For applications demanding extreme durability and wear resistance, PVD is one of the most advanced and effective coatings available today. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a simple layer like paint; it is a high-tech vacuum deposition process that bonds a thin film to a substrate at a molecular level. This creates an incredibly hard surface that significantly outperforms most traditional coating methods in hardness and longevity.
The question isn't whether PVD is the "best" coating, but rather if it's the right one for your specific goal. PVD excels at enhancing the surface properties of a material—like hardness and wear resistance—without altering its dimensions, making it an elite choice for precision components and premium finishes.

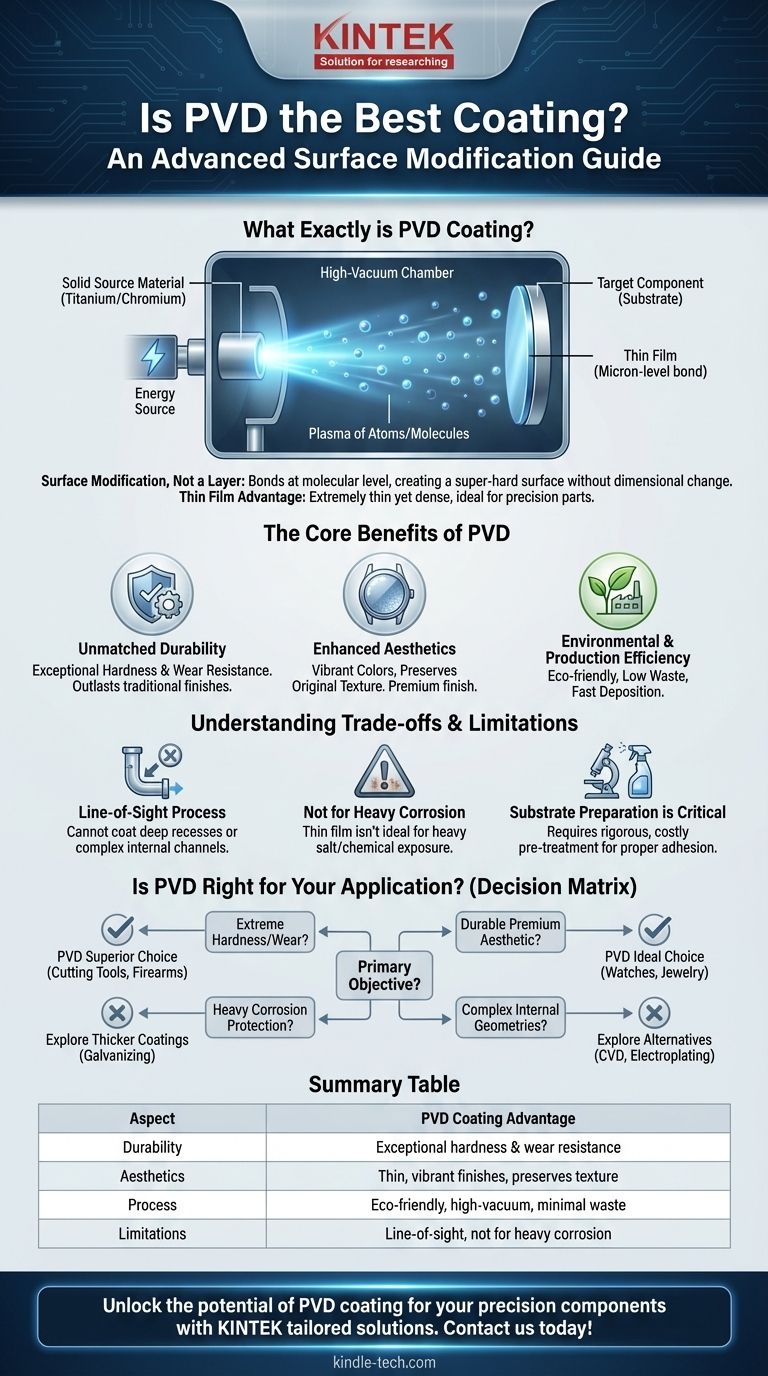
What Exactly is PVD Coating?
To understand if PVD is the right choice, you must first understand what it is and, more importantly, what it isn't. It fundamentally differs from traditional coating methods.
It's a Surface Modification, Not a Layer
Unlike paint or powder coating that adds a substantial layer, PVD bonds with the metal surface at the micron level. It becomes an integral part of the surface itself.
This process essentially changes the physical properties of the outermost layer of the component, creating a new, super-hard surface condition with very minimal material buildup.
The Thin-Film Advantage
PVD is often called "Thin Film Deposition" for a reason. The resulting coating is extremely thin, yet incredibly dense and hard.
This is a critical advantage for precision parts, such as engine components, cutting tools, or fine watch casings, where even a tiny change in dimensions could compromise function.
How the Process Works
The entire PVD process takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber. A solid source material (like titanium or chromium) is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules.
This vapor is then precisely deposited onto the target component, where it condenses and bonds to the surface, forming the desired thin film.
The Core Benefits of PVD
The unique nature of the PVD process delivers a specific set of powerful advantages that are difficult to achieve with other methods.
Unmatched Durability
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and highly resistant to wear, friction, and heat. This is why they are a standard in demanding industries for coating items like drill bits, medical implants, and engine parts.
A PVD finish will outlast virtually any traditional finish, maintaining its integrity and appearance even under constant use.
Enhanced Aesthetics Without Compromise
Because the PVD film is so thin and translucent, it doesn't obscure the original texture of the underlying material. You can add vibrant colors like gold, black, or rose gold while still seeing the brushed or polished finish of the metal beneath.
This allows for premium, durable aesthetics that are impossible to achieve with thick, opaque coatings.
Environmental and Production Efficiency
The PVD process is environmentally friendly, as it does not use the toxic substances or produce the hazardous waste associated with processes like chrome plating.
Furthermore, computer-controlled PVD machines offer fast deposition speeds and can be integrated into efficient production lines, suitable for both large-scale manufacturing and small custom batches.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single technology is the best for every situation. To make an informed decision, you must recognize where PVD might not be the ideal choice.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized material inside the PVD chamber travels in a straight line. This means it can only coat surfaces that it can "see."
Deep recesses, complex internal channels, or hidden areas on a component will not be coated effectively. This is a critical limitation for parts with intricate internal geometries.
Not Primarily for Corrosion Protection
While a PVD coating is very dense, its extreme thinness means it's not the best choice for protecting against heavy corrosion, such as exposure to salt water or harsh chemicals.
For these applications, thicker, sacrificial coatings like galvanizing or specialized polymer coatings are often more effective.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The molecular bond that gives PVD its strength can only form on a perfectly clean and prepared surface. Any oil, dust, or microscopic imperfection will prevent proper adhesion.
This means PVD requires a rigorous and costly pre-treatment process, which can add to the overall expense and complexity of the operation.
Is PVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Your decision should be based on your primary objective. PVD is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but an advanced tool for specific high-performance needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: PVD is likely the superior choice, especially for cutting tools, firearms, or high-friction components.
- If your primary focus is a durable, premium aesthetic: PVD offers long-lasting color finishes for products like watches, jewelry, or high-end hardware without hiding the material's texture.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty corrosion protection: You should evaluate thicker, more traditional coatings designed specifically to resist harsh chemical or environmental exposure.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries: PVD's line-of-sight nature is a limitation, and you may need to explore processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or electroplating.
By understanding its function as a surface modification rather than a simple coating, you can confidently determine where PVD offers an unbeatable advantage.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Coating Advantage |
|---|---|
| Durability | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance for demanding applications. |
| Aesthetics | Thin, vibrant finishes that preserve the underlying material's texture. |
| Process | Environmentally friendly, high-vacuum deposition with minimal waste. |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight process; not ideal for heavy corrosion protection or complex internal geometries. |
Unlock the potential of PVD coating for your precision components. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for laboratories seeking superior surface modifications. Whether you're enhancing cutting tools, medical implants, or high-end hardware, our expertise ensures optimal performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD solutions can meet your specific needs and elevate your product's quality and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















