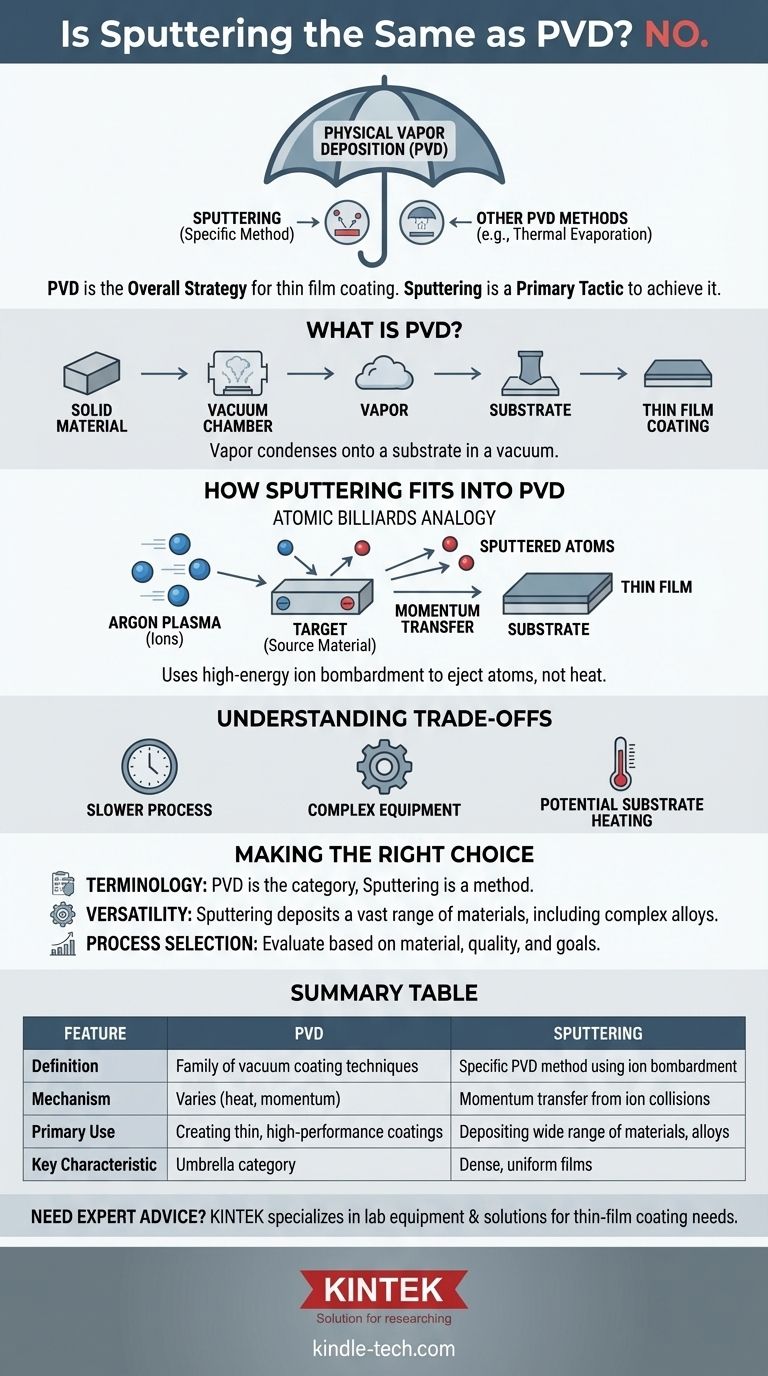
No, sputtering is not the same as PVD. Instead, sputtering is a specific method that falls under the broader category of processes known as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). To put it simply, PVD is the overall strategy for creating a thin film coating, while sputtering is one of the primary tactics used to achieve that goal.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) describes a family of vacuum-based coating techniques. Sputtering is one of the most important methods within that family, using high-energy ion bombardment to create a vapor, distinguishing it from other PVD methods like thermal evaporation, which uses heat.
What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
The Core Principle of PVD
Physical Vapor Deposition is a process where a solid material is converted into a vapor within a vacuum chamber. This vapor then travels and condenses onto the surface of an object (called a substrate), forming a very thin, high-performance coating.
A Category of Processes
PVD is not one single process but a class of them. The key difference between various PVD techniques lies in how the solid source material is turned into a vapor. This is where sputtering comes into the picture.
How Sputtering Fits into PVD
The Sputtering Mechanism
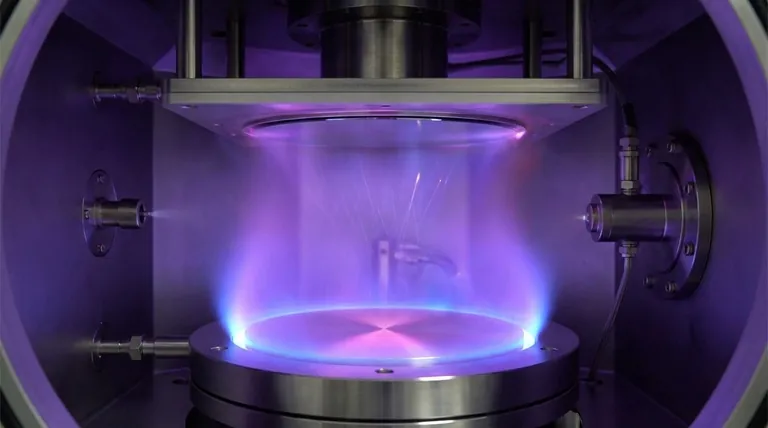
Sputtering is a PVD method that uses momentum transfer instead of heat. The process begins by introducing an inert gas, typically argon, into the vacuum chamber and creating a plasma.
An "Atomic Billiards" Analogy
The source material, known as the target, is given a high negative electrical charge. This causes positive argon ions from the plasma to accelerate and violently collide with the target.
Think of this as a game of atomic-scale billiards. The argon ions are the cue balls, striking the target and knocking loose individual atoms of the coating material.
Deposition onto the Substrate
These "sputtered" atoms are ejected from the target with significant energy. They then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the substrate, building up a dense and uniform thin film, one atom at a time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sputtering is Not Always Fastest
While highly controllable, sputtering can sometimes be a slower deposition process compared to thermal evaporation techniques. The rate at which atoms are ejected from the target is a critical parameter that must be carefully managed.
Process and Equipment Complexity
Controlling the plasma, ion energy, and chamber pressure requires sophisticated equipment and expertise. The setup for sputtering is generally more complex than for simpler thermal evaporation methods.
Potential for Substrate Heating
The high-energy bombardment involved in sputtering can transfer heat to the substrate. This can be a concern when coating temperature-sensitive materials like plastics or certain electronic components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The distinction between PVD as a category and sputtering as a method is crucial for selecting the right coating process for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is on correct terminology: Always remember that PVD is the overarching category, and sputtering is a specific technique within it.
- If your primary focus is on material versatility: Sputtering is an extremely powerful PVD method that allows for depositing a vast range of materials, including complex alloys and compounds that cannot be thermally evaporated.
- If your primary focus is on selecting a process: Understand that sputtering is just one option under the PVD umbrella; you must also evaluate other methods based on your material, desired film quality, and production goals.
Understanding this fundamental hierarchy is the first step toward making informed decisions in thin-film technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Sputtering (A PVD Method) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A family of vacuum-based coating techniques | A specific PVD method using ion bombardment |
| Mechanism | Varies by method (e.g., heat, momentum) | Momentum transfer from ion collisions |
| Primary Use | Creating thin, high-performance coatings | Depositing a wide range of materials, including alloys |
| Key Characteristic | Umbrella category | Known for dense, uniform films |
Need expert advice on selecting the right PVD or sputtering process for your laboratory's specific application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your thin-film coating needs. Our expertise ensures you get the precise, high-performance coatings required for your research or production. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















