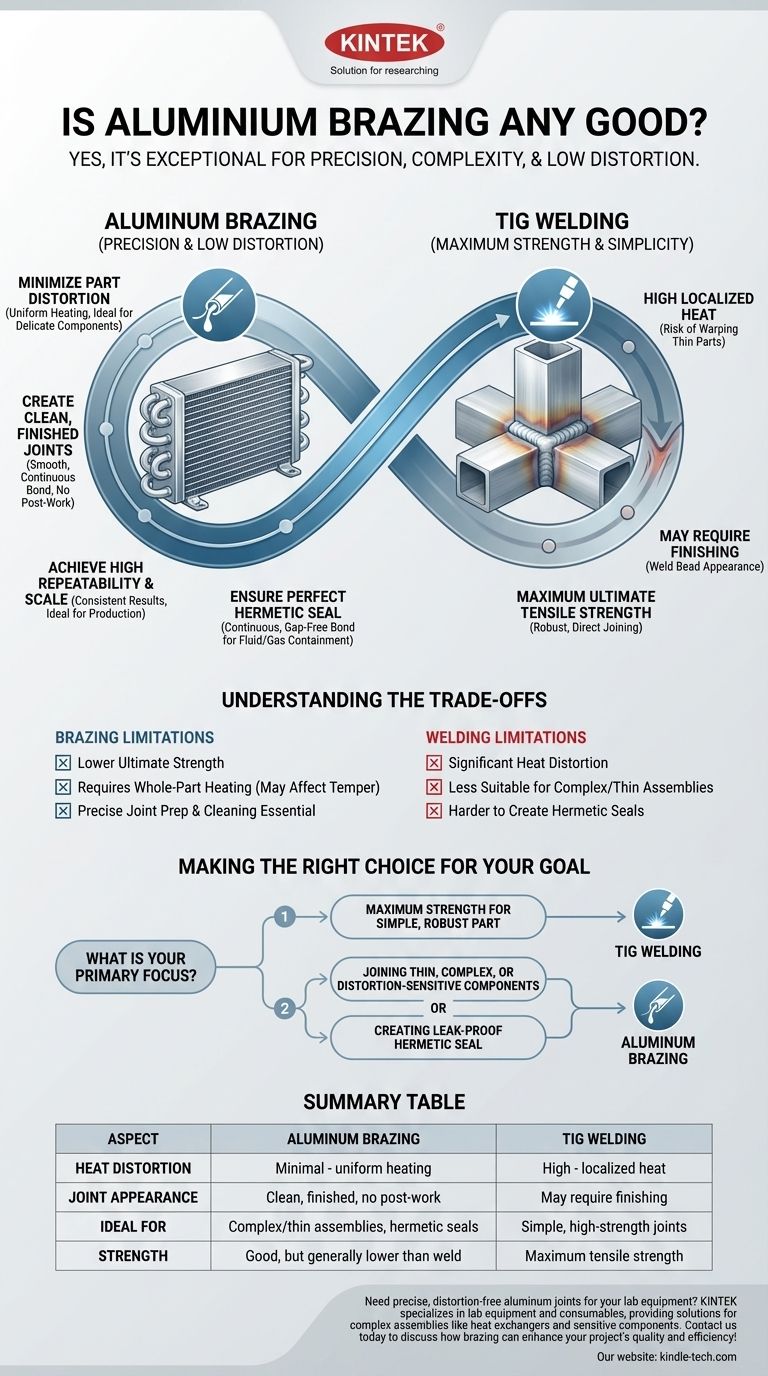
Yes, aluminum brazing is an exceptionally effective joining method for specific applications. It excels at creating clean, highly repeatable joints with minimal part distortion, making it ideal for complex or delicate assemblies where traditional welding would be impractical or damaging.
The core question is not whether aluminum brazing is "good," but rather when it is the superior choice. Brazing shines in situations where precision, low heat distortion, and the ability to join complex assemblies cleanly are more critical than the absolute, localized strength of a weld.

Why Choose Brazing Over Other Methods?
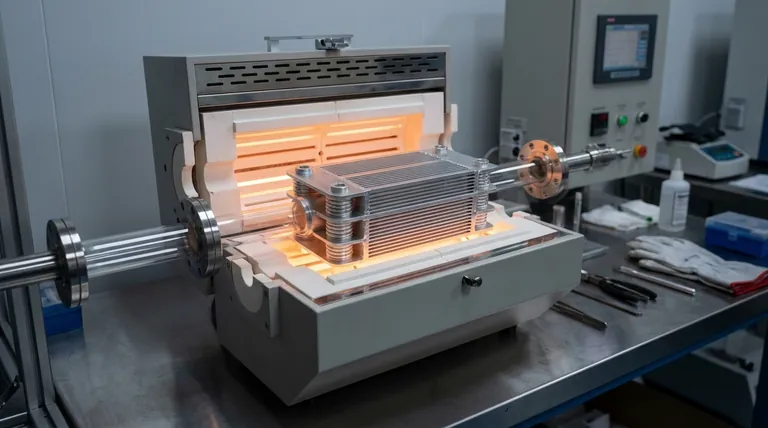
Understanding the unique advantages of aluminum brazing clarifies its role. The process involves heating the entire assembly to melt a filler metal, which flows into the joint via capillary action without melting the base aluminum.
Minimize Part Distortion
The most significant advantage is the uniform heating and cooling of the assembly. This process minimizes the thermal stress that causes warping.
In contrast, welding introduces intense, localized heat, which can easily distort or damage thin aluminum components.
Create Clean, Finished Joints
Brazing produces exceptionally clean and neat joints that often require no additional finishing work.
The filler material is drawn precisely into the joint, creating a smooth, continuous bond. This is a major benefit for both aesthetic and functional parts.
Achieve High Repeatability and Scale
The controlled nature of furnace brazing, a common method, ensures highly repeatable results from one part to the next.
This makes the process ideal for production environments and for creating complex assemblies with numerous joints, such as heat exchangers, where consistency is critical.
Ensure a Perfect, Hermetic Seal
The capillary action of the brazing process creates a continuous, gap-free bond.
This results in a hermetically sealed joint, which is essential for any application that must contain a fluid or gas without leaking.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every scenario. To make an informed decision, you must recognize the limitations of brazing compared to a method like TIG welding.
Joint Strength
While a properly executed brazed joint is strong, it generally does not match the ultimate tensile strength of a high-quality TIG weld. The filler material, by design, has a lower melting point and different mechanical properties than the base aluminum.
Heat Treatment Requirements
Brazing requires heating the entire part to a temperature very near the aluminum's melting point. This requires a furnace or highly controlled torch work and affects the material's temper, or hardness, which may require subsequent heat treatment.
Joint Preparation
Successful brazing is highly dependent on proper joint design and cleanliness. The parts must have a very tight, uniform gap between them to facilitate capillary action, and surfaces must be meticulously cleaned of oxides and contaminants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a simple, robust part: TIG welding is often the better and more direct choice.
- If your primary focus is joining thin, complex, or distortion-sensitive components: Aluminum brazing is the superior method.
- If your primary focus is creating a leak-proof hermetic seal on a multi-joint assembly: Brazing provides a level of reliability that is very difficult to match with welding.
By understanding its unique strengths in precision and low-stress joining, you can leverage aluminum brazing for results that welding simply cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Aluminum Brazing | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distortion | Minimal (uniform heating) | High (localized heat) |
| Joint Appearance | Clean, finished, no post-work | May require finishing |
| Ideal For | Complex/thin assemblies, hermetic seals | Simple, high-strength joints |
| Strength | Good, but generally lower than weld | Maximum tensile strength |
Need precise, distortion-free aluminum joints for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for complex assemblies like heat exchangers and sensitive components. Our expertise ensures hermetic seals and repeatable results for your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how brazing can enhance your project's quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tubular furnace work? A Guide to Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















