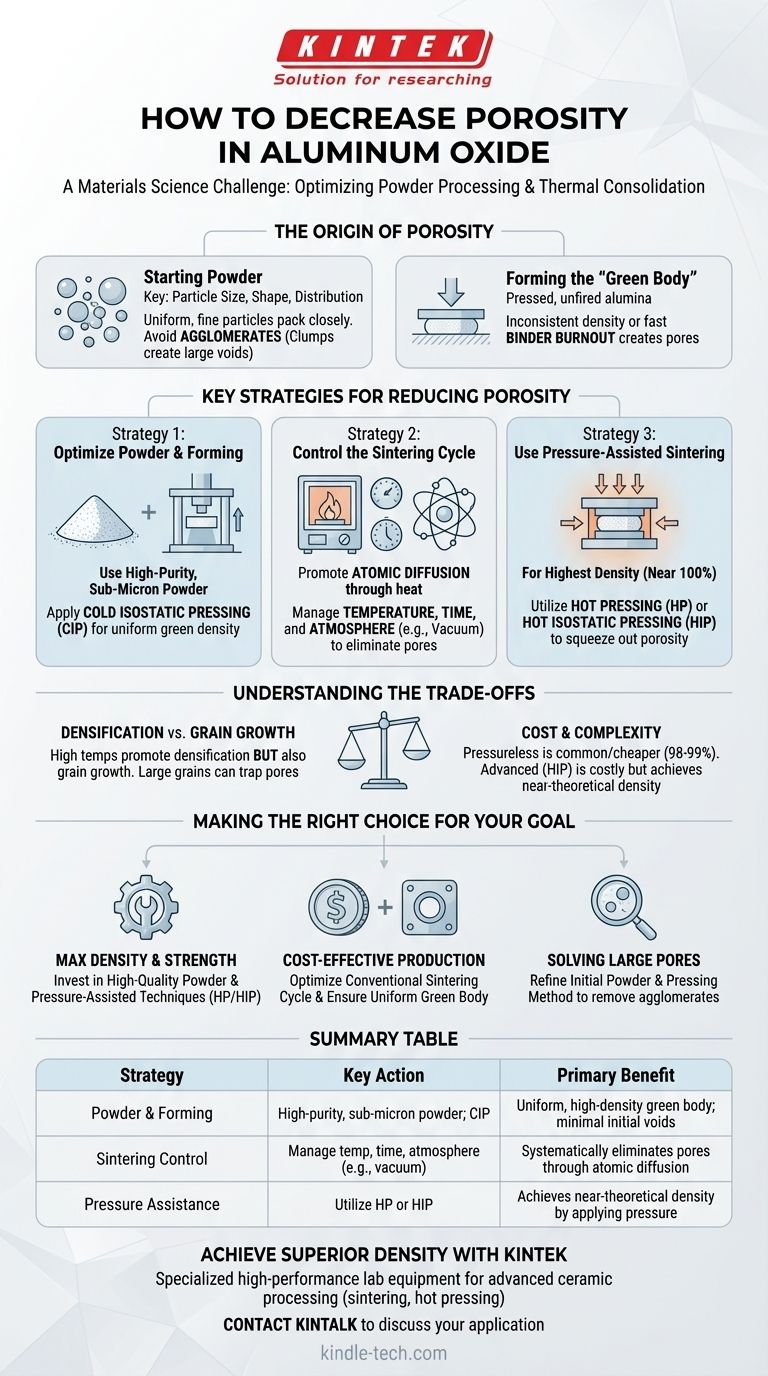
To be clear, decreasing porosity in aluminum oxide (alumina) is fundamentally a materials science challenge centered on powder processing and thermal consolidation. The key is to optimize the starting powder characteristics and, most importantly, the sintering process, where heat and sometimes pressure are used to fuse ceramic particles together and eliminate the empty spaces between them.
Porosity in an alumina ceramic is the residual empty space left between powder particles after processing. Achieving a dense, low-porosity final part requires controlling every step, from the initial powder quality to the final heating cycle, to ensure these voids are systematically eliminated.

The Origin of Porosity in Alumina
To reduce porosity, you must first understand where it comes from. Voids are introduced at two main stages: powder packing and thermal processing.
The Role of the Starting Powder
The characteristics of the initial aluminum oxide powder are the foundation for the final product's density. Poor powder quality makes it nearly impossible to achieve low porosity.
Key factors include particle size, shape, and distribution. Ideally, you want a powder with fine, uniformly sized particles that can pack together closely, leaving minimal space between them.
Large clumps of particles, known as agglomerates, are a primary source of failure. These clumps create large voids in the initial packed structure that are extremely difficult to remove during sintering.
Forming the "Green Body"
The "green body" is the term for the alumina powder that has been pressed or formed into its desired shape but not yet fired.
An inconsistent or low-density green body directly translates to high porosity in the final ceramic. If pressure is not applied uniformly during forming, areas of lower density will exist, which will consolidate poorly.
Additionally, organic binders and plasticizers, often added to help shape the powder, must be burned out completely and slowly. If this burnout happens too quickly, the escaping gases can create new pores.
Key Strategies for Reducing Porosity
Effective porosity reduction involves a systematic approach that addresses the powder, the green body, and the final firing (sintering) stage.
Strategy 1: Optimize the Powder and Forming
Start with a high-purity, sub-micron alumina powder with a narrow particle size distribution. If necessary, use milling techniques (like ball milling) to break up any agglomerates before processing.
To improve green body density, use advanced compaction methods. Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) applies pressure uniformly from all directions and is far superior to simple uniaxial (one-direction) pressing for creating a homogeneously dense green body.
Strategy 2: Control the Sintering Cycle
Sintering is the thermal process that transforms the porous green body into a dense ceramic. This is the most critical stage for porosity control.
The goal is to heat the part to a temperature high enough to encourage atomic diffusion, which allows material to move and fill in the pores. The key variables are temperature, time, and atmosphere. Higher temperatures and longer times generally lead to higher density.
Sintering in a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere (like hydrogen) can help remove trapped gases from within the pores, allowing them to shrink and close.
Strategy 3: Use Pressure-Assisted Sintering
For applications demanding the highest possible density (approaching 100%), pressure must be applied during the sintering process.
Hot Pressing (HP) involves simultaneously heating and applying uniaxial pressure to the part. An even more effective method is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), which applies high-temperature gas pressure from all directions to squeeze out any remaining porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Reducing porosity is not without its challenges and requires balancing competing factors.
Densification vs. Grain Growth
This is the classic dilemma in ceramics processing. While high temperatures promote densification (pore removal), they also promote grain growth.
If grains grow too large too quickly, they can grow around pores, trapping them inside the grain. Once a pore is trapped within a grain, it becomes impossible to remove through further sintering. The ideal process maximizes densification while minimizing grain growth.
Cost and Complexity
Standard, pressureless sintering is the most common and cost-effective method. However, it can be difficult to achieve densities above 98-99% with this technique.
Advanced methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) can achieve near-theoretical density but require specialized, expensive equipment, drastically increasing the cost and complexity of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for reducing porosity should be guided by the required performance and budget for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: Invest in high-quality starting powders and utilize pressure-assisted techniques like Hot Pressing or Hot Isostatic Pressing.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production for general use: Concentrate on optimizing the conventional sintering cycle (temperature, time, and atmosphere) and ensuring you have a uniform, high-density green body.
- If you are struggling with large, inconsistent pores: Your problem likely lies in the initial powder or green body stage. Investigate your powder for agglomerates and refine your pressing method to ensure uniform compaction.
Ultimately, controlling porosity is about carefully managing every variable from the raw powder to the final firing, giving you direct control over the final properties of your aluminum oxide component.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Powder & Forming | Use high-purity, sub-micron powder; Apply Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Creates a uniform, high-density green body with minimal initial voids |
| Sintering Control | Precisely manage temperature, time, and atmosphere (e.g., vacuum) | Systematically eliminates pores through atomic diffusion |
| Pressure Assistance | Utilize Hot Pressing (HP) or Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Achieves near-theoretical density by applying pressure during heating |
Achieve superior density and performance in your alumina components.
The strategies outlined are foundational, but successful implementation often requires specialized equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and pressing systems designed for advanced ceramic processing like sintering and hot pressing.
Whether you are developing a new material or optimizing an existing process, our team can provide the reliable tools and consumables you need to control porosity effectively.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific alumina application and how our solutions can help you achieve your density goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- Why is cold working better than hot working? A Guide to Choosing the Right Metal Forming Process
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- What is the difference between sintering and pressing? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy Processes



















