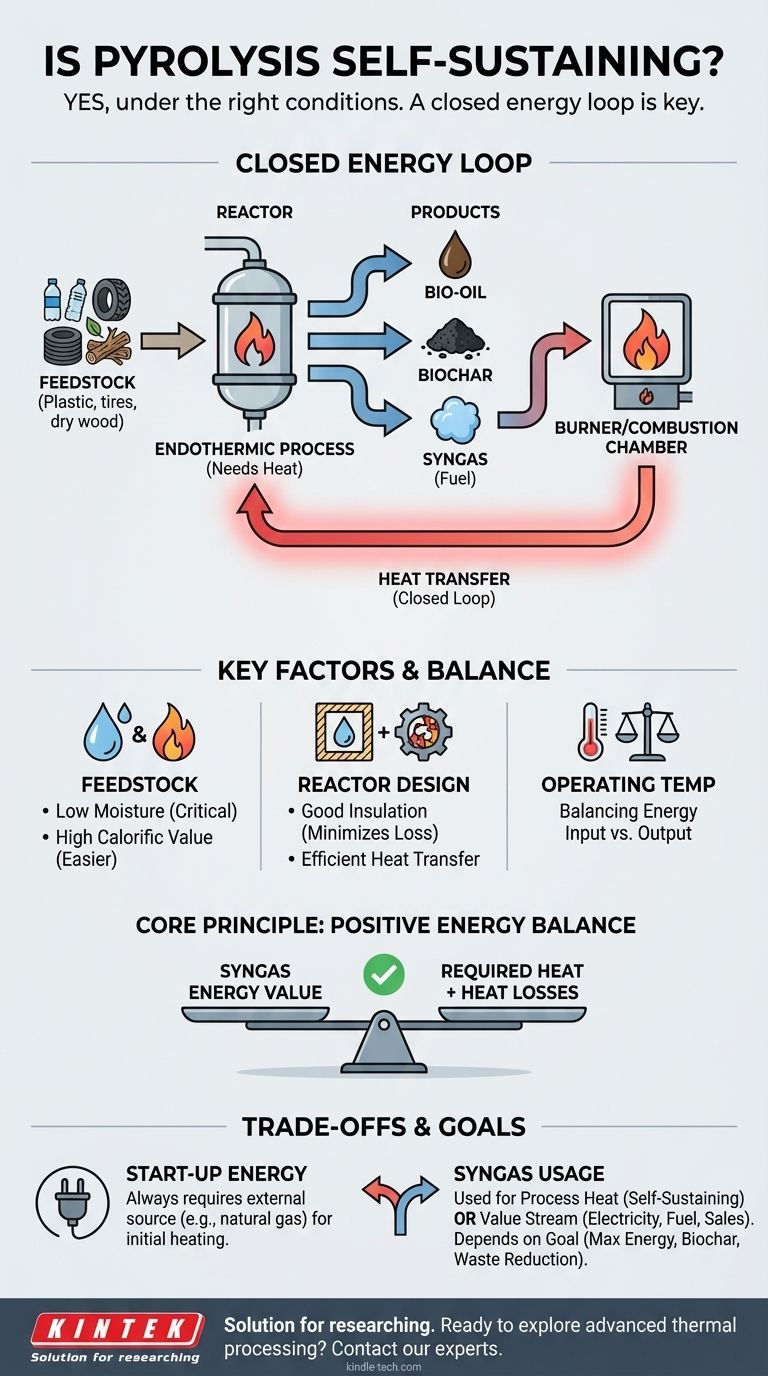
Under the right conditions, yes, pyrolysis can be a self-sustaining process. This is achieved when the non-condensable, combustible gases (syngas) produced during the reaction are captured and used as the fuel source. This creates a closed energy loop, where the process generates the heat it needs to continue breaking down new feedstock without a continuous external energy supply. However, achieving this state is not automatic and depends heavily on system efficiency and the type of material being processed.
The core principle of self-sustaining pyrolysis is achieving a positive energy balance. The energy value of the combustible gases produced must be sufficient to supply the heat required for the endothermic reaction and overcome all heat losses from the system.

The Energy Dynamics of Pyrolysis
To understand how pyrolysis can sustain itself, we must first look at its fundamental energy requirements and outputs.
An Endothermic Foundation
Pyrolysis is fundamentally an endothermic process. This means it requires a constant input of thermal energy to break down the complex molecules in the feedstock into simpler, smaller molecules. The reaction will not start or continue without an external heat source.
The Source of On-Site Fuel
The process breaks down organic material into three primary products:
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A liquid fuel.
- Biochar (or Char): A solid, carbon-rich material.
- Syngas: A mix of non-condensable gases, including hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and other hydrocarbons.
The key to self-sustainment lies in the syngas. This gas mixture is highly combustible and can be treated as an on-site fuel.
Closing the Energy Loop
A self-sustaining system is designed to "close the energy loop." The syngas is piped from the reactor to a burner or combustion chamber. The heat generated from burning the syngas is then transferred back to the pyrolysis reactor, providing the necessary endothermic heat to process the incoming feedstock.
Key Factors Determining Self-Sustainment
Whether a specific pyrolysis operation can become self-sustaining depends entirely on a few critical variables.
Feedstock Characteristics
The material you put in is the single most important factor.
- Moisture Content: High moisture content is the primary enemy of energy efficiency. A significant amount of energy must be spent just to boil off water before the pyrolysis reaction can even begin. Feedstocks like green wood or wet sludge make self-sustainment extremely difficult without extensive pre-drying.
- Calorific Value: The inherent energy content of the feedstock matters. Materials with high energy density, like plastics, tires, and oily waste, produce more energy-rich syngas, making it much easier to achieve self-sustainment.
Reactor Design and Insulation
The engineering of the system is critical for managing energy.
- Heat Loss: Poorly insulated reactors constantly lose heat to the surrounding environment. This energy leak means more syngas must be burned simply to maintain temperature, potentially making self-sustainment impossible.
- Heat Transfer: An efficient design ensures the heat generated from syngas combustion is effectively transferred to the new feedstock inside the reactor with minimal waste.
Operating Temperature
Higher pyrolysis temperatures (e.g., >600°C) require more energy to maintain but can also alter the composition of the syngas, potentially increasing its calorific value. Finding the optimal temperature is a balancing act between energy input required and energy output generated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving a self-sustaining process involves important considerations and is not always the best economic choice.
The Cost of Self-Sufficiency
The primary trade-off is that you are consuming a potentially valuable product. The syngas used to fuel the process could otherwise be used to generate electricity, be upgraded into transportation fuels, or sold as a chemical precursor. A self-sustaining system lowers operational energy costs, but at the expense of a potential revenue stream.
Start-up Energy Is Always Required
No pyrolysis system is self-starting. An external fuel source, such as natural gas, propane, or an electric heater, is always needed to bring the reactor up to its initial operating temperature. Self-sustainment only refers to the process's ability to run continuously once it reaches a stable state.
Process Stability and Control
Maintaining a stable energy balance requires sophisticated monitoring and control systems. Fluctuations in feedstock moisture, density, or chemical composition can disrupt the equilibrium, forcing the system to rely on its auxiliary start-up fuel source to maintain temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you should aim for a self-sustaining system depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy generation: Design a highly efficient system that not only self-sustains but produces excess syngas to fuel a turbine or engine, requiring dry, high-calorific feedstock.
- If your primary focus is high-value products like biochar: Self-sustainment is a key method for reducing operating costs. The goal is to use the absolute minimum amount of syngas needed, maximizing the yield of your target product.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Achieving self-sustainment is a critical goal to make the disposal process economically viable, often justifying investment in feedstock pre-treatment like drying.
Ultimately, achieving self-sustaining pyrolysis is an engineering challenge that balances feedstock properties with efficient system design to close the energy loop.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Self-Sustainment |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Moisture | High moisture requires more energy, making it difficult. |
| Feedstock Calorific Value | High-energy materials (plastics, tires) make it easier. |
| Reactor Insulation | Poor insulation causes heat loss, preventing it. |
| System Efficiency | Efficient heat transfer is critical for success. |
Ready to explore how pyrolysis can power your waste conversion or material processing goals? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions and laboratory equipment. Our expertise can help you design an efficient system to achieve energy independence. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific feedstock and operational objectives!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
People Also Ask
- What are the two advantages of using brazing when joining metal? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Complex Metal Assemblies
- What is an example of cold working and hot working? Control Metal Properties for Your Project
- What is the physical sputtering method? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Deposition
- Why is pyrolysis expensive? Unpacking the High Costs of Advanced Waste Conversion
- What are the disadvantages of electron beam deposition? Key Trade-offs in Film Quality & Adhesion
- What is the role of a laboratory stirrer or homogenizer in waste paper pretreatment? Maximize Fermentation Yields
- What is the trend in Synthetic Diamonds? Exponential Growth Reshaping the Gemstone Market
- Which heat treatment gives highest hardness? Quenching to Form Martensite for Maximum Hardness













