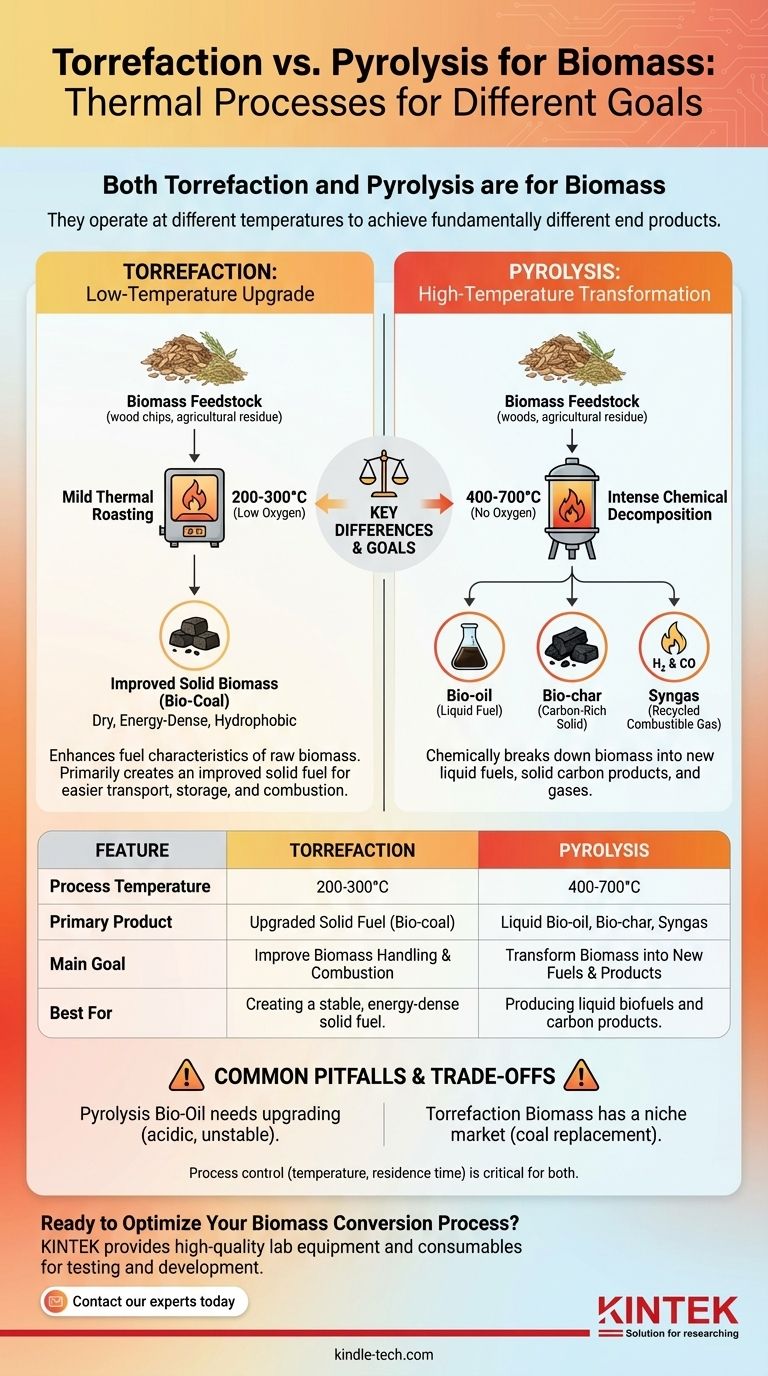
Both torrefaction and pyrolysis are thermal processes designed for biomass, but they operate at different temperatures to achieve fundamentally different goals. Pyrolysis is an intense, high-temperature process that chemically decomposes biomass into new products like liquid bio-oil and solid bio-char. In contrast, torrefaction is a milder, low-temperature "roasting" process that primarily upgrades the solid biomass itself, making it a more energy-dense and stable fuel.
The choice between torrefaction and pyrolysis is not a matter of which is "for" biomass, as both are. The critical distinction lies in your desired end product: pyrolysis transforms biomass into new liquid and solid outputs, while torrefaction improves biomass to create a better version of the solid fuel.

What is Pyrolysis? A High-Temperature Transformation
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that subjects biomass to high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen, preventing combustion and instead causing the material to break down into valuable new substances.
The Core Principle: Heating Without Oxygen
The process involves heating biomass feedstock rapidly in a reactor at temperatures between 400-700°C. This intense heat, combined with a very short residence time (often less than two seconds for fast pyrolysis), forces a chemical decomposition of the material's lignocellulose structure.
The Key Products: Bio-oil, Bio-char, and Syngas
Pyrolysis breaks biomass down into three distinct products:
- Bio-oil: A dark, viscous liquid that is the primary target of most fast pyrolysis operations. It can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used to produce specialty chemicals.
- Bio-char: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It can be used as a fuel, a soil amendment to improve fertility, or for carbon sequestration.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (like hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that are typically recycled to provide the heat needed to run the pyrolysis process itself.
Feedstock Versatility
A significant advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to process a wide variety of biomass. Suitable feedstocks include agricultural residues like corn stalks and rice husks, forest residues like wood chips and sawdust, and even certain industrial or municipal organic wastes.
What is Torrefaction? A Low-Temperature Upgrade
If pyrolysis is a complete transformation, torrefaction is best understood as a sophisticated enhancement. It is a milder thermal process designed to improve the fuel characteristics of raw biomass.
The Core Principle: "Roasting" Biomass
Torrefaction heats biomass in a low-oxygen environment at much lower temperatures than pyrolysis, typically between 200-300°C. This process is often compared to roasting coffee beans.
The Primary Goal: Creating an Enhanced Solid Fuel
The goal is not to create liquids or gases, but to produce a superior solid fuel. The heat drives off moisture and volatile organic compounds, breaking down the less energy-dense components of the biomass.
Why This Matters for Logistics and Use
The resulting torrefied biomass, often called "bio-coal," is a dry, energy-dense, and hydrophobic (water-resistant) material. This makes it far cheaper to transport and easier to store than bulky, wet raw biomass. It can also be easily crushed and co-fired in existing coal power plants with minimal modification.
Understanding the Key Differences
The decision to use one process over the other comes down to a few critical distinctions.
Temperature and Intensity
- Torrefaction: A mild, low-temperature (200-300°C) process.
- Pyrolysis: An intense, high-temperature (400-700°C) decomposition.
Primary Output
- Torrefaction: A single primary product: an improved, energy-dense solid bio-coal.
- Pyrolysis: Three distinct products: a liquid bio-oil, a solid bio-char, and combustible gases.
End Goal
- Torrefaction: To improve the handling, storage, and combustion properties of solid biomass.
- Pyrolysis: To create entirely new liquid fuels and valuable carbon products from biomass.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Neither technology is a perfect solution, and understanding their limitations is crucial for effective implementation.
The Challenge of Pyrolysis Bio-Oil
While bio-oil is a promising renewable fuel, it is not a direct "drop-in" replacement for petroleum. The raw bio-oil produced by fast pyrolysis is acidic, unstable, and contains impurities like tar that must be removed through a secondary upgrading or refining process before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
The Niche Role of Torrefaction
Torrefied biomass is an excellent solid fuel, but it still competes in a market dominated by raw biomass and fossil fuels. Its primary application is as a coal replacement for co-firing in large power plants, which represents a more specific market compared to the broad potential applications of bio-oil and bio-char.
Process Control is Critical
The success of both processes depends heavily on precise control of variables. Factors like feedstock moisture content, reactor temperature, and material residence time must be carefully managed to ensure the desired products are produced efficiently and consistently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate technology, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-value liquid fuel or a stable carbon soil amendment: Pyrolysis is the correct pathway, as it is designed to chemically transform biomass into these distinct new products.
- If your primary focus is improving raw biomass for easier transport, storage, and direct combustion: Torrefaction is the ideal process for creating a dense, water-resistant, and energy-rich solid fuel.
Ultimately, understanding your target output is the key to selecting the right thermal treatment for your biomass feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Torrefaction | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 200-300°C | 400-700°C |
| Primary Product | Upgraded solid fuel (Bio-coal) | Liquid bio-oil & solid bio-char |
| Main Goal | Improve biomass handling & combustion | Transform biomass into new fuels & products |
| Best For | Creating a stable, energy-dense solid fuel | Producing liquid biofuels and carbon products |
Ready to Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Process?
Choosing between torrefaction and pyrolysis is a critical decision that depends entirely on your target product and operational goals. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for testing and developing these thermal processes. Whether you're researching bio-oil yields or optimizing torrefied fuel properties, our solutions help you achieve precise, reliable results.
Let KINTEK support your laboratory's biomass innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover the right equipment for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















