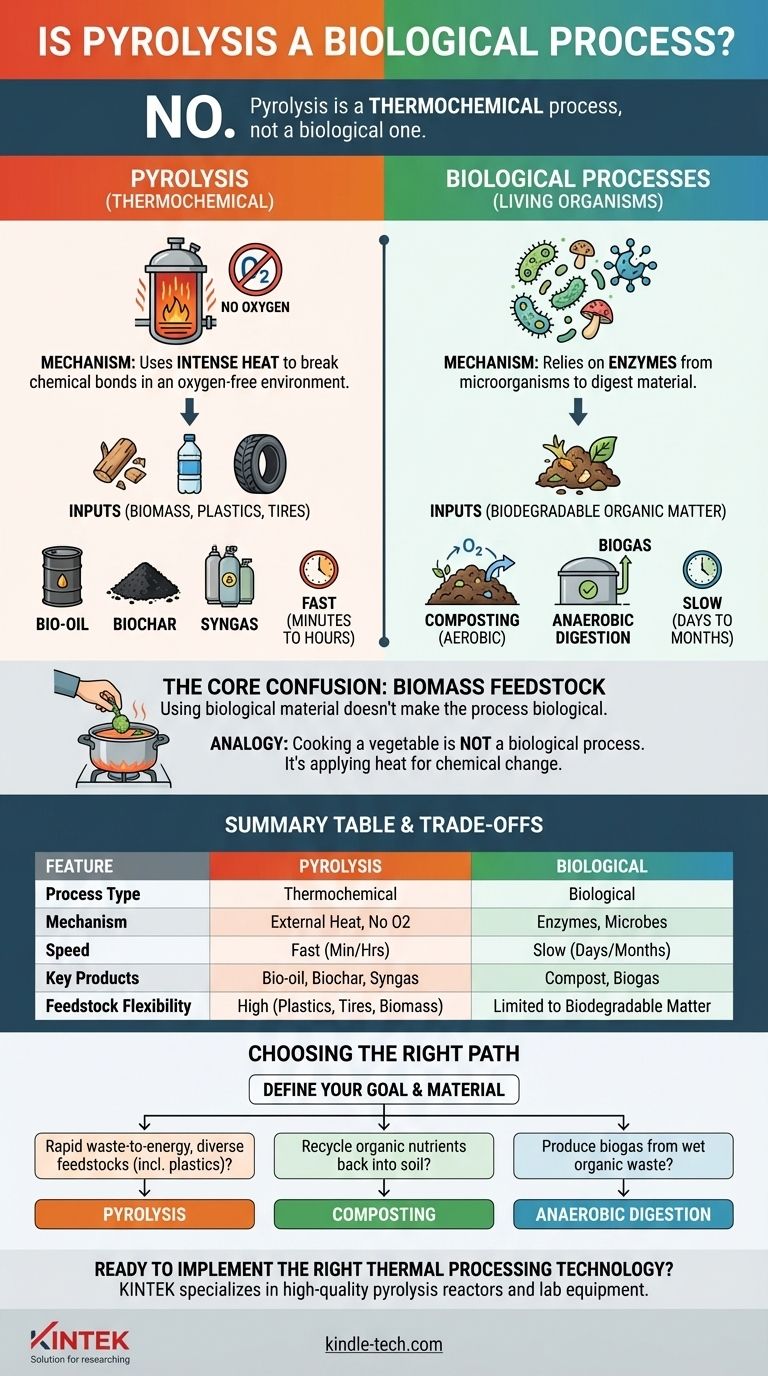
In short, no. Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process, not a biological one. It relies on intense heat to break down materials in an oxygen-free environment, whereas biological processes depend on living organisms like bacteria or fungi to achieve decomposition.
The core distinction lies in the mechanism: pyrolysis uses external heat to force chemical bonds to break, while biological processes use enzymes from microorganisms to digest material. The common use of biological matter (biomass) as a feedstock for pyrolysis is often the source of this confusion.

What Defines Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a specific type of thermal decomposition characterized by its unique conditions and outcomes. Understanding these factors makes its distinction from biological processes clear.
A Thermochemical Reaction
The name itself, from the Greek words pyro (fire) and lysis (separation), describes the process perfectly. It is a thermochemical reaction, meaning it uses heat (thermo) to induce a fundamental change in a material's chemical composition (chemical).
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
Pyrolysis occurs in a reactor or vessel that is either a vacuum or has been purged with an inert gas. This absence of oxygen is non-negotiable.
If oxygen were present, the material would simply burn in a process called combustion. By removing oxygen, the heat doesn't burn the material but instead breaks it down into smaller, often valuable, molecules.
The Inputs and Outputs
This process is highly versatile and can be applied to a wide range of feedstocks, including organic materials like biomass and inorganic ones like plastics and tires.
The primary outputs are typically a liquid fuel (bio-oil), a solid, carbon-rich residue (biochar), and a mixture of flammable gases (syngas).
The Mechanism of Biological Decomposition
Biological processes operate on entirely different principles, relying on the metabolic functions of living organisms.
Driven by Living Organisms
Biological decomposition is mediated by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. These organisms produce enzymes that break down complex organic matter to extract nutrients and energy for their own survival.
Key Examples: Composting and Digestion
Two common examples are composting and anaerobic digestion.
Composting is an aerobic process (it requires oxygen) where microbes decompose organic waste into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. Anaerobic digestion is an anaerobic process (it occurs without oxygen) where different microbes break down waste to produce biogas.
Understanding the Key Point of Confusion
The overlap in terminology, particularly around "biomass" and "anaerobic" conditions, can be misleading. The distinction lies in how the breakdown is initiated.
Using Biological Material Isn't a Biological Process
While pyrolysis frequently uses biomass (wood, crop residue, etc.) as a feedstock, the process itself is not biological. The origin of the material does not define the nature of the reaction.
An Analogy: Cooking
Think of it this way: cooking a vegetable is not a biological process, even though the vegetable is from a biological source. The process is the application of heat to create a chemical change (cooking), just as pyrolysis is the application of extreme heat to cause thermochemical decomposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Pyrolysis vs. Biological Methods
Choosing between these methods depends entirely on the feedstock, desired outcome, and operational constraints.
Speed and Scale
Pyrolysis is an engineered, industrial process that is extremely fast, often completing in minutes to hours. Biological processes are naturally slow, taking days, weeks, or even months to complete.
Feedstock Flexibility
Pyrolysis can process a very wide range of materials, including non-biodegradable plastics, tires, and mixed waste streams. Biological methods are restricted to biodegradable organic matter.
Control and End Products
Pyrolysis offers a high degree of control. By precisely managing temperature and processing time, operators can influence the ratio of bio-oil, biochar, and syngas produced. Biological processes are less tunable and yield entirely different products like compost or biogas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate technology, you must first define your objective and your starting material.
- If your primary focus is rapid waste-to-energy conversion for diverse feedstocks (including plastics): Pyrolysis is the appropriate thermochemical pathway.
- If your primary focus is recycling organic nutrients back into the soil from garden or food waste: Aerobic composting is the ideal biological process.
- If your primary focus is producing methane-rich biogas from wet organic waste like manure or sewage sludge: Anaerobic digestion is the correct biological choice.
Understanding the fundamental difference between applying external heat and leveraging microorganisms is the key to selecting the right technology for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Biological Processes (e.g., Composting) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Thermochemical | Biological |
| Primary Mechanism | External heat in an oxygen-free environment | Enzymes from microorganisms (bacteria, fungi) |
| Speed | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slow (days to months) |
| Key Products | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas | Compost, Biogas |
| Feedstock Flexibility | High (plastics, tires, biomass) | Limited to biodegradable organic matter |
Ready to implement the right thermal processing technology for your lab or project?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis reactors and related systems, to help you achieve precise and efficient material breakdown. Whether your focus is on waste-to-energy conversion, material analysis, or sustainable product development, our expertise ensures you get the right solution.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















