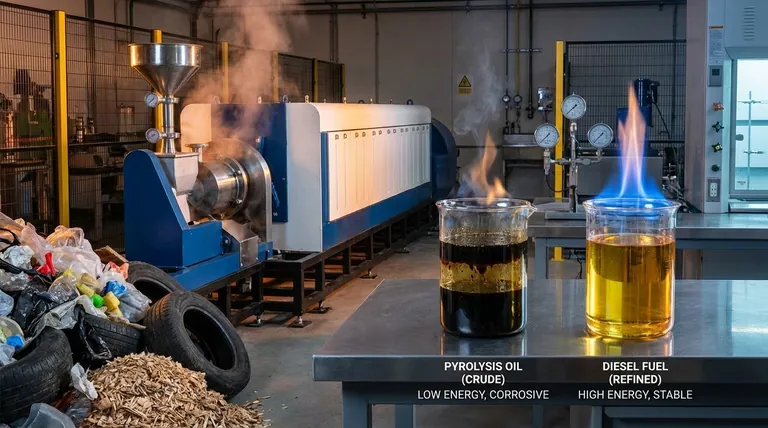
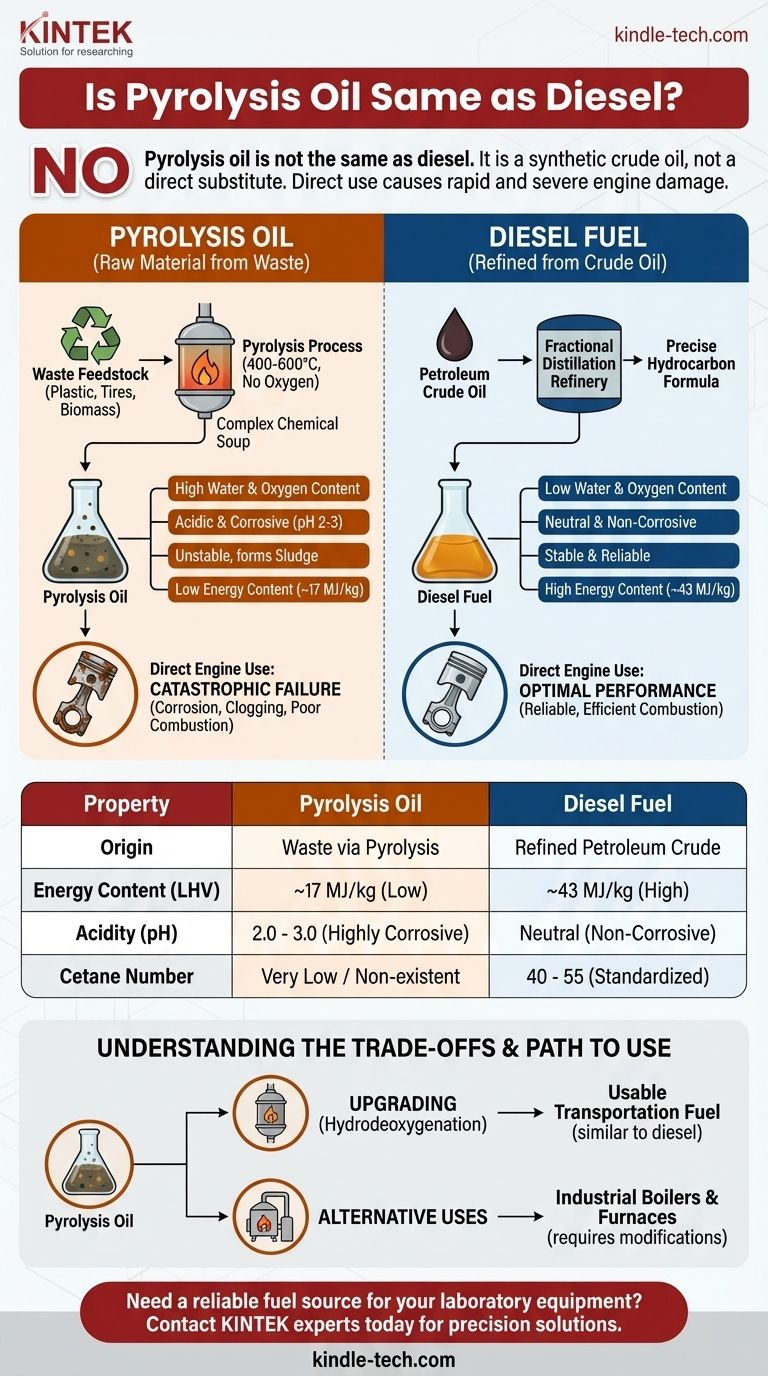
No, pyrolysis oil is not the same as diesel. While both are combustible liquids that can be used as fuel, they are fundamentally different in their origin, chemical composition, and physical properties. Pyrolysis oil is a crude, unrefined product derived from waste, whereas diesel is a highly refined and standardized fuel fraction from petroleum crude oil.
The critical takeaway is to view pyrolysis oil not as a direct substitute for diesel, but as a synthetic crude oil. Using it directly in an unmodified diesel engine will cause rapid and severe damage due to its corrosive nature and poor combustion characteristics.

What is Pyrolysis Oil? The Raw Material
Pyrolysis oil, sometimes called bio-oil or tire-derived fuel (TDF) oil, is the liquid product of pyrolysis. It represents a potential pathway for converting waste into a valuable energy carrier.
The Pyrolysis Process
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-starved environment. When feedstocks like plastic waste, scrap tires, or biomass are heated to 400-600°C without air, they break down into three products: a solid (char), a gas (syngas), and a liquid (pyrolysis oil).
A Complex Chemical Soup
Unlike diesel, pyrolysis oil is a highly complex and unstable mixture of hundreds of different chemical compounds. It is characterized by high water content (15-30%), high oxygen content (35-40% for bio-oil), and the presence of acids, aldehydes, ketones, and phenols. It also contains fine particles of char and ash.
Diesel: A Refined and Stable Fuel
Diesel fuel is one of the most common and well-understood fuels in the world. Its properties are tightly controlled by international standards to ensure reliable engine performance.
Fractional Distillation of Crude Oil
Diesel is produced at a refinery through the fractional distillation of petroleum crude oil. It is a specific "cut" or fraction that boils in a well-defined temperature range, separating it from lighter fractions like gasoline and heavier ones like lubricating oil.
A Precise Hydrocarbon Formula
Standard diesel fuel is composed almost entirely of hydrocarbons—chains of hydrogen and carbon atoms (typically C10 to C20). It has very low oxygen and water content, is chemically stable, and is non-acidic. Additives are often included to improve lubricity, ignition quality, and cold-weather performance.
Key Differences That Matter in an Engine
The chemical differences between pyrolysis oil and diesel lead to vastly different behaviors within an engine's fuel system and combustion chamber.
Energy Content (Heating Value)
The high water and oxygen content in pyrolysis oil means it contains significantly less energy per kilogram. The Lower Heating Value (LHV) of pyrolysis oil is typically around 17 MJ/kg, which is less than half that of diesel fuel at ~43 MJ/kg. This means you would need more than twice the amount of oil to do the same amount of work.
Acidity and Corrosiveness
Pyrolysis oil is highly acidic, with a pH often between 2.0 and 3.0. This makes it extremely corrosive to the common metals (steel, aluminum, brass) and elastomers (seals, gaskets) used in standard fuel pumps, lines, and injectors. Diesel fuel is neutral and non-corrosive.
Ignition Quality (Cetane Number)
Diesel engines rely on the auto-ignition of fuel when it's injected into hot, compressed air. This ignition quality is measured by the cetane number. Diesel has a specified cetane number (typically 40-55). Pyrolysis oil has a very low or non-existent cetane number, meaning it will not ignite properly, leading to incomplete combustion, misfires, and engine knocking.
Stability and Contaminants
Pyrolysis oil is thermally unstable. When heated, its reactive compounds can polymerize, forming thick sludge and solids that will quickly clog fuel filters and injectors. The presence of char and ash further contributes to injector fouling and engine wear. Diesel is formulated to be stable under the heat and pressure of a fuel system.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Using Pyrolysis Oil
While pyrolysis oil presents an intriguing waste-to-energy solution, its direct use as a fuel is fraught with technical challenges.
The Problem with Direct Use
Attempting to run an unmodified diesel engine on raw pyrolysis oil will lead to catastrophic failure. The immediate effects would be fuel system corrosion, clogged filters and injectors from polymerization, and poor combustion causing excessive smoke, deposits, and potential mechanical damage.
The Path to Usable Fuel: Upgrading
To be used as a transportation fuel, pyrolysis oil must undergo significant secondary processing, known as upgrading. This often involves a catalytic process like hydrodeoxygenation (HDO), which uses hydrogen at high pressure and temperature to remove oxygen, water, and other contaminants. This process converts the unstable oil into stable, energy-dense hydrocarbons similar to conventional diesel.
Alternative Uses: Boilers and Furnaces
Raw pyrolysis oil can sometimes be co-fired in external combustion systems like industrial boilers or furnaces. However, even in these applications, the system must be specifically designed or modified with corrosion-resistant materials and specialized burners to handle the oil's aggressive properties and lower energy content.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the fundamental nature of these two liquids is crucial for any project involving them.
- If your primary focus is to fuel a standard diesel engine: You must use refined diesel fuel that meets established industry specifications like ASTM D975 (in the US) or EN 590 (in Europe).
- If your primary focus is to utilize waste via pyrolysis: Recognize that the resulting oil is a crude intermediate, not a finished fuel. It must either be sold to a refinery for upgrading or used in specialized industrial boilers designed to handle corrosive fuels.
Ultimately, knowing the properties of your fuel is the first and most critical step toward a successful and reliable energy application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Pyrolysis Oil | Diesel Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Waste (plastic, tires, biomass) via pyrolysis | Refined petroleum crude oil |
| Energy Content (LHV) | ~17 MJ/kg | ~43 MJ/kg |
| Acidity (pH) | 2.0 - 3.0 (Highly corrosive) | Neutral (Non-corrosive) |
| Cetane Number | Very Low / Non-existent | 40 - 55 (Standardized) |
| Primary Use | Industrial boilers (with modifications) or upgrading | Standard diesel engines |
Need a reliable fuel source for your laboratory equipment or process heating?
Understanding fuel properties is critical for safe and efficient operation. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for laboratories that demand precision and reliability. Whether you require equipment compatible with specific fuels or expert advice on your application, our team is here to help.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time











