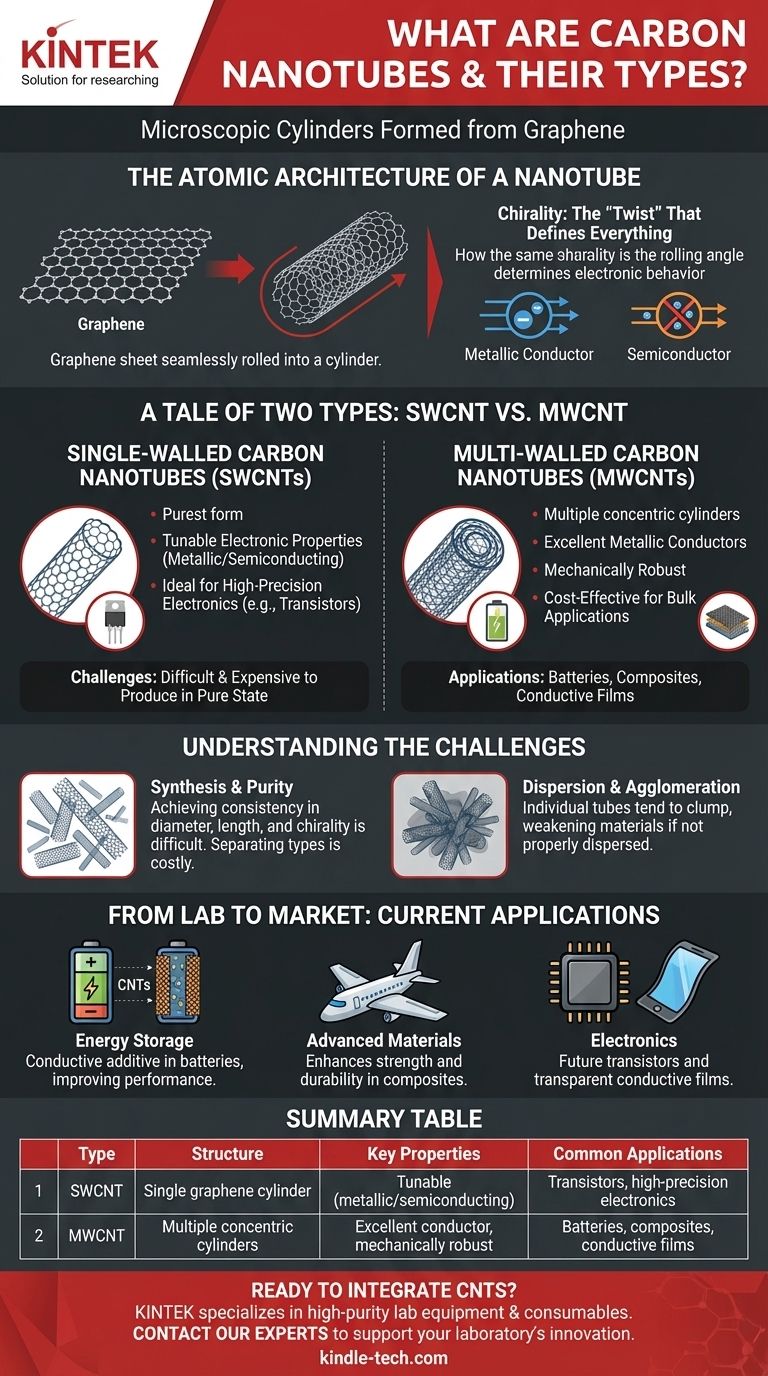
In essence, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are microscopic cylinders formed from a rolled-up sheet of single-layer carbon atoms, known as graphene. These incredibly small but powerful structures are primarily categorized by their construction: single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), which consist of a single atomic cylinder, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), which are composed of multiple concentric cylinders nested within each other. Their unique structure gives them extraordinary properties that far surpass traditional materials.
The true significance of carbon nanotubes lies not in their novelty, but in their unprecedented combination of extreme strength, low weight, and tunable electrical properties. This makes them a foundational material for breakthroughs in energy storage, advanced composites, and next-generation electronics.
The Atomic Architecture of a Nanotube
From Graphene to a Cylinder
Imagine a single sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice—this is graphene. A carbon nanotube is created when this sheet is seamlessly rolled into a cylinder.
This simple geometric transformation is the source of the CNT's remarkable properties. The bonds between the carbon atoms are immensely strong, creating a flawless and lightweight structure.
Chirality: The "Twist" That Defines Everything
The specific angle at which the graphene sheet is "rolled" is called its chirality. This microscopic twist is the single most important factor in determining a nanotube's electronic behavior.
Depending on this angle, a nanotube can behave either as a metallic conductor, allowing electrons to flow freely like in copper, or as a semiconductor, like silicon. This ability to predetermine electronic properties at the atomic level is a key reason for the intense interest in CNTs for electronics.
A Tale of Two Types: SWCNT vs. MWCNT
The most fundamental distinction between nanotubes is the number of walls they possess. This directly impacts their properties, cost, and ideal applications.
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs)
An SWCNT is the purest form of a carbon nanotube, consisting of just one cylindrical wall.
Their defining feature is that their electronic properties (metallic or semiconducting) are directly controlled by their specific chirality. This makes them the ideal candidate for highly precise electronic applications, such as transistors. However, they are significantly more difficult and expensive to produce in a pure, uniform state.
Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
MWCNTs consist of two or more concentric tubes nested inside one another, similar to the rings of a tree.
Because they are a mix of different layers, each with its own chirality, MWCNTs almost always behave as excellent metallic conductors. They are also mechanically more robust and much cheaper to synthesize in bulk, making them the go-to choice for applications where bulk conductivity or mechanical strength is the primary goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While their potential is vast, the practical application of CNTs is constrained by several key challenges that are the focus of intense research.
The Challenge of Synthesis and Purity
Manufacturing CNTs with perfectly consistent diameters, lengths, and chirality is extremely difficult. Most synthesis methods, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), produce a mixture of different types.
Separating these mixtures to isolate a specific type of nanotube (e.g., only semiconducting SWCNTs) is a complex and costly process, which currently limits their use in mass-market microelectronics.
Dispersion and Agglomeration
Due to powerful atomic forces, individual nanotubes tend to clump together, or agglomerate. This makes it difficult to disperse them evenly within a host material, such as a polymer or concrete.
If not properly dispersed, these clumps can act as defect points, weakening the final material instead of strengthening it.
From Lab to Market: Current Applications
Despite the challenges, CNTs are already making a significant impact in several industries, particularly where他们的独特属性可以立即提供价值。
Energy Storage
The primary commercial use for CNTs today is as a conductive additive in the electrodes of lithium-ion batteries.
Their high conductivity and surface area create an efficient electrical network within the electrode, improving charging speeds, extending battery life, and increasing overall energy density. This is a key application in the push for "green" technologies like electric vehicles.
Advanced Materials and Composites
When properly dispersed, CNTs can drastically enhance the properties of other materials. Adding even a small fraction of CNTs by weight can significantly increase the strength and durability of polymers, concrete, and ceramics.
These composites are finding use in aerospace, high-performance sporting goods, and construction.
Electronics and Conductive Films
SWCNTs are a leading candidate to replace silicon in future transistors, promising smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient computer chips.
Furthermore, CNTs can be sprayed to create thin, transparent, and conductive films, which have applications in flexible displays, touch screens, and solar cells.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between nanotube types is entirely dependent on your technical objective and budget.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics (like transistors): SWCNTs are necessary due to their precisely definable semiconducting properties, but be prepared for high costs and synthesis challenges.
- If your primary focus is mechanical reinforcement or bulk conductivity (like in batteries or composites): MWCNTs provide an excellent, cost-effective balance of performance and commercial availability.
- If your primary focus is developing transparent conductive films: Both SWCNTs and thin MWCNTs can be used, with the choice depending on the required trade-off between transparency and conductivity.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental differences between nanotube types is the key to unlocking their immense potential for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Type | Structure | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| SWCNT | Single graphene cylinder | Tunable (metallic/semiconducting) | Transistors, high-precision electronics |
| MWCNT | Multiple concentric cylinders | Excellent conductor, mechanically robust | Batteries, composites, conductive films |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables for nanotechnology applications. Our expertise can help you select the right materials and synthesis tools for your specific goals, whether you're working with SWCNTs for electronics or MWCNTs for composites. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Master Your Electrochemical Analysis
- What is the proper procedure for cleaning a glassy carbon sheet after use? A Definitive Guide to Ensure Reliable Results
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties



















