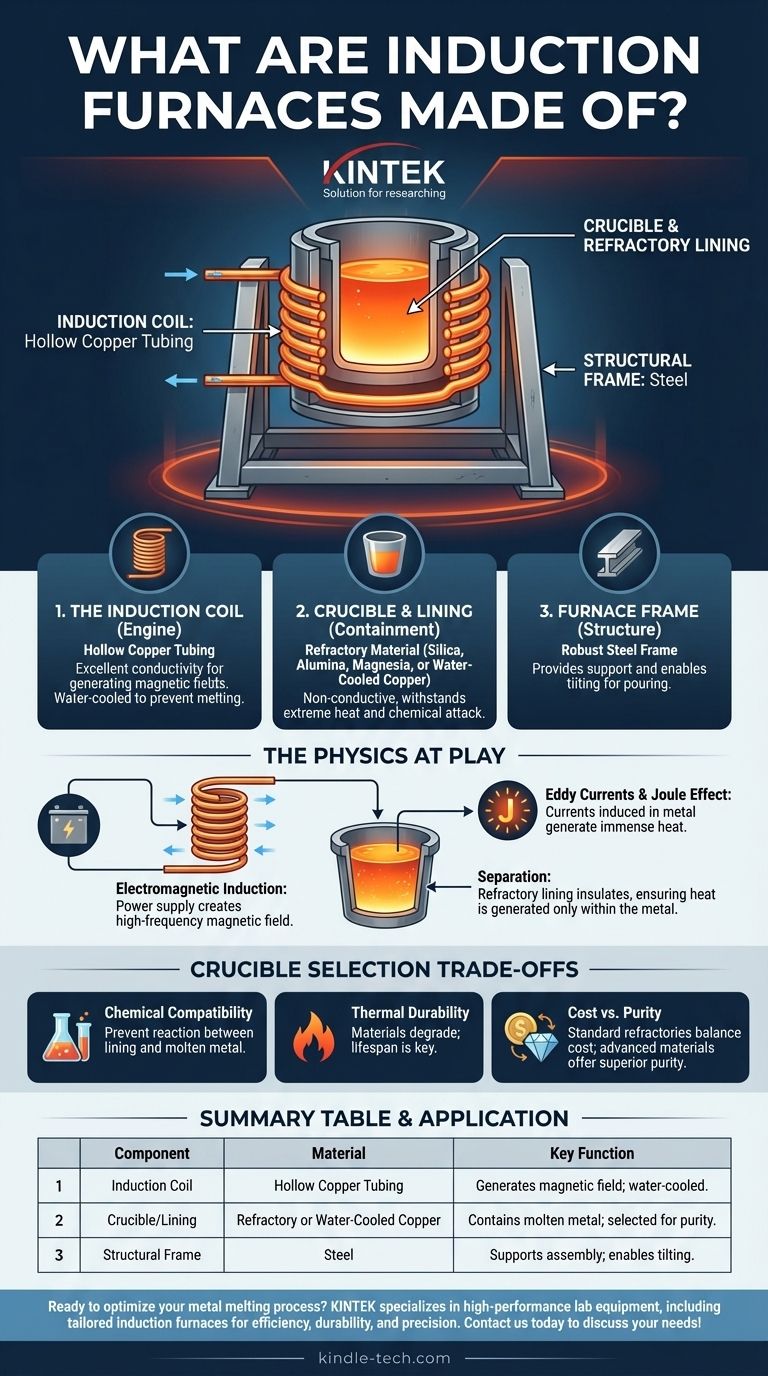
At its core, an induction furnace is not made of a single material, but is a sophisticated system of components. The key materials are a water-cooled copper coil to generate heat and a specialized ceramic or metallic crucible to contain the molten metal, all supported by a structural frame.
The selection of materials for an induction furnace is dictated entirely by the physics of induction heating. You need a highly conductive material (the coil) to create a magnetic field and a highly durable, non-reactive material (the crucible) to withstand the extreme heat and contain the metal.

The Core Components of an Induction Furnace
An induction furnace functions by using a powerful, alternating magnetic field to heat metal. This principle requires a clear separation of roles between the component generating the field and the one containing the superheated material.
The Induction Coil: The Engine of the Furnace
The heart of the furnace is the induction coil. This is almost universally made from hollow copper tubing.
Copper is chosen for its excellent electrical conductivity, which is essential for generating a strong magnetic field with minimal energy loss. The tubing is hollow so that cooling water can be continuously circulated through it, preventing the coil itself from melting under the immense electrical load.
The Crucible and Refractory Lining: Containing the Molten Metal
The crucible is the vessel that holds the metal charge and, eventually, the molten bath. Its material is critical for the success of the melting process and is chosen based on the metal being melted.
Commonly, this is a refractory lining, a ceramic material that is a poor conductor of electricity but can withstand extreme temperatures. Materials include:
- Silica (SiO₂): Often used for melting iron and some steels.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃): A versatile choice for many ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Magnesia (MgO): Used for melting steel alloys with high manganese content.
- Calcium Oxide (CaO): As noted in advanced applications, prefabricated calcium oxide crucibles significantly improve the quality and purity of the final melted metal.
For highly reactive metals like titanium or zirconium, a special water-cooled copper crucible is used. This prevents any chemical reaction between the molten metal and the crucible, ensuring maximum purity.
The Furnace Frame and Structure
The entire assembly of the coil and crucible is held in place by a robust structural frame, typically made of steel. This frame provides the necessary support and often includes mechanisms for tilting the furnace to pour out the molten metal.
Why These Materials Are Chosen: The Physics at Play
The material choices are not arbitrary; they are direct consequences of the physical principles that make an induction furnace work.
Electromagnetic Induction
The furnace's power supply sends a high-frequency alternating current through the copper coil. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
The Joule Effect
When conductive material, like scrap metal, is placed inside the crucible, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents (called eddy currents) within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates immense heat, a phenomenon known as the Joule effect.
The Need for Separation and Containment
The refractory lining is a critical insulator. It must contain the molten metal at thousands of degrees while being non-conductive, so it is not heated by the magnetic field. This separation ensures that heat is generated only within the metal charge, making the process highly efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Crucible Selection
Choosing the right crucible or refractory lining is the most important operational decision. An incorrect choice can lead to failed melts, equipment damage, and metal contamination.
Chemical Compatibility
The primary concern is preventing a chemical reaction between the lining and the molten metal. For example, using a silica-based (acidic) lining to melt a high-manganese steel (a basic process) will cause the lining to rapidly erode and contaminate the steel.
Thermal Durability
Refractory linings are consumable items. They degrade over time due to extreme temperatures, chemical attack, and physical erosion from the turbulent molten metal. The material choice impacts the lining's lifespan and maintenance schedule.
Cost vs. Purity
Standard refractory materials like silica and alumina offer a good balance of performance and cost for most common applications. Advanced materials like pure calcium oxide or specialized water-cooled copper crucibles deliver superior metal purity but at a significantly higher initial and operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The construction of your furnace, specifically its lining, must be matched to your metallurgical goal.
- If your primary focus is melting standard cast iron or carbon steels: An acidic silica-based refractory lining is the most cost-effective and common choice.
- If your primary focus is melting a variety of alloy steels or non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper: A more neutral or basic refractory like alumina provides greater versatility and chemical stability.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity with reactive metals like titanium: A specialized water-cooled copper crucible is the only viable option to prevent contamination of the melt.
Ultimately, understanding what an induction furnace is made of is to understand how to control a precise and powerful metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Coil | Hollow Copper Tubing | Generates magnetic field; water-cooled for heat management |
| Crucible/Lining | Refractory (e.g., Silica, Alumina) or Water-Cooled Copper | Contains molten metal; chosen based on metal type and purity needs |
| Structural Frame | Steel | Supports furnace assembly and enables tilting for pouring |
Ready to optimize your metal melting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific metallurgical needs. Whether you're melting standard alloys or require ultra-pure results with reactive metals, our expertise ensures efficiency, durability, and precision. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















