At its core, a ceramic is a solid material made of inorganic, non-metallic compounds, shaped and then hardened by firing at extremely high temperatures. While we often think of pottery or tiles, the world of ceramics extends to advanced applications like spacecraft heat shields, medical implants, and cutting-edge electronics, all thanks to a unique set of underlying properties.
The essential takeaway is that ceramics are defined by their powerful atomic bonds. These bonds make them incredibly hard, heat-resistant, and chemically stable, but also inherently brittle—a critical trade-off that governs their use in every application.
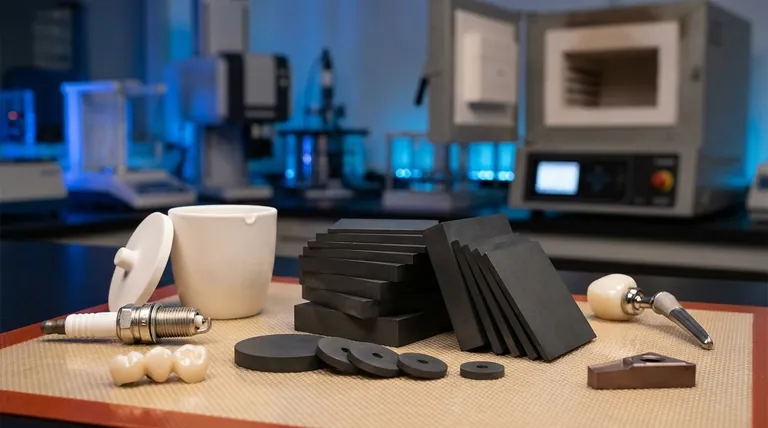

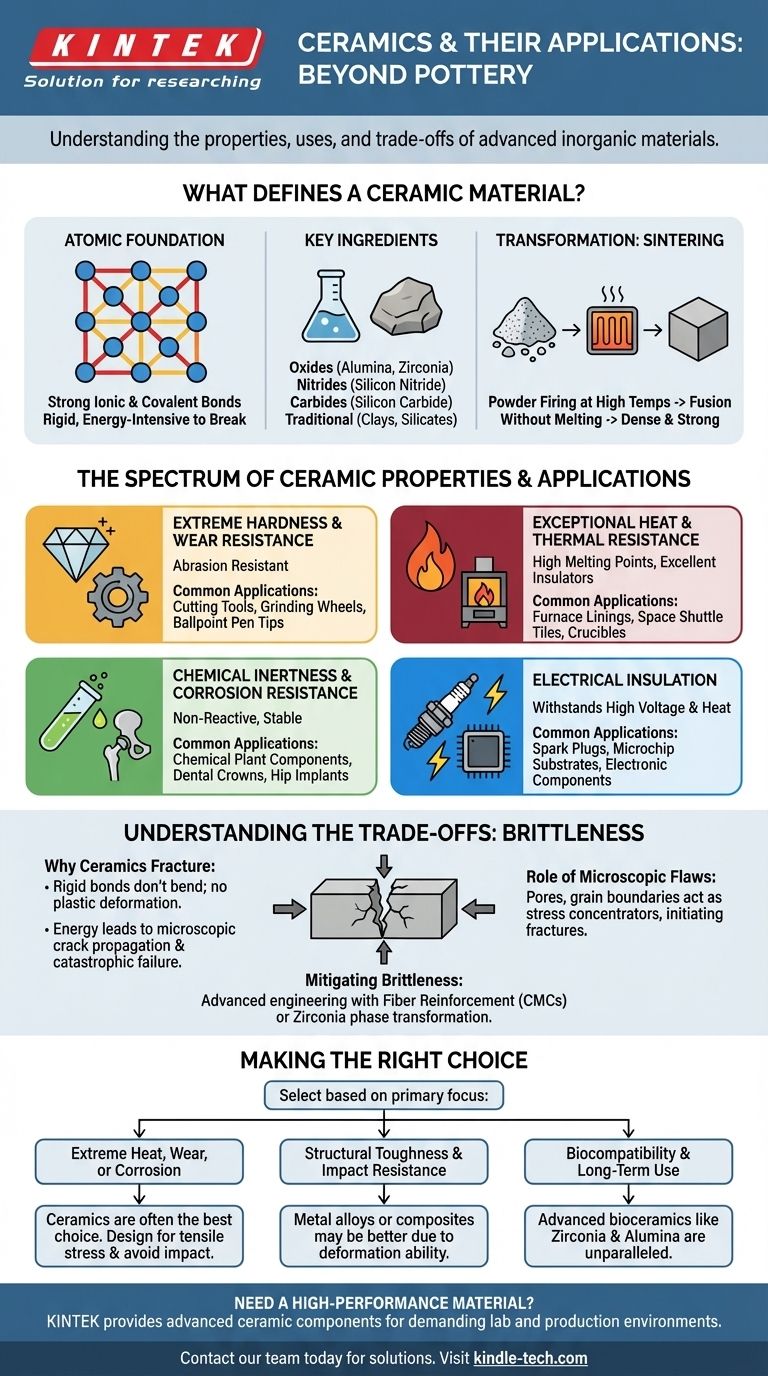
What Defines a Ceramic Material?
To understand a ceramic's behavior, we must look at its fundamental structure. Unlike metals, which have a "sea" of shared electrons that allows them to bend and deform, ceramics are built on a much more rigid foundation.
The Atomic Foundation: Ionic and Covalent Bonds
The properties of a ceramic originate from its strong ionic and covalent bonds. These bonds lock atoms firmly in place, requiring a tremendous amount of energy to break.
This rigid atomic lattice is the source of a ceramic's signature hardness and high melting point. It's also the reason they don't deform under stress—they fracture instead.
Key Ingredients and Formulations
Ceramics are not one single material but a vast class. They are typically classified by their chemical composition.
Common types include oxides (like alumina or zirconia), nitrides (like silicon nitride), and carbides (like silicon carbide). Traditional ceramics, like pottery, are primarily based on natural clays and silicates.
The Transformation: Sintering
Raw ceramic powders are first formed into a desired shape, a stage known as the "green body." This part is fragile and porous.
To achieve their final strength and density, they are fired at high temperatures in a process called sintering. The heat causes the powder particles to fuse together—without melting—creating a dense, solid, and incredibly strong final product.
The Spectrum of Ceramic Properties
The rigid atomic structure gives ceramics a profile of properties that are often superior to metals and polymers in specific environments.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Because of their strong bonds, ceramics are exceptionally hard and resistant to abrasion. This makes them ideal for applications involving friction and wear.
You see this in industrial cutting tools, abrasive grinding wheels, and even the ceramic ball in a ballpoint pen.
Exceptional Heat and Thermal Resistance
Most ceramics have very high melting points and maintain their strength at temperatures that would cause metals to soften and fail. Many also have low thermal conductivity, making them excellent insulators.
This is why they are used for furnace linings, crucible containers for molten metal, and the iconic thermal protection tiles on space shuttles.
Chemical Inertness and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics do not react with most chemicals, acids, and alkalis. They do not rust or corrode like metals.
This stability is critical for components in chemical processing plants and for biomedical implants like dental crowns and hip joints, which must survive in the body's corrosive environment for decades.
Electrical Insulation
While some advanced ceramics are engineered to be semiconductors or even superconductors, the vast majority are excellent electrical insulators.
This property is fundamental to electronics, from the simple ceramic body of a spark plug that withstands high voltage and heat, to the substrate wafers on which microchips are built.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Challenge of Brittleness
The single greatest limitation of ceramic materials is their brittleness. This is the other side of the coin to their hardness and strength.
Why Ceramics Fracture
Unlike metals that can bend or dent (a process called plastic deformation), the rigid bonds in a ceramic do not allow atoms to slide past one another.
When the stress on a ceramic part exceeds its limit, the energy has nowhere to go. A microscopic crack forms and propagates through the material almost instantly, leading to a sudden, catastrophic failure.
The Role of Microscopic Flaws
The real-world strength of a ceramic component is almost always determined by pre-existing microscopic flaws. These can be tiny pores, grain boundaries, or surface scratches introduced during manufacturing.
These flaws act as stress concentrators, meaning the stress at the tip of a tiny crack can be many times higher than the overall stress on the part, initiating a fracture.
Mitigating Brittleness with Advanced Engineering
Modern materials science focuses heavily on creating "tougher" ceramics. This is achieved by engineering the microstructure to stop cracks from spreading.
Techniques include reinforcing the ceramic with fibers (creating a ceramic matrix composite, or CMC) or using materials like zirconia, which can change its crystal structure at a crack tip to absorb energy and halt its growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a ceramic means deliberately choosing its unique strengths while designing around its primary weakness.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme heat, wear, or corrosive environments: Ceramics are often the best or only option, but you must design the component to manage tensile stress and avoid impact.
- If your primary focus is structural toughness and the ability to withstand impact: A metal alloy or a fiber-reinforced polymer composite is almost always a better choice due to their ability to deform without failing.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and chemical inertness for medical use: Advanced bioceramics like zirconia and alumina are unparalleled for long-term implants.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation, especially at high temperatures: Ceramics provide robust and reliable performance where polymers would melt or degrade.
Ultimately, understanding that a ceramic's power and its peril both stem from its rigid atomic bonds is the key to leveraging these remarkable materials effectively.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Extremely hard, resists abrasion | Cutting tools, grinding wheels, ballpoint pen tips |
| Heat & Thermal Resistance | High melting point, excellent insulator | Furnace linings, space shuttle tiles, crucibles |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion, acids, and alkalis | Chemical plant components, dental crowns, hip implants |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator (most types) | Spark plugs, microchip substrates, electronic components |
| Key Limitation | Brittle; fractures under tensile stress or impact | Design requires careful stress management |
Need a high-performance material solution for your lab or production process? The unique properties of ceramics—like extreme heat resistance, chemical inertness, and superior hardness—can solve complex challenges. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components for demanding environments. Let our experts help you select the right material for your specific application. Contact our team today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- How do you process silicon carbide? Choose the Right Method for Your Application
- What is the material used in high temperature furnace? Selecting the Right Ceramic for Extreme Heat
- What is the role of polycrystalline alumina (Al2O3) substrates in YSZ thin film preparation? Enhance Film Integrity
- What is pressureless sintered silicon carbide? A Guide to High-Performance Ceramics
- What are the applications of ceramics in dentistry? Restore Function and Aesthetics with Advanced Materials
- What are the drawbacks of tungsten carbide? Understanding the Brittleness vs. Hardness Trade-off
- Is ceramic chemically inert? Unlock the Power of Ultimate Chemical Resistance
- How long does ceramic last? Maximize Your Coating's Lifespan & Protection



















