When comparing lab-grown diamonds, it's essential to understand that neither High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) nor Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is definitively "better" in all aspects. HPHT diamonds are often considered higher quality "as-grown" because the process mimics the earth's natural formation and typically requires less post-growth treatment. However, the CVD method is more cost-effective, and once a diamond is cut, polished, and certified, the origin method is virtually indistinguishable to the naked eye.
The core difference is not one of final quality, but of process philosophy and cost. HPHT prioritizes creating a high-quality crystal from the start, while CVD prioritizes manufacturing efficiency, relying on standard post-growth treatments to achieve its final quality.

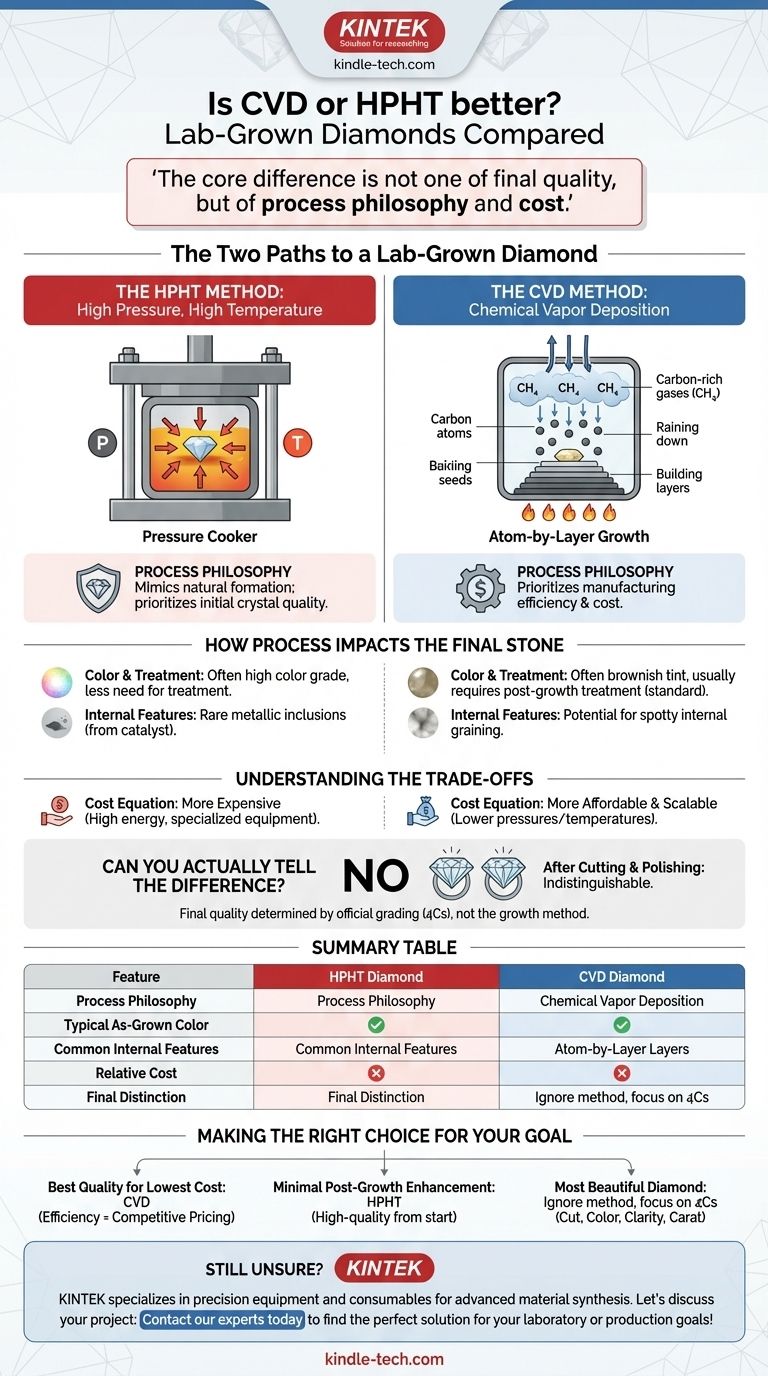
The Two Paths to a Lab-Grown Diamond
To understand the differences, you must first understand how each diamond is made. Both methods produce a stone that is chemically, physically, and optically identical to a mined diamond.
The HPHT Method: High Pressure, High Temperature
The HPHT process replicates the natural diamond-growing conditions found deep within the Earth.
A small diamond "seed" is placed in a chamber with carbon and a metal catalyst. This chamber is subjected to immense pressure and extreme temperatures, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a larger diamond. It is essentially a "pressure cooker" for diamonds.
The CVD Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition
The CVD process is more akin to building a crystal atom-by-atom.
A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases. These gases are heated, causing the carbon atoms to separate and "rain down" onto the seed, slowly building up layers and growing into a larger diamond crystal.
How Process Impacts the Final Stone
The differences in the growth environment create distinct characteristics in the "raw" diamond crystal, which are then addressed during cutting and polishing.
Color and the Need for Treatment
As-grown CVD diamonds often exhibit a brownish tint due to the nature of their rapid, layered growth. To counteract this, most CVD diamonds undergo a post-growth treatment (ironically, often the HPHT process) to improve their color. This is a permanent and standard step.
HPHT diamonds, having been formed in a more stable, high-pressure environment, are less likely to have color issues from the start and often do not require post-growth treatment to achieve high color grades.
Internal Characteristics
The fast growth of CVD can sometimes result in spotty internal graining or other minor marks within the crystal structure.
Conversely, HPHT diamonds can occasionally trap microscopic fragments of the metal catalyst used in their growth chamber. However, in modern, high-quality HPHT diamonds, these metallic inclusions are rare and typically invisible without magnification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Your choice between CVD and HPHT is ultimately a choice between different sets of manufacturing trade-offs.
The Cost Equation
The HPHT method is more expensive. It requires a massive amount of energy and highly specialized, durable equipment to maintain the necessary pressure and temperature.
The CVD method is more affordable and scalable. It operates at lower pressures and more moderate temperatures, reducing energy consumption and overall manufacturing cost. This cost savings is often passed on to the consumer.
Can You Actually Tell the Difference?
No. Once cut, polished, and set in jewelry, it is impossible for anyone, even a trained jeweler, to tell the difference between an HPHT and a CVD diamond without advanced laboratory equipment.
The final quality of the stone you purchase is determined by its official grading report (the 4Cs), not the method used to grow it. A D-color, VVS1-clarity CVD diamond is, for all practical purposes, identical to a D-color, VVS1-clarity HPHT diamond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Instead of asking which method is "better," ask which one aligns with your personal priorities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the best quality for the lowest cost: A well-graded CVD diamond is often the ideal choice, as its manufacturing efficiencies typically result in more competitive pricing.
- If your primary focus is a diamond that required minimal post-growth enhancement: An HPHT diamond is the clear winner, as its growth process more frequently produces a high-quality stone from the start without needing color treatment.
- If your primary focus is simply the most beautiful diamond you can afford: Ignore the growth method entirely and concentrate on the 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat—as detailed on the stone's grading certificate.
Ultimately, both methods produce a real and brilliant diamond, so your final decision should be guided by the certified quality and beauty of the individual stone, not its origin story.
Summary Table:
| Feature | HPHT Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Process Philosophy | Mimics natural formation; prioritizes initial crystal quality | Atom-by-layer growth; prioritizes manufacturing efficiency & cost |
| Typical As-Grown Color | Often high color grade, less need for treatment | Often has a brownish tint, usually requires post-growth treatment |
| Common Internal Features | Rare metallic inclusions (from catalyst) | Potential for spotty internal graining |
| Relative Cost | Higher due to energy-intensive process | More affordable and scalable |
| Final Distinction | Indistinguishable after cutting and polishing; quality determined by the 4Cs | Indistinguishable after cutting and polishing; quality determined by the 4Cs |
Still Unsure Which Diamond is Right for You?
Navigating the nuances of lab-grown diamonds can be complex. The best choice depends on your specific needs for quality, budget, and personal values.
KINTEK specializes in precision equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis, including the technologies that make these diamonds possible. Our expertise can help you understand the processes behind your purchase.
Let's discuss your project: Whether you're a researcher, jeweler, or manufacturer, we can provide the insights and equipment you need.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty



















