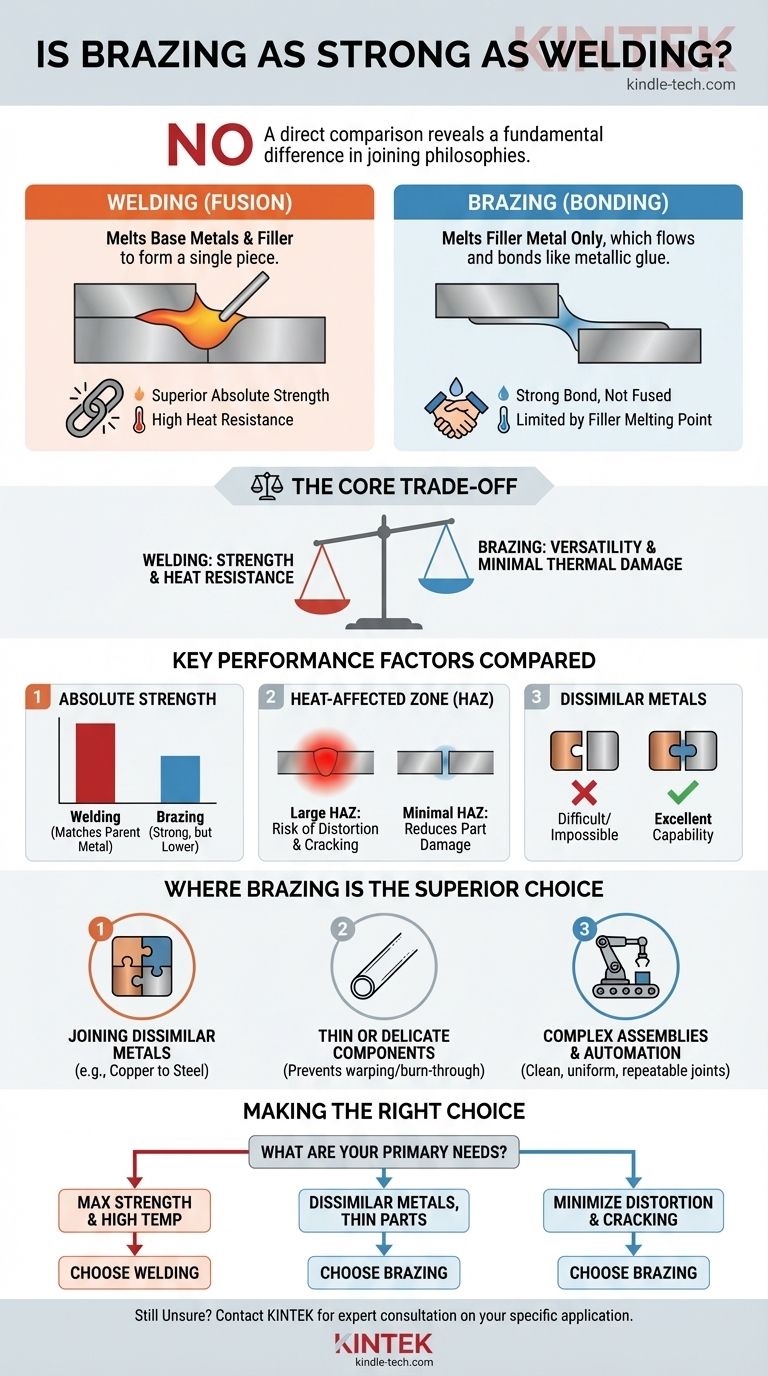
In a direct comparison, no, brazing is not as strong as welding. A welded joint is fundamentally stronger because it involves melting and fusing the base metals themselves, often with a compatible filler material, to form a single, continuous piece. Brazing, in contrast, joins metals by melting a filler metal that flows between the parts without melting the base materials, creating a strong bond but not a fused structure.
The core decision between welding and brazing is a trade-off. Welding provides superior absolute strength and heat resistance, while brazing offers greater versatility for joining dissimilar metals and minimizing thermal damage to the parent materials.

The Fundamental Difference: Melting vs. Bonding
To understand the strength differential, you must first understand the core mechanism of each process. They are not two versions of the same thing; they are entirely different joining philosophies.
How Welding Achieves Strength
Welding works by fusion. It melts the edges of the base metals, creating a molten pool that is often mixed with a melted filler rod. When this pool cools and solidifies, the original parts and the filler metal have become a single, homogenous piece of metal. This continuity is the source of its exceptional strength.
How Brazing Creates a Bond
Brazing works by capillary action and metallurgical bonding. The process heats the base metals to a temperature high enough to melt a filler metal, but below the melting point of the base metals. This molten filler is drawn into the tight-fitting joint, where it adheres to the surfaces of the base metals and solidifies, acting like a powerful metallic glue.
Strength and Performance Compared
While welding wins on raw tensile strength, that isn't the only factor that defines a successful joint. The impact of the process on the materials being joined is equally critical.
Absolute Strength
For a given joint, a properly executed weld will almost always be stronger than a braze. The fused, continuous grain structure of a weld can match or even exceed the strength of the original parent metal.
Heat Resistance
Welded joints are far more resistant to high temperatures. A brazed joint will fail if the application temperature approaches the melting point of its filler metal, which is by definition much lower than the melting point of the base metals.
The Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
This is a critical distinction. The intense, localized heat of welding creates a heat-affected zone (HAZ) around the joint. This area of base metal doesn't melt but its metallurgical properties can be negatively altered, potentially leading to brittleness or cracking.
Brazing uses significantly lower overall temperatures. This minimizes the size and impact of the HAZ, reducing the risk of thermal distortion, warping, or metallurgical damage to the parent materials. This is especially important for materials like cast iron.
Where Brazing Is the Superior Choice
The limitations of welding create clear scenarios where brazing is not just an alternative, but the optimal solution.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
Brazing excels at joining different types of metals, such as copper to steel or aluminum to brass. Attempting to weld most dissimilar metals is metallurgically impossible, as their different melting points, thermal expansion rates, and composition would result in an extremely weak and brittle joint.
Thin or Delicate Components
The lower heat and gentle thermal profile of brazing make it ideal for joining thin-walled tubes or delicate parts. Welding would easily warp, distort, or even burn through such materials.
Complex Assemblies and Automation
Brazing produces clean, uniform joints that typically require little to no finishing. Processes like vacuum brazing can create exceptionally high-quality, impurity-free joints, making the method highly repeatable and suitable for high-volume automated production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between brazing and welding requires looking beyond a simple strength chart and analyzing the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and high-temperature performance: Welding is the correct choice, as the fusion of base metals creates the most robust and heat-resistant connection.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals, thin-walled tubing, or delicate components: Brazing is the superior method, as its lower heat input prevents damage and enables the joining of otherwise incompatible materials.
- If your primary focus is minimizing part distortion and the risk of cracking in the base metal: Brazing provides a significant advantage due to its much smaller and less severe heat-affected zone.
Ultimately, selecting the right process means defining what "strong enough" is for your specific application and material constraints.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Welding | Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Strength | Superior (fuses base metals) | Strong, but lower than welding |
| Heat Resistance | High (matches base metal) | Limited by filler metal melting point |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | Large, can cause distortion/cracking | Minimal, reduces part damage |
| Dissimilar Metals | Difficult or impossible | Excellent capability |
| Ideal For | Thick sections, max strength, high temps | Thin/delicate parts, dissimilar metals, automation |
Still Unsure Which Process is Best for Your Lab Equipment or Components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right solutions for your laboratory and manufacturing challenges. Whether your project requires the brute strength of welding or the precision and versatility of brazing, our expertise in material joining can help you achieve optimal results while protecting the integrity of your materials.
Let our specialists guide you to the most efficient and reliable joining method for your specific application. Contact KINTEK today for a expert consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing



















