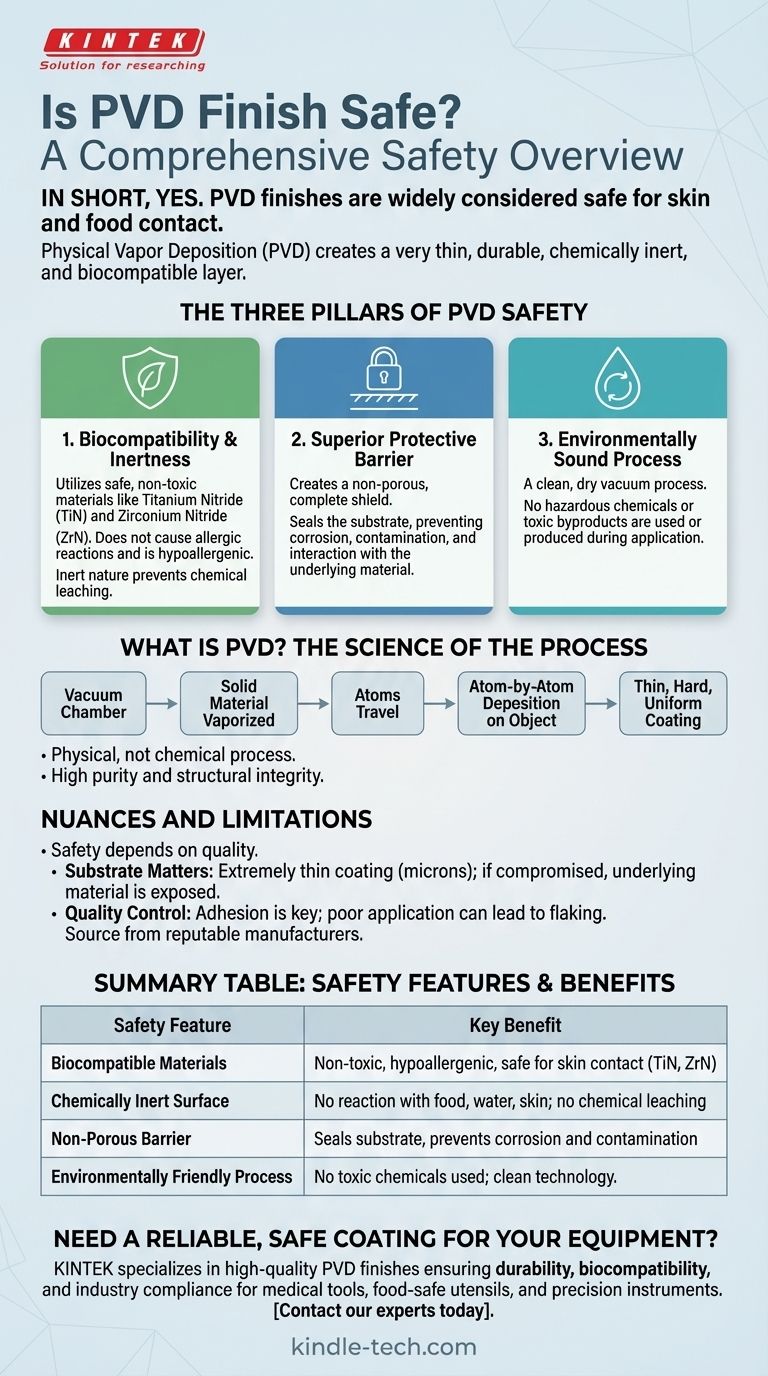
In short, yes. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) finishes are overwhelmingly considered safe for a wide range of consumer products, including those that come into contact with your skin and food. This safety stems from the fact that the process creates a very thin, durable, and chemically inert layer of material that is biocompatible.
The safety of a PVD finish is not due to a single factor, but a combination of three key elements: the use of inert materials, the creation of a stable and non-reactive surface, and an application process that is inherently clean and free of harsh chemicals.

What Exactly Is a PVD Finish?
To understand its safety, you first need to understand what a PVD coating is. It is not a paint, a sealant, or a traditional chemical plating.
A Thin, Strong Shield
PVD is a process performed in a vacuum chamber where a solid material is vaporized into its atomic components. These atoms then travel across the chamber and deposit onto the target object, forming a very thin—yet extremely hard and dense—coating.
This coating bonds to the substrate at a molecular level, creating a finish that is far more durable and corrosion-resistant than most traditional coating methods.
The Science of the Process
As noted in technical descriptions, the process is physical, not chemical. It involves vaporizing a source material and then depositing it atom by atom.
This method is exceptionally clean and produces a coating of very high purity and uniformity. It's this purity and structural integrity that form the foundation of its safety.
The Pillars of PVD Safety
The confidence in PVD's safety for consumer use comes from its inherent material properties and the nature of its application.
Pillar 1: Biocompatibility and Inertness
The materials most commonly used for decorative PVD coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), are biocompatible. This means they are non-toxic and do not produce an immune or allergic response when in contact with the human body.
Because the final PVD layer is so stable and chemically inert, it does not leach chemicals or react with foods, water, or skin. This is why PVD is a preferred coating for medical implants, surgical tools, and high-end cutlery.
Pillar 2: A Superior Protective Barrier
A PVD coating is not porous. It creates a complete, solid barrier over the underlying material (the substrate).
As long as this coating remains intact, it effectively seals the substrate from any interaction with its environment. This ensures that the properties you are interacting with are those of the safe PVD material, not the metal underneath.
Pillar 3: An Environmentally Sound Application
Unlike processes like electroplating, which rely on baths of hazardous chemicals, PVD is an environmentally friendly "dry" process.
No toxic byproducts are created during the coating application, making it safer for the environment and the workers involved in manufacturing. This "clean" aspect is a key part of its overall safety profile.
Understanding the Nuances and Limitations
While PVD is fundamentally safe, a complete technical assessment requires acknowledging its dependencies and potential points of failure. True durability and safety are a function of quality.
The Substrate Still Matters
The PVD coating is only a few microns thick. If the coating is severely scratched, gouged, or eventually wears away after years of heavy use, the material underneath will become exposed. The safety of the product would then depend on the composition of that base material.
Quality Control is Paramount
The "excellent adhesion" mentioned in technical papers is a result of a well-controlled process. A poorly applied PVD coating could, in theory, flake or chip.
For this reason, it is crucial to source PVD-coated products from reputable manufacturers who have stringent quality control measures to ensure a proper molecular bond.
Making an Informed Decision
PVD is an exceptional technology, and you can feel confident in its safety when you choose products wisely based on their intended use.
- If your primary focus is everyday items (jewelry, watches, faucets): PVD is an outstanding choice that offers a durable, hypoallergenic, and safe finish.
- If your primary focus is food contact (cutlery, utensils): Seek out products explicitly marketed as "food-safe" to ensure the manufacturer has used appropriate PVD materials and quality control for that purpose.
- If your primary focus is cost above all else: Be aware that extremely cheap PVD-coated items may have cut corners on the substrate material or the quality of the application, potentially compromising long-term durability.
Ultimately, choosing a product with a PVD finish is a reliable decision for both safety and performance.
Summary Table:
| Safety Feature | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Biocompatible Materials | Non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and safe for skin contact (e.g., TiN, ZrN). |
| Chemically Inert Surface | Does not react with food, water, or skin, ensuring no chemical leaching. |
| Non-Porous Barrier | Seals the substrate completely, preventing corrosion and contamination. |
| Environmentally Friendly Process | No toxic chemicals used during application, making it a clean technology. |
Need a reliable, safe coating for your laboratory equipment or consumables? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality PVD finishes that ensure durability, biocompatibility, and compliance with industry safety standards. Whether you're developing medical tools, food-safe utensils, or precision instruments, our coatings provide the protection and performance you demand. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's PVD solutions can enhance your product's safety and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance



















