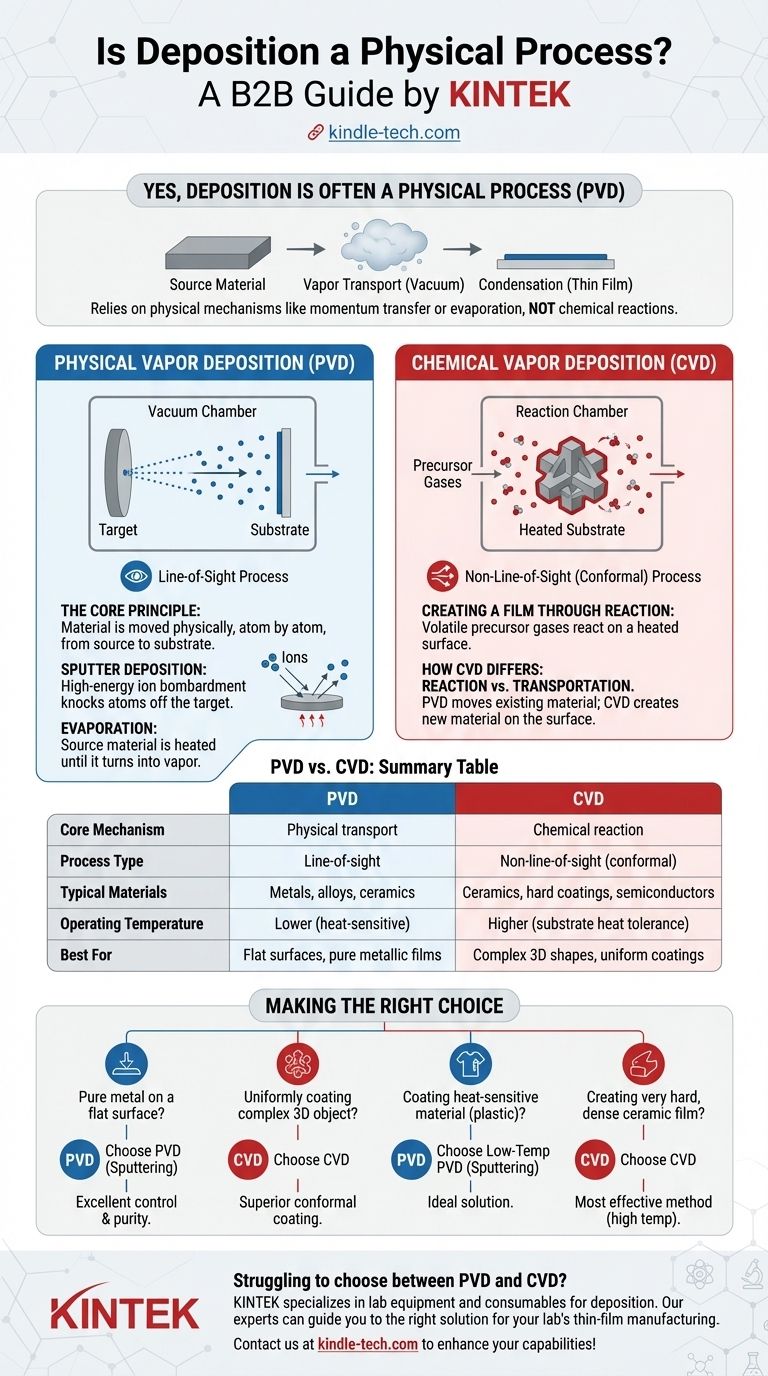
Yes, deposition is often a physical process, categorized under the umbrella term Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). In these techniques, a solid or liquid source material is transformed into a vapor, transported through a vacuum or low-pressure environment, and then condensed onto a substrate to form a thin film. This entire process relies on physical mechanisms like momentum transfer or evaporation, not chemical reactions.
The core distinction in thin-film technology is between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), which physically transports material from a source to a substrate, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which uses chemical reactions to grow a film from precursor gases. Understanding this difference is the key to selecting the right manufacturing process.

What is Physical Deposition (PVD)?
Physical Vapor Deposition encompasses a group of processes where the deposited material is the same as the source material, simply moved from one place to another.
The Core Principle: A Mechanical Process
At its heart, PVD is a line-of-sight process. Material is ejected from a source (called a target) and travels in a straight line until it hits the substrate, where it condenses and builds up a film layer by layer.
This process is carried out in a vacuum chamber to ensure the vaporized atoms do not collide with air molecules, allowing them to travel freely to their destination.
Sputter Deposition: A Key Example
Sputtering is one of the most common and versatile PVD techniques. It works by bombarding a solid target material with high-energy ions, typically from an inert gas like argon.
This bombardment acts like a subatomic sandblaster, physically knocking atoms off the target. These ejected atoms then travel across the chamber and deposit onto the substrate.
As the reference material notes, sputtering is a complex process with many parameters, but this complexity provides a high degree of control over the final film's properties, such as its density and crystal structure.
Evaporation: The Other Major PVD Method
The other primary PVD method is thermal evaporation. In this technique, the source material is heated in a vacuum until it evaporates or sublimes.
The resulting vapor then rises, travels through the chamber, and condenses on a cooler substrate, forming the desired thin film. This is conceptually simpler than sputtering but offers less control over the film's microstructure.
The Alternative: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
To fully understand PVD, it is essential to contrast it with its chemical counterpart, CVD.
Creating a Film Through Reaction
In CVD, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber. These gases are not the final film material itself.
Instead, they react or decompose on a heated substrate's surface to produce the desired solid film. Unwanted byproducts are then pumped away.
How CVD Differs from PVD
The fundamental difference is reaction versus transportation. PVD moves existing material; CVD creates new material on the surface.
Because CVD relies on gases that can flow around objects, it is not a line-of-sight process. This gives it a significant advantage in coating complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between PVD and CVD depends entirely on the application, the materials involved, and the desired outcome.
When to Choose Physical Deposition (PVD)
PVD is often preferred for depositing a very wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, and certain ceramics that are difficult to create through chemical reactions.
It generally operates at lower temperatures than CVD, making it suitable for coating heat-sensitive substrates like plastics. It is the go-to choice for creating extremely pure metallic films.
When Chemical Deposition (CVD) is Better
CVD excels at creating highly conformal coatings that cover complex geometries and sharp corners without thinning. It is often used to produce very hard, durable ceramic coatings (like titanium nitride) and is a foundational process in semiconductor manufacturing.
The trade-off is the need for high temperatures and the handling of precursor gases, which can be toxic, corrosive, or pyrophoric.
Making the Right Choice for Your Thin Film
Your selection hinges on balancing the properties of the film with the limitations of the substrate and the complexity of the part.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metal or alloy onto a flat surface: Sputtering (PVD) offers excellent control and purity.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating a complex 3D object: CVD is almost always the superior choice due to its non-line-of-sight nature.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material like plastic: A low-temperature PVD process like sputtering is the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a very hard, dense ceramic or dielectric film: CVD is often the most effective method, assuming the substrate can withstand the heat.
Ultimately, both physical and chemical deposition are powerful tools for engineering surfaces with specific properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical transport of material (e.g., sputtering, evaporation) | Chemical reaction on substrate surface |
| Process Type | Line-of-sight | Non-line-of-sight (conformal) |
| Typical Materials | Metals, alloys, certain ceramics | Ceramics, hard coatings, semiconductors |
| Operating Temperature | Lower (suitable for heat-sensitive substrates) | Higher (requires substrate heat tolerance) |
| Best For | Flat surfaces, pure metallic films, heat-sensitive materials | Complex 3D shapes, uniform coatings, hard ceramics |
Struggling to choose between PVD and CVD for your thin-film application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for deposition processes, helping laboratories optimize their thin-film manufacturing. Our experts can guide you to the right solution based on your material, substrate, and performance requirements. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of deposition in chemistry? From Gas to Solid for Advanced Material Engineering
- What is thin film in wave optics? Harness Light Interference for Precision Optical Design
- What are the useful applications of carbon nanotubes? Enhance Materials for Batteries, Composites, and Electronics
- What are 3 products that carbon nanotubes can be used in? Enhancing Batteries, Tires, and Composites
- What are the applications of thin film in nanotechnology? Building the Future, One Atom at a Time
- What are the sputtering target specifications? The Key to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps involved in the sputtering process? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the function of film deposition? To Engineer Superior Surface Properties


























