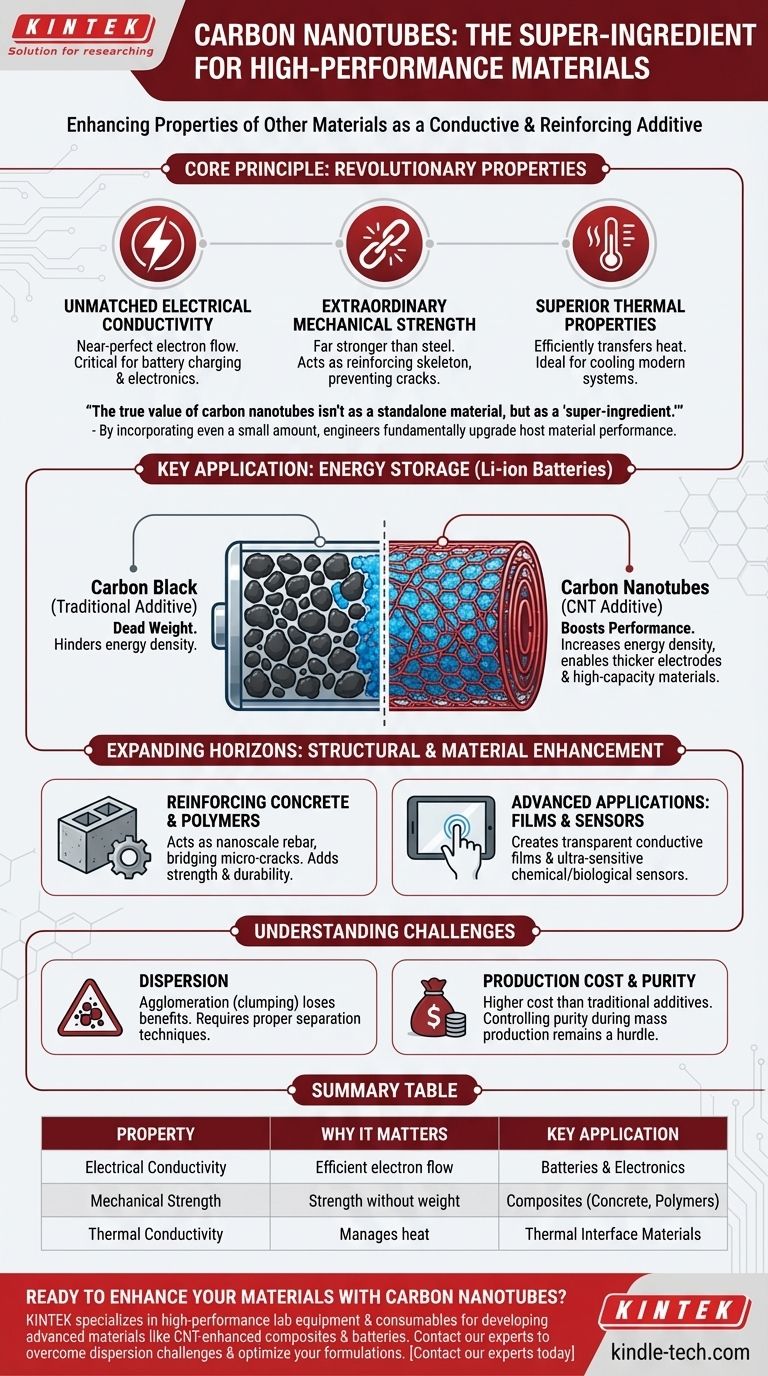
At their core, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are used as high-performance additives to enhance the properties of other materials. Their primary commercial application today is as a conductive additive in the electrodes of lithium-ion batteries, but they are also increasingly used to strengthen composites like concrete and polymers, and in advanced electronics such as transparent films and sensors.
The true value of carbon nanotubes isn't as a standalone material, but as a "super-ingredient." By incorporating even a small amount of CNTs, engineers can impart their extraordinary electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties into a host material, fundamentally upgrading its performance.

The Core Principle: Why Carbon Nanotubes Are Revolutionary
To understand their applications, you must first understand their unique physical properties, which stem directly from their cylindrical, rolled-up graphene structure.
Unmatched Electrical Conductivity
The atomic structure of a carbon nanotube creates a near-perfect pathway for electrons to flow with very little resistance. This makes them one of the most electrically conductive materials known.
This property is the reason they are so transformative in batteries, where efficient electron movement is critical for charging and discharging.
Extraordinary Mechanical Strength
Relative to their microscopic size and low weight, CNTs possess immense tensile strength and stiffness. They are among the strongest and stiffest materials ever discovered, far surpassing steel on a pound-for-pound basis.
This allows them to act as a reinforcing skeleton within other materials, preventing cracks and adding significant durability.
Superior Thermal Properties
In addition to conducting electricity, CNTs are also excellent conductors of heat. They can efficiently transfer thermal energy away from a source.
This makes them valuable in thermal interface materials used to cool modern electronics and other high-performance systems.
Key Application Deep Dive: Energy Storage
The most significant market for CNTs today is in lithium-ion batteries, where they are solving critical performance bottlenecks.
The Role of Conductive Additives in Batteries
Battery electrodes are a mixture of active material (which stores the lithium), a binder (glue), and a conductive additive. Traditional additives, like carbon black, are needed to ensure electrons can move throughout the electrode, but they add "dead weight" that doesn't store energy.
How CNTs Boost Battery Performance
Because CNTs are so much more conductive than carbon black, a much smaller amount is needed. This reduces inactive material, allowing for more active material to be packed in, which directly increases the battery's energy density.
Their strength also provides mechanical support to the electrode, enabling the use of thicker electrodes and high-capacity materials like silicon that tend to expand and crack during use.
Expanding the Horizon: Structural and Material Enhancement
Beyond batteries, CNTs are being used to create a new generation of advanced composite materials.
Reinforcing Concrete and Polymers
When dispersed into concrete or asphalt, CNTs act as a nanoscale rebar, bridging micro-cracks as they form. This dramatically increases the material's strength, durability, and lifespan.
In polymers (plastics), they add strength while also making the plastic electrically conductive, which is useful for applications like anti-static packaging for electronics or lightweight electromagnetic shielding.
Advanced Applications: Films and Sensors
CNTs can be used to create films that are both electrically conductive and optically transparent. This opens up possibilities for flexible touch screens, transparent heaters for de-icing windows, and thin-film solar cells.
Their high surface area and extreme sensitivity to their chemical environment also make them ideal candidates for next-generation chemical and biological sensors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While their properties are exceptional, CNTs are not a simple drop-in solution. Their adoption comes with practical engineering challenges.
The Challenge of Dispersion
The very properties that make CNTs strong also cause them to bundle together in clumps, a process called agglomeration. If not properly separated and dispersed evenly throughout the host material, their benefits are lost.
Significant research and development focus on proprietary dispersion techniques and chemical functionalization to overcome this core challenge.
Production Cost and Purity
Though modern production methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) have drastically lowered costs, high-purity CNTs are still more expensive than traditional additives.
Furthermore, controlling the exact type, diameter, and purity of CNTs during mass production remains a technical hurdle that can impact final performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use carbon nanotubes depends entirely on the performance you need to unlock.
- If your primary focus is energy storage: Use CNTs to replace traditional conductive additives to enable higher energy density, faster charging, and longer cycle life in lithium-ion batteries.
- If your primary focus is materials science: View CNTs as a functional additive to create stronger, lighter, and more durable composites or to imbue non-conductive materials like plastic with electrical conductivity.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics: Explore CNTs as the foundational material for creating next-generation transparent conductive films, thermal management solutions, and ultra-sensitive sensors.
Ultimately, carbon nanotubes are a master additive, enabling engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible with existing materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Enables efficient electron flow | Conductive additive in batteries & electronics |
| Mechanical Strength | Adds strength and durability without weight | Reinforcing composites (concrete, polymers) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Manages heat in high-performance systems | Thermal interface materials for cooling |
Ready to enhance your materials with carbon nanotubes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for developing and testing advanced materials like CNT-enhanced composites and batteries. Our expertise can help you overcome dispersion challenges and optimize your formulations. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the best substrate for graphene? It depends on your application's specific needs.
- What are the advantages of ion beam sputtering? Achieve Superior Thin Film Quality and Precision
- What are the applications of graphene properties? Unlocking Next-Generation Electronics & Materials
- How are carbon nanotubes characterized? A Guide to Verifying Quality and Performance
- What are the synthesis methods for graphene? A Guide to Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Production
- What are the best sources of graphene? Choose the Right Carbon Source for Your Application
- What are the substrates used in CVD? Key Materials for Thin Film Deposition
- What is the mechanism of sputtering? A Guide to Precision Thin-Film Deposition



















