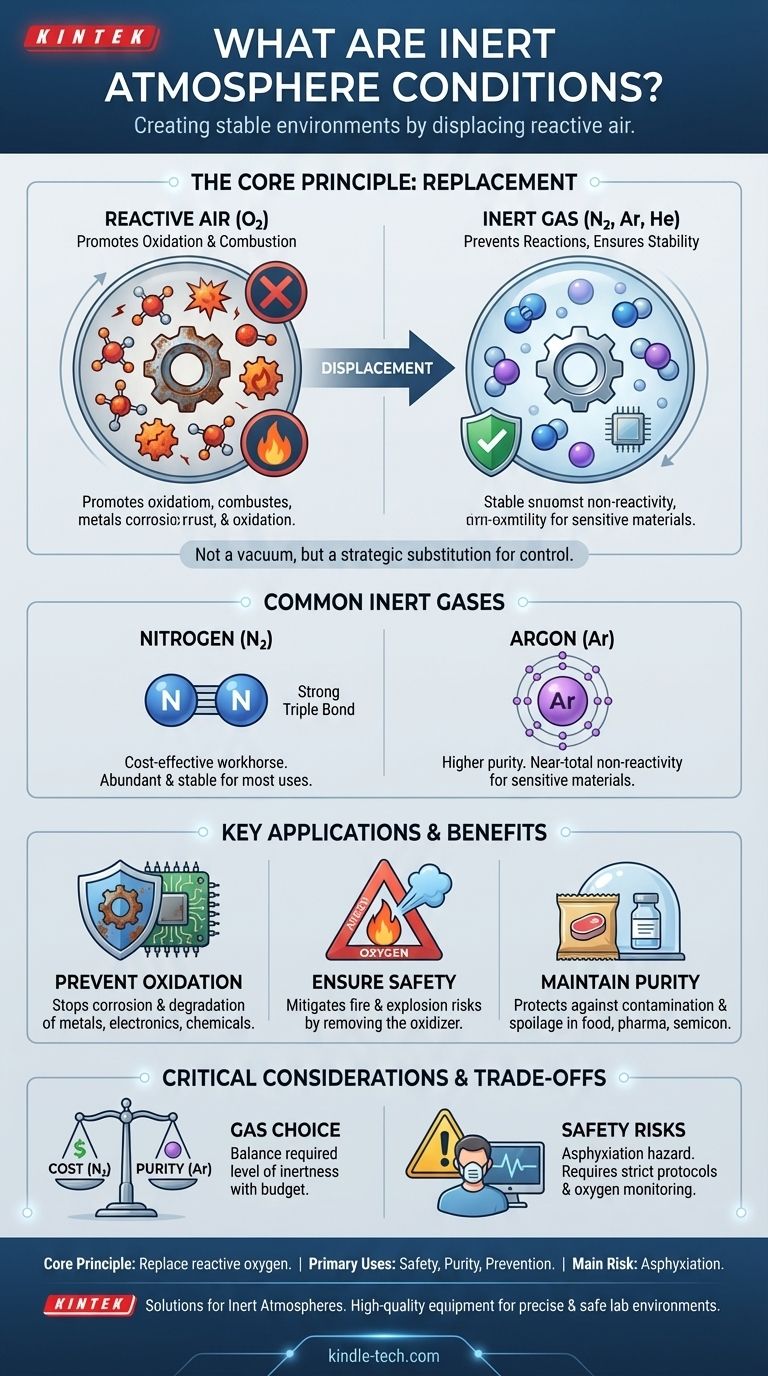
In short, inert atmosphere conditions are environments where the normal, reactive air has been intentionally replaced with a non-reactive (inert) gas. This is done to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, primarily oxidation and combustion, by removing the oxygen that fuels them. The goal is to create a stable and predictable environment for sensitive materials or processes.
An inert atmosphere is not a vacuum or an absence of gas; it is the deliberate replacement of a reactive atmosphere (like air) with a non-reactive one. This strategic substitution is the key to controlling chemical stability, ensuring safety, and preserving the purity of materials.

The Core Principle: Replacing Reactive Elements
To understand inert atmospheres, you must first understand what makes a gas "inert." It's a matter of chemical stability.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
An inert gas is one that does not readily participate in chemical reactions under a given set of conditions. This stability typically comes from having a full outer shell of electrons.
The most common inert gases are the noble gases (like Argon and Helium) and, for most practical purposes, **Nitrogen (N₂) **. Nitrogen is extremely stable due to the powerful triple bond holding its two atoms together, which requires a large amount of energy to break.
The Primary Target: Displacing Oxygen
The main reason for creating an inert atmosphere is to displace oxygen. Oxygen is highly reactive and is the primary driver of many undesirable processes.
These processes include oxidation (like rust on metal or spoilage in food), combustion (fire), and the degradation of sensitive chemical compounds. By removing oxygen, you remove the key ingredient for these reactions.
Key Applications and Benefits
Using an inert atmosphere provides critical protection across many scientific and industrial fields. Its benefits are directly tied to the problems it solves by eliminating reactive gases.
Preventing Oxidation and Corrosion
Many materials, from metal powders and electronic components to fine chemicals, degrade when exposed to air.
An inert gas blanket prevents oxygen and moisture from reaching the material's surface, dramatically extending its life and preserving its intended properties. This is fundamental in high-tech manufacturing and chemical storage.
Ensuring Safety: Mitigating Fire and Explosion Risks
Fire requires three things: fuel, heat, and an oxidizer (usually oxygen). This is often called the fire triangle.
By displacing oxygen with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, you remove one of the essential legs of the triangle. This technique, known as inerting, is a critical safety measure used in chemical reactors and fuel tanks to prevent catastrophic explosions.
Maintaining Product Purity and Stability
In fields like pharmaceuticals, food packaging, and semiconductor manufacturing, even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a product.
An inert atmosphere protects against airborne microbial contaminants and prevents the slow degradation of the product itself. This is why potato chip bags are filled with nitrogen—it keeps the chips from going stale (oxidizing) and provides a protective cushion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While incredibly useful, implementing an inert atmosphere requires careful planning and an awareness of the potential downsides.
Gas Choice Matters: Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inerting. It is abundant (making up ~78% of air) and relatively inexpensive to produce.
Argon is significantly more inert than nitrogen, especially at high temperatures where nitrogen can sometimes react with metals. However, it is also much rarer and more expensive. The choice depends on the required level of purity versus the project budget.
The Critical Danger of Asphyxiation
An inert atmosphere is, by definition, an unbreathable one. Oxygen displacement poses a severe and often silent risk to personnel.
Any area using inert gas must have strict safety protocols, including oxygen monitoring, clear signage, and proper ventilation procedures. Accidental entry into an inerted space can cause immediate asphyxiation.
Achieving and Maintaining the Atmosphere
Creating an inert environment requires specialized equipment like gloveboxes or Schlenk lines for lab work, or complex purging systems for industrial vessels.
The primary challenge is preventing leaks. Since the surrounding air is rich in oxygen, even a small leak can quickly compromise the integrity of the inert atmosphere, undoing its protective benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best inert gas is determined entirely by your application's specific requirements for reactivity, temperature, and cost.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, cost-effective blanketing: Nitrogen is the default industry standard due to its low cost and sufficient inertness for most common applications.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metallurgy or protecting extremely sensitive materials: Argon is the superior choice for its near-total non-reactivity, justifying its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application like welding certain alloys or leak detection: A Helium or a specific gas mixture might be necessary to achieve the desired technical properties.
Ultimately, mastering inert atmospheres is about deliberately controlling the chemical environment to achieve predictable, safe, and high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Replaces reactive air (oxygen) with non-reactive gases to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective), Argon (high purity), Helium (specialized uses). |
| Primary Uses | Preventing oxidation/corrosion, mitigating fire/explosion risks, maintaining product purity. |
| Key Equipment | Gloveboxes, Schlenk lines, industrial purging systems. |
| Main Consideration | Safety risks (asphyxiation), gas cost vs. purity, and maintaining atmosphere integrity. |
Need to create a stable, safe, and pure environment for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for generating and maintaining inert atmospheres. Whether you require cost-effective nitrogen blanketing or high-purity argon systems for sensitive materials, our expertise ensures your lab operates with precision and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments



















