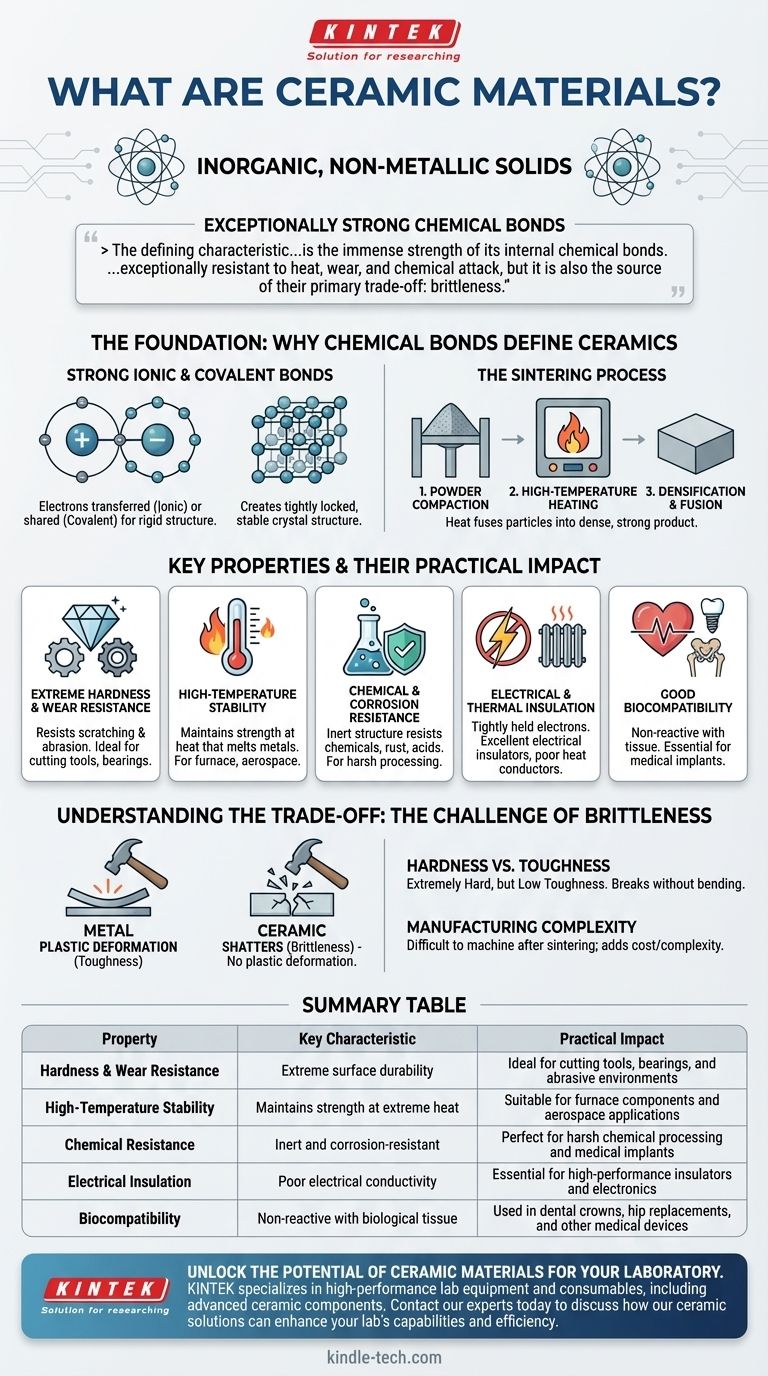
At their core, ceramic materials are inorganic, non-metallic solids defined by their exceptionally strong chemical bonds. Unlike metals, which are held together by a flexible sea of electrons, the atoms in ceramics are locked into rigid ionic or covalent bonds. This fundamental structure is the source of their most valued properties: extreme hardness, high-temperature stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion.
The defining characteristic of any ceramic is the immense strength of its internal chemical bonds. This structure makes them exceptionally resistant to heat, wear, and chemical attack, but it is also the source of their primary trade-off: brittleness.
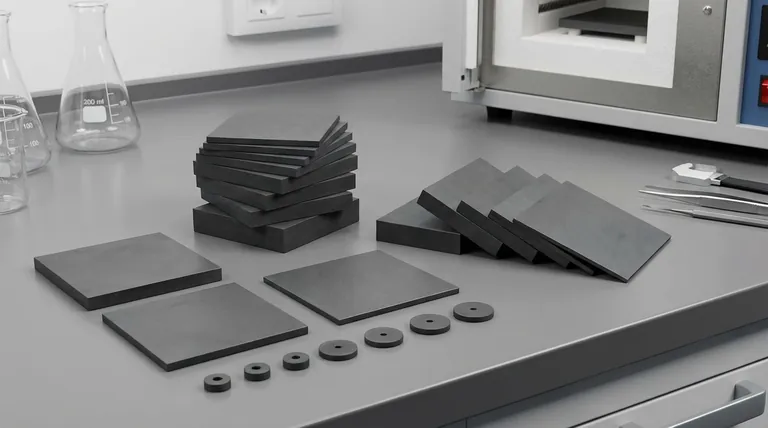

The Foundation: Why Chemical Bonds Define Ceramics
To truly understand ceramics, we must look at their atomic structure. Their properties are not arbitrary; they are a direct result of how their atoms are held together.
Strong Ionic and Covalent Bonds
The atoms in advanced ceramics are linked by either ionic bonds (where electrons are transferred) or covalent bonds (where electrons are shared). Both of these bond types are incredibly strong and rigid.
This creates a tightly locked, stable crystal structure. This structure fiercely resists any force trying to displace its atoms, which is the root of a ceramic's hardness and strength.
The Sintering Process
Most advanced ceramic parts are created through sintering. In this process, fine ceramic powders are compacted into a desired shape and then heated to a high temperature, just below their melting point.
This heat causes the individual particles to fuse, creating a dense, solid, and incredibly strong final product.
Key Properties and Their Practical Impact
The unique atomic structure of ceramics gives rise to a set of highly desirable engineering properties that are difficult to achieve with other material classes like metals or polymers.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Because the bonds are so strong, it is very difficult to scratch or physically wear down a ceramic surface. This makes them ideal for applications involving high friction or abrasion, such as cutting tools or bearing components.
High-Temperature Stability
The energy required to break the bonds in a ceramic is immense. As a result, these materials maintain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause metals to soften and melt or polymers to degrade.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic materials are generally very inert. Their stable structure makes them highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation (rust), and damage from harsh chemicals and acids.
Electrical and Thermal Insulation
The tightly held electrons in ceramic bonds are not free to move around. This makes most ceramics excellent electrical insulators and poor conductors of heat, a property known as low thermal conductivity.
Good Biocompatibility
Many advanced ceramics do not react with biological tissue. This makes them essential materials for medical implants, such as dental crowns and hip replacements, where inertness inside the human body is critical.
Understanding the Trade-off: The Challenge of Brittleness
No material is perfect. The same atomic structure that gives ceramics their incredible strength also creates their most significant limitation.
Hardness vs. Toughness
Ceramics are extremely hard, meaning they resist surface indentation and scratches. However, they typically have low toughness, which is the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
When a ceramic material reaches its breaking point, it doesn't bend like metal—it shatters. The rigid bonds do not allow for the plastic deformation that absorbs the energy from a sharp impact.
Manufacturing Complexity
The extreme hardness of ceramics makes them very difficult to machine or shape after they have been sintered. This often adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing process compared to metals.
When to Choose a Ceramic Material
Making the right material choice requires aligning its properties with the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is durability in harsh environments: Ceramics are an unmatched choice for applications involving extreme heat, corrosive chemicals, or high levels of wear and abrasion.
- If your primary focus is insulation: The inability of ceramics to conduct heat and electricity makes them essential for high-performance electrical insulators and thermal barriers.
- If your primary focus is withstanding sudden impact: You must account for the inherent brittleness of ceramics; a metal alloy or composite material may be a more suitable choice for high-shock applications.
Understanding these core properties and their trade-offs allows you to leverage the unique strengths of ceramic materials for the most demanding technical challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Extreme surface durability | Ideal for cutting tools, bearings, and abrasive environments |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains strength at extreme heat | Suitable for furnace components and aerospace applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert and corrosion-resistant | Perfect for harsh chemical processing and medical implants |
| Electrical Insulation | Poor electrical conductivity | Essential for high-performance insulators and electronics |
| Biocompatibility | Non-reactive with biological tissue | Used in dental crowns, hip replacements, and other medical devices |
Unlock the potential of ceramic materials for your laboratory.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components designed for durability and precision in demanding environments. Whether you need custom ceramic parts for high-temperature furnaces, chemically resistant tools, or specialized insulating components, our expertise ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our ceramic solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- Does ceramic get stronger under pressure? Harnessing Compressive Strength for Superior Performance
- What kind of material is used for dental crowns? A Guide to Aesthetics, Durability & Cost
- What is better than Rockwool insulation? Maximize Thermal or Fire Performance
- What is the maximum temperature for ceramics? Find the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- What are the characteristics of sintered ceramics? Achieve High-Performance with Engineered Materials
- Does ceramic react with anything? Uncover the Limits of Chemical Inertness
- What is the type of silicon carbide? A Guide to Polymorphs, Grades, and Applications
- What is the strongest zirconia phase? Tetragonal Zirconia Offers Unmatched Toughness



















