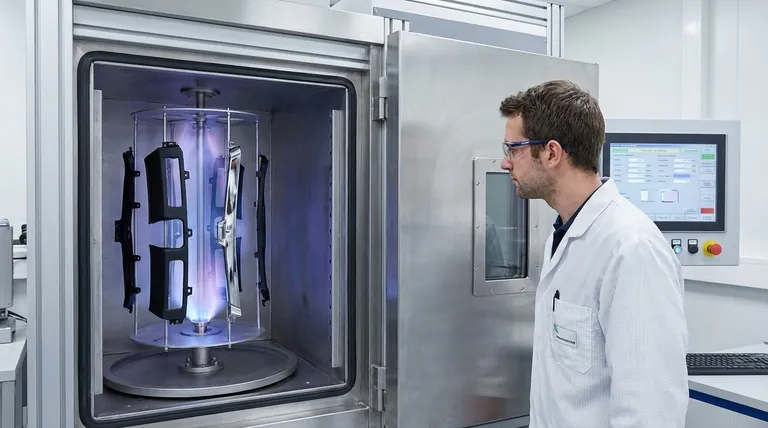
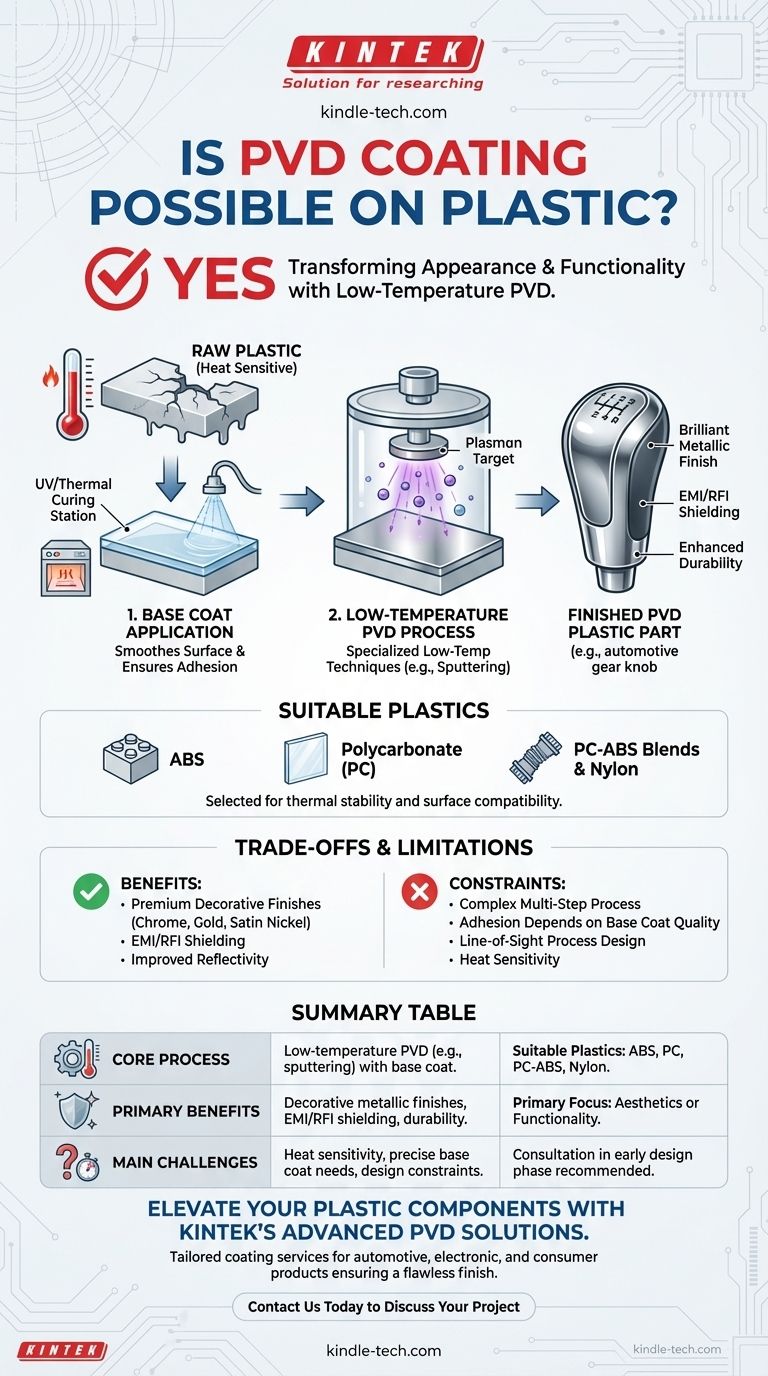
Yes, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is not only possible on plastic but is a widely used industrial process. This technique is commonly employed to apply a thin metallic or ceramic film onto plastic substrates, transforming their appearance and functional properties for industries ranging from automotive to consumer electronics.
The core challenge with coating plastics is their low melting point. Therefore, applying a PVD coating to a polymer requires a specialized low-temperature process and often depends on meticulous surface preparation, such as a base coat, to ensure proper adhesion and a high-quality finish.

How PVD on Plastic Works
Unlike the high-temperature PVD processes used for robust metals and ceramics, coating plastic requires a more nuanced approach. The success of the process hinges on managing temperature and ensuring the coating has a stable surface to bond with.
The Core Challenge: Heat Sensitivity
Standard PVD processes can operate at temperatures up to 800°F (427°C), which would easily melt or deform most plastic materials.
To overcome this, specialized low-temperature PVD techniques are used. These processes, such as sputtering, operate at temperatures that polymers can safely withstand while still achieving a durable, high-quality film.
The Critical Role of a Base Coat
Directly applying a PVD coating to raw plastic often results in poor adhesion and magnifies any surface imperfections.
To solve this, a UV-cured or thermal lacquer base coat is typically applied first. This initial layer serves two critical functions: it creates a smooth, glass-like surface for the PVD film and provides an ideal chemical foundation for strong molecular bonding.
Common Plastics Suitable for PVD
While many plastics can be coated, some are favored due to their thermal stability and surface characteristics.
Commonly used plastics include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), Polycarbonate (PC), PC-ABS blends, Nylon, and various polyesters. These materials respond well to the necessary pre-treatments and can withstand the low-temperature vacuum environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PVD offers significant benefits for plastic components, it's essential to understand its practical limitations. The process is more complex than simply coating a piece of metal.
Adhesion and Overall Durability
The final durability of the part is not solely dependent on the PVD film itself. The performance is a function of the entire system: the plastic substrate, the quality of the base coat, and the PVD layer.
Any failure in the underlying base coat will lead to a failure of the PVD coating, regardless of the film's inherent toughness.
Material and Design Constraints
The need for a low-temperature process means not all plastics are suitable candidates. Polymers with very low heat deflection temperatures may not be compatible.
Furthermore, the design of the part must allow for uniform application of both the base coat and the PVD film, as PVD is a line-of-sight process.
Process Complexity
Metallizing plastic with PVD is a multi-step endeavor involving cleaning, pre-treatment, base coat application and curing, and finally, the PVD process itself. This complexity can influence production time and cost compared to other finishing methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD coating is an excellent technology for enhancing plastic parts, but its successful implementation depends on aligning the process with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is a premium decorative finish: PVD is a superior choice for achieving brilliant metallic looks (chrome, satin nickel, gold) on plastics like ABS and polycarbonate for automotive, cosmetic, or consumer products.
- If your primary focus is a functional property: For applications like EMI/RFI shielding or creating reflective surfaces, ensure the selected plastic and base coat system can meet the durability and environmental demands of the final product.
- If you are in the early design phase: Select a plastic known for its compatibility with PVD (e.g., PC-ABS) and consult with a coating specialist to ensure your part geometry is optimized for the process.
Ultimately, PVD coating effectively elevates plastic from a simple substrate to a material with high-performance surface characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Low-temperature PVD (e.g., sputtering) with a base coat for adhesion |
| Suitable Plastics | ABS, Polycarbonate (PC), PC-ABS blends, Nylon |
| Primary Benefits | Decorative metallic finishes (chrome, gold), EMI/RFI shielding, enhanced durability |
| Main Challenges | Heat sensitivity of plastics, need for precise base coat application, part design constraints |
Elevate your plastic components with KINTEK's advanced PVD coating solutions. Specializing in lab equipment and consumables, we provide tailored coating services that enhance the appearance, functionality, and durability of your plastic parts. Whether for automotive trim, electronic housings, or consumer products, our expertise ensures a flawless finish. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can add value to your laboratory or manufacturing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use



















