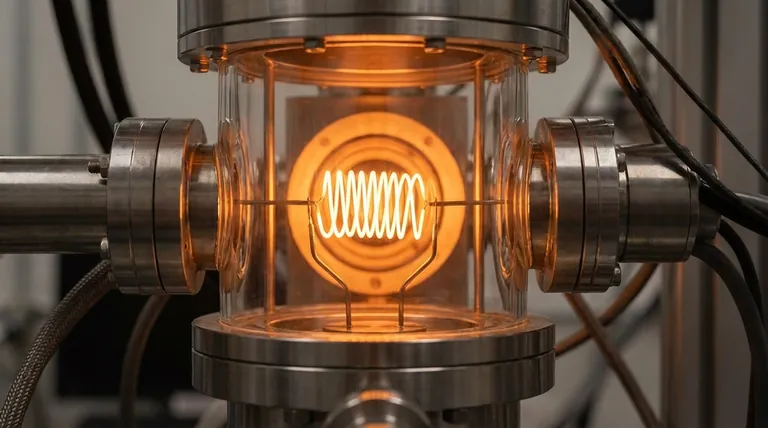
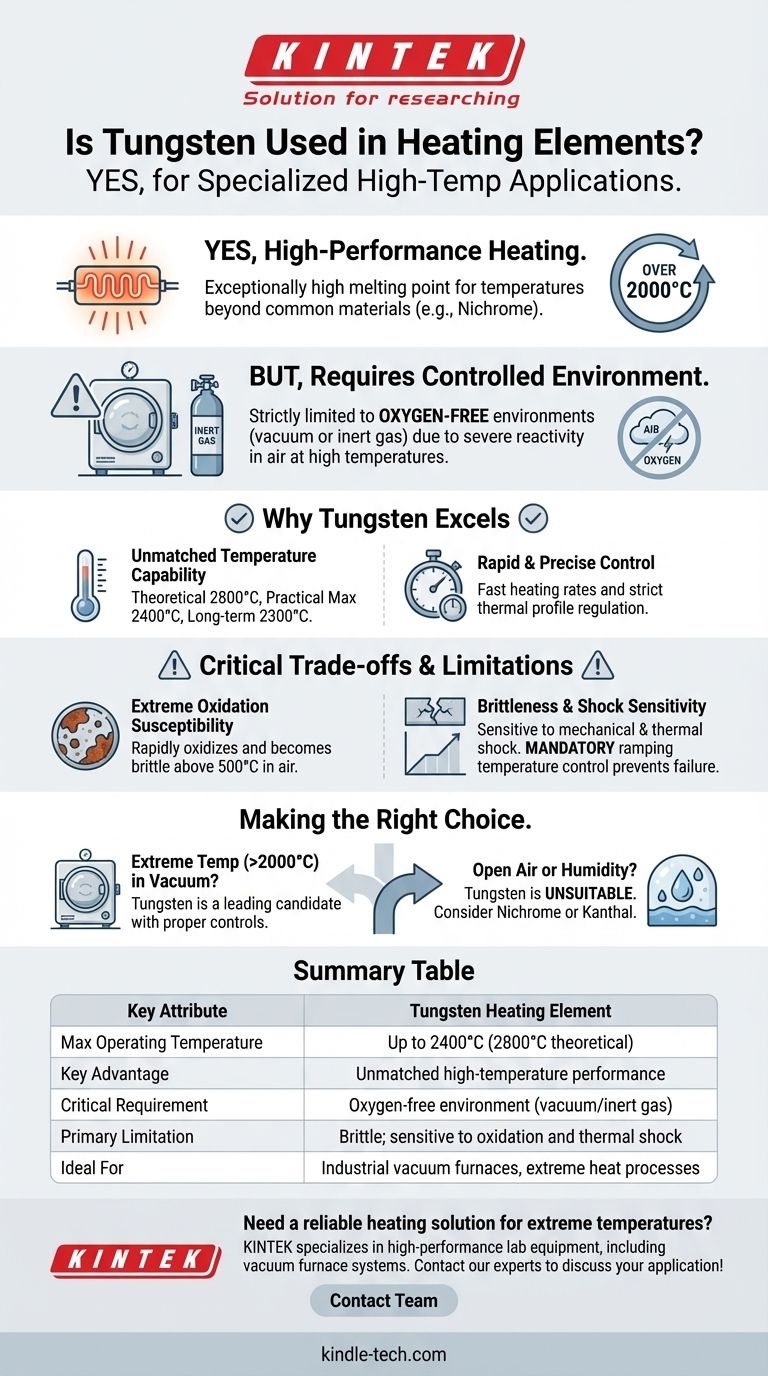
Yes, tungsten is used for high-performance heating elements, but only in highly specialized applications. Its exceptionally high melting point allows it to operate at temperatures far beyond what common materials like nichrome can withstand. However, its use is strictly limited to controlled, oxygen-free environments due to its severe reactivity in air at high temperatures.
Tungsten enables unparalleled heating performance at extreme temperatures (over 2000°C), but this capability comes at a cost. It demands a sophisticated, controlled environment—typically a vacuum or inert gas—to protect it from rapid oxidation and embrittlement, which cause catastrophic failure.
Why Tungsten Excels for High-Temperature Heating
Tungsten is a material of extremes. Its properties make it an excellent choice for applications like industrial vacuum furnaces, where reaching exceptionally high temperatures is the primary goal.
Unmatched Temperature Capability
The primary reason to choose tungsten is its ability to operate at incredibly high temperatures. It has a theoretical duty temperature of 2800°C (5075°F).
In practice, tungsten mesh heating elements have a maximum operational temperature of 2400°C and a recommended long-term use temperature of 2300°C.
Rapid and Precise Control
When used in a properly designed system, tungsten elements provide very fast heating rates and allow for precise temperature regulation within the heating chamber. This is critical for processes that require strict thermal profiles.
The Heating Mechanism
The process is fundamentally about energy conversion. As electricity flows through the tungsten, kinetic energy from the electrons is transferred to the tungsten atoms. This atomic-level agitation manifests as intense heat, which then radiates to warm the surrounding chamber.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs and Limitations
The decision to use tungsten is dictated more by its limitations than its strengths. Failing to respect its operational requirements will lead to immediate and total failure of the element.
Extreme Susceptibility to Oxidation
This is tungsten's most significant weakness. It cannot be exposed to air at temperatures above 500°C (932°F).
Exposure to oxygen or water vapor at high temperatures causes tungsten to rapidly oxidize and become brittle, destroying the element. This is why tungsten heaters are only used in vacuum furnaces or chambers filled with a pure, inert gas.
The Problem of Brittleness
Tungsten is inherently brittle, especially after being subjected to high temperatures. It is highly sensitive to both mechanical and thermal shock.
Dropping the element or heating it up too quickly from a cold start can cause it to crack and fail.
Sensitivity to Shock
To prevent failure from thermal shock, a ramping temperature control system is not just recommended—it is mandatory.
This system slowly and carefully increases the temperature during startup, allowing the element to heat up uniformly and mitigating the stresses that lead to embrittlement and cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a heating element material requires matching its properties to the operating environment and performance goals. Tungsten is a powerful but demanding tool.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (above 2000°C) in a vacuum: Tungsten is a leading candidate, provided you can implement the necessary environmental controls and ramp-up procedures.
- If your application operates in open air or involves humidity: Tungsten is entirely unsuitable and will fail quickly; you must consider robust iron-chromium-aluminum (e.g., Kanthal) or nickel-chromium (Nichrome) alloys instead.
By understanding its demanding environmental requirements, you can successfully leverage tungsten's unique properties for unparalleled high-temperature performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Attribute | Tungsten Heating Element |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 2400°C (2800°C theoretical) |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched high-temperature performance |
| Critical Requirement | Oxygen-free environment (vacuum/inert gas) |
| Primary Limitation | Brittle; sensitive to oxidation and thermal shock |
| Ideal For | Industrial vacuum furnaces, extreme heat processes |
Need a reliable heating solution for extreme temperatures? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnace systems designed for materials like tungsten. Our experts can help you select the right heating elements and ensure your system operates safely and efficiently. Contact our team today to discuss your high-temperature application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- Is tungsten a good heating element? Unlock Extreme Temperatures in Vacuum Environments
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes













