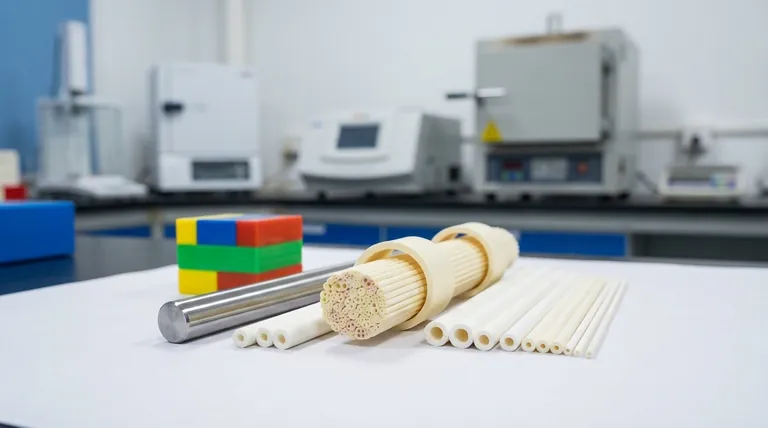
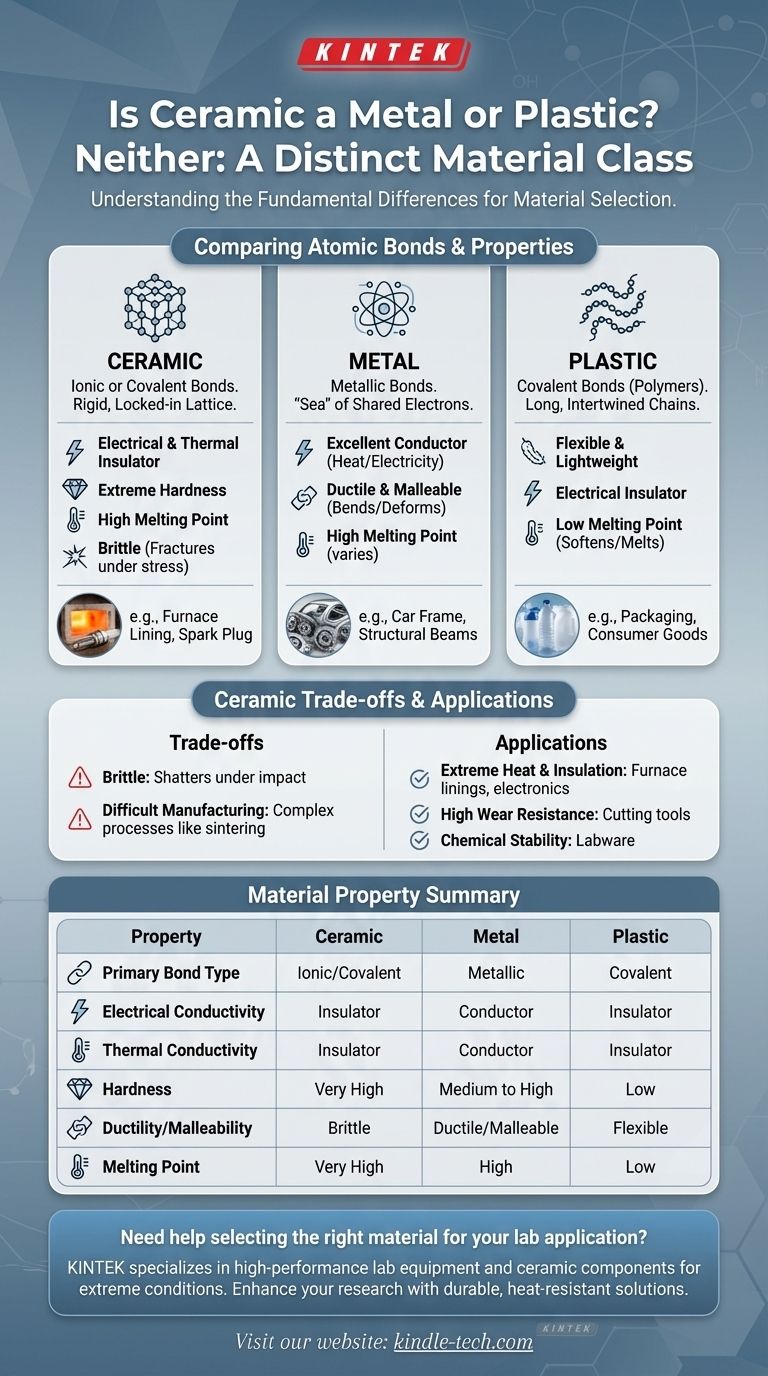
In short, ceramic is neither a metal nor a plastic. It is a distinct class of material with its own unique atomic structure and a fundamentally different set of properties. Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic solids, often crystalline, composed of a metal and a non-metal held together by incredibly strong ionic or covalent bonds.
The core difference between ceramics, metals, and plastics lies in their atomic bonds. The rigid, locked-in structure of a ceramic gives it extreme hardness and heat resistance, while the flexible bonds of metals and plastics allow them to bend and deform.

What Defines a Material? The Role of Atomic Bonds
To understand why ceramic is its own category, we must look at the atomic level. The way atoms bond together dictates a material's strength, conductivity, and melting point.
Metals: A "Sea" of Shared Electrons
Metals are characterized by metallic bonds. In this structure, atoms are arranged in a crystalline lattice, but their outer electrons are not tied to any single atom. They form a delocalized "sea" of electrons that flows freely.
This electron sea is why metals are excellent conductors of electricity and heat. It also allows the metal atoms to slide past one another without breaking apart, which is why metals are ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (can be hammered into sheets).
Plastics: Long, Intertwined Chains
Plastics are polymers, which are extremely long chains of molecules (typically based on carbon) linked by strong covalent bonds. However, these long chains are held to each other by much weaker forces.
This structure is why plastics are generally flexible, lightweight, and have low melting points. When heated, the weak forces between the chains are easily overcome, allowing the material to soften and melt.
Ceramics: A Rigid, Locked Lattice
Ceramics are typically formed by ionic or strong covalent bonds between a metal and a non-metal element (like oxides, nitrides, or carbides). These bonds create a very stable and rigid crystalline structure.
Unlike the fluid electron sea in metals, the electrons in ceramics are tightly held in place. This makes ceramics excellent electrical and thermal insulators. The immense strength of these bonds gives ceramics their signature hardness and extremely high melting points.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The unique properties of ceramics come with significant trade-offs that are critical to understand when choosing a material.
The Price of Hardness is Brittleness
The same rigid atomic lattice that makes a ceramic incredibly hard also makes it brittle. When a strong impact occurs, there is no way for the atoms to slide past each other as they do in a metal.
Instead of bending, the energy from the impact has nowhere to go but into breaking the strong atomic bonds, causing the material to fracture catastrophically. A metal will dent; a ceramic will shatter.
Manufacturing and Machining Challenges
The high melting points and extreme hardness of ceramics make them difficult to process. They cannot be easily cast or machined like metals or molded like plastics.
Manufacturing ceramic parts often involves complex processes like sintering (fusing powders together with heat), which can be more expensive and time-consuming, especially for intricate shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these fundamental differences allows you to select the appropriate material for a specific task.
- If your primary focus is durability under extreme heat or electrical insulation: Ceramic is the definitive choice for applications like furnace linings, spark plugs, or electronic substrates.
- If your primary focus is strength combined with the ability to bend or deform without breaking: Metal is the correct material for structural components, from car frames to building supports.
- If your primary focus is low cost, light weight, and easy formability: Plastic is the ideal solution for countless applications, such as packaging, consumer goods, and casings.
Ultimately, classifying a material correctly is the first step in harnessing its unique strengths for your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Property | Ceramic | Metal | Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Bond Type | Ionic/Covalent | Metallic | Covalent (within chains) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Insulator | Conductor | Insulator |
| Thermal Conductivity | Insulator | Conductor | Insulator |
| Hardness | Very High | Medium to High | Low |
| Ductility/Malleability | Brittle | Ductile/Malleable | Flexible |
| Melting Point | Very High | High | Low |
Need help selecting the right material for your lab application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic components designed for extreme conditions. Our expertise ensures you get durable, heat-resistant solutions tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our materials can enhance your research and processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Ball Valve Seat
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
People Also Ask
- How does a corundum tube function in a vacuum vertical tube furnace? Key Roles in Vapor Transport and Heat Resistance
- What is the temperature range of alumina tube? A Guide to Maximizing Performance and Lifespan
- What are the typical properties of high-alumina (Al2O3) refractories? Enhance Performance with High-Temp Resilience
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes



















