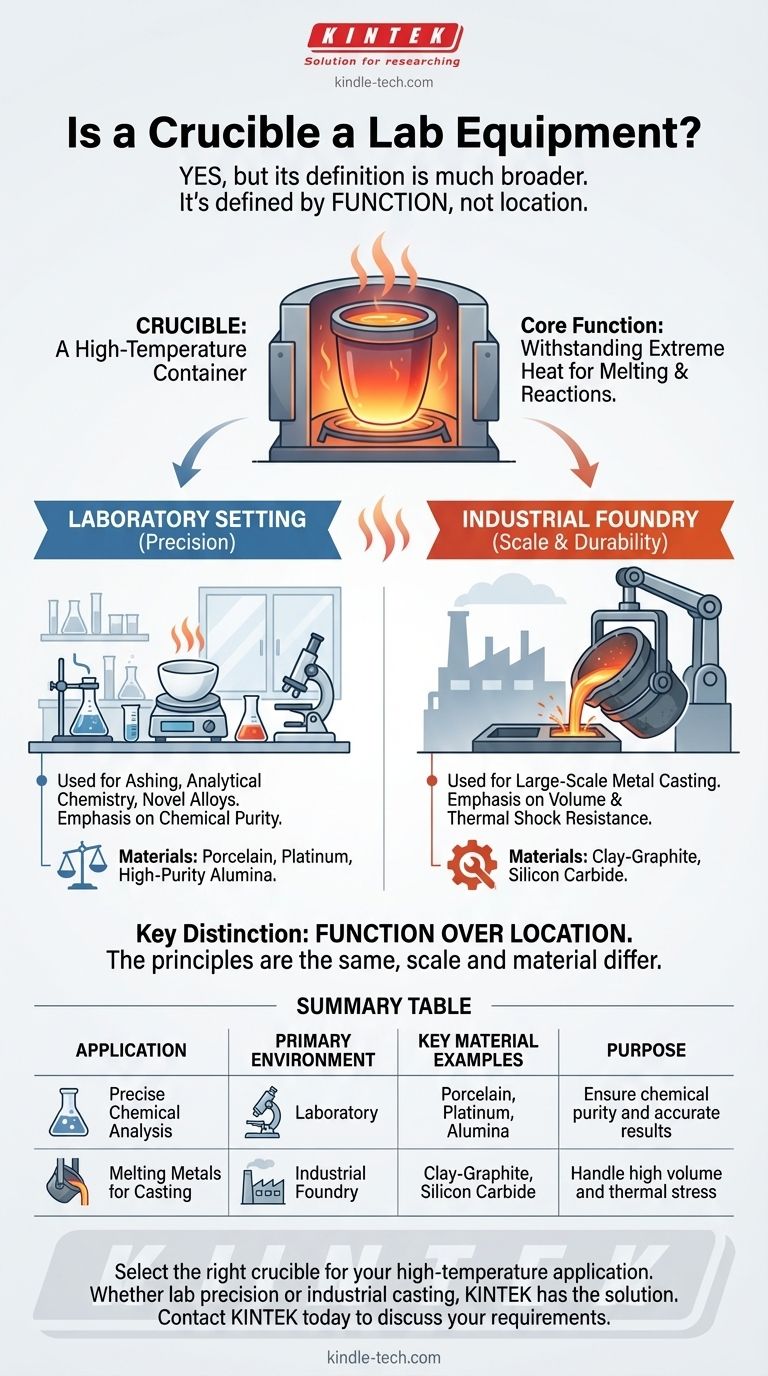
Yes, a crucible is a piece of laboratory equipment, but its definition is much broader than that. A crucible is fundamentally a container engineered to withstand extremely high temperatures. This core function makes it an indispensable tool for melting metals and performing high-temperature chemical reactions in both scientific laboratories and industrial foundries.
A crucible's identity is defined by its function—withstanding extreme heat to contain and alter materials—not by its location. While it is a staple in many labs, it is equally essential in large-scale metal casting and industrial work.

What Defines a Crucible?
The Core Function: Containing Extreme Heat
A crucible's primary purpose is to serve as a vessel for substances that need to be heated to their melting point or higher. It acts as a durable pot, typically placed within a furnace or heated by a direct flame, holding its contents safely as they transform from solid to liquid.
Essential Material Properties
To be effective, a crucible must possess two critical properties. First, its melting point must be significantly higher than the material it holds. Second, it must be chemically stable at high temperatures to avoid reacting with the molten contents, which would contaminate the melt and degrade the crucible itself.
The Crucible in Different Environments
In a Laboratory Setting
Within a lab, crucibles are essential for analytical chemistry and materials science. They are used for processes like ashing, where a sample is burned to determine its inorganic content, or for creating novel alloys in metallurgical research. Here, the emphasis is on precision and preventing sample contamination.
In an Industrial Foundry
In industrial contexts, such as a metal casting foundry, crucibles serve the same fundamental purpose but on a much larger scale. Their job is to melt large quantities of metal for casting into molds. In this environment, durability, capacity, and the ability to withstand repeated thermal shock are the most important factors.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Function Over Location
Why Context Matters
The distinction between a lab crucible and an industrial one often comes down to material and scale. A lab might use a small porcelain crucible for chemical purity, while a foundry will use a large, rugged clay-graphite crucible designed for volume and repeated use.
A Common Misconception
Viewing a crucible as only lab equipment is a limiting perspective. Its role as a high-temperature vessel is a fundamental concept in both science and industry. The principles are the same, even if the scale and specific application differ greatly.
How to Apply This to Your Task
- If your primary focus is precise chemical analysis: You require a laboratory-grade crucible, likely made of porcelain, platinum, or high-purity alumina, to ensure chemical inertness and accurate results.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for casting or craftwork: You need a more robust industrial-style crucible made from materials like clay-graphite or silicon carbide that can handle the thermal stress and volume of the task.
Understanding that a crucible is defined by its purpose—mastering extreme heat—is the key to selecting the right tool for any high-temperature job.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Application | Primary Environment | Key Material Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precise Chemical Analysis | Laboratory | Porcelain, Platinum, Alumina | Ensure chemical purity and accurate results |
| Melting Metals for Casting | Industrial Foundry | Clay-Graphite, Silicon Carbide | Handle high volume and thermal stress |
Select the right crucible for your high-temperature application.
Whether you're conducting precise chemical analysis in a lab or melting metals for industrial casting, KINTEK has the crucible you need. Our range of laboratory and industrial-grade crucibles, made from materials like porcelain, alumina, and clay-graphite, ensures durability, chemical stability, and optimal performance for your specific task.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and let our experts help you find the perfect solution for mastering extreme heat.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C



















