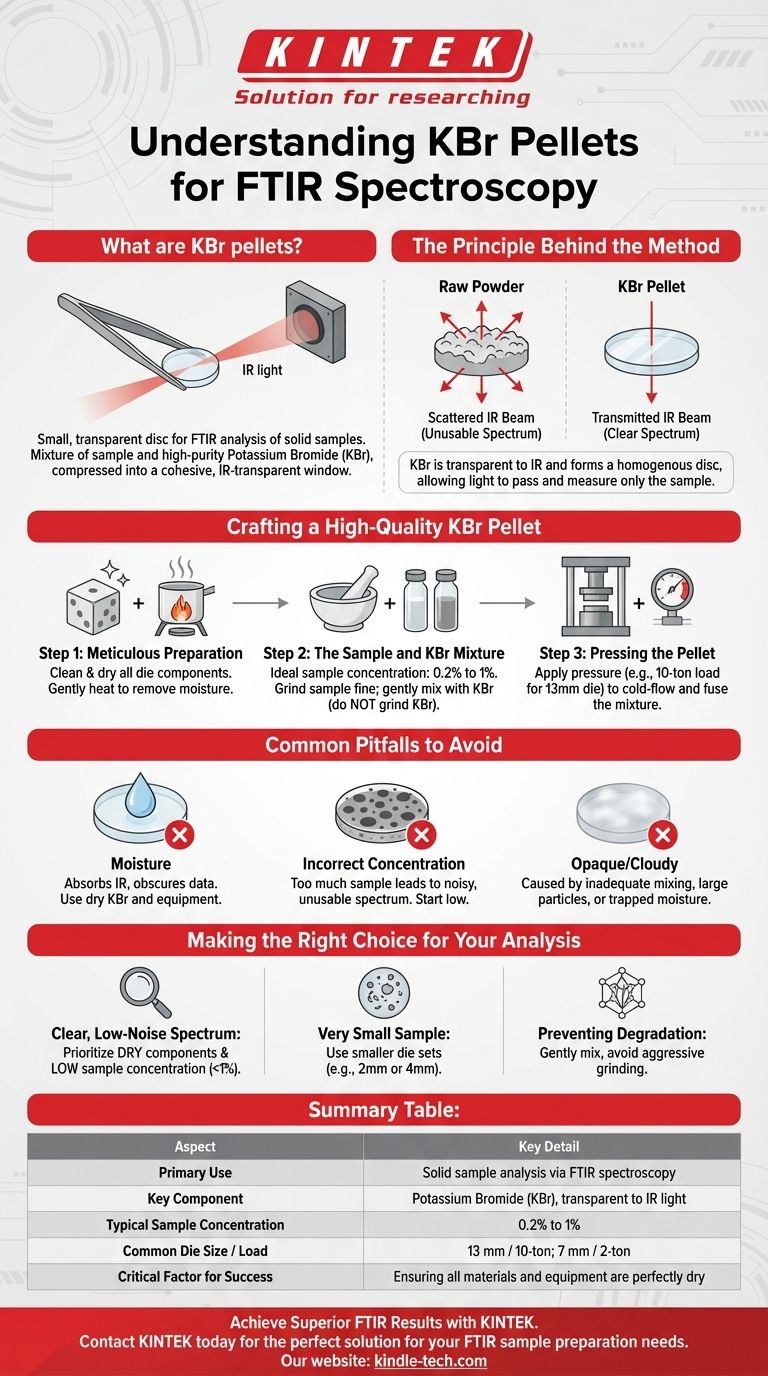
In analytical chemistry, a KBr pellet is a small, solid, and typically transparent disc used to analyze solid samples via Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It is created by intimately mixing a small amount of the sample with high-purity potassium bromide (KBr) powder, which is transparent to infrared light. This mixture is then compressed under immense pressure in a die to form a cohesive pellet that can be placed directly in the path of an IR beam.
Analyzing a solid material with infrared light requires a medium that won't interfere with the measurement. The KBr pellet method solves this by dispersing the sample within a KBr matrix, which acts as a clear window, allowing the spectrometer to measure only the sample's unique spectral fingerprint.

The Principle Behind the KBr Pellet Method
Why Potassium Bromide (KBr)?
Potassium bromide is the standard material for this technique because it is transparent to a wide range of infrared radiation. This means the KBr itself does not absorb the IR light in the region of interest, ensuring that any absorption recorded by the spectrometer is due to the sample alone.
The KBr also has a plastic quality under high pressure, allowing it to flow and form a homogenous, glass-like disc when compressed. This clarity is essential for allowing the maximum amount of light to pass through to the detector.
How the Pellet Enables Analysis
By grinding the solid sample into a fine powder and dispersing it throughout the KBr, you create a uniform suspension. When pressed, this locks the sample particles in place within the transparent matrix.
This allows the infrared beam to pass through the sample without being significantly scattered, which would otherwise happen with a raw powder. The result is a clean, measurable absorption spectrum that is characteristic of the sample's molecular structure.
Crafting a High-Quality KBr Pellet
The quality of your FTIR spectrum is directly dependent on the quality of your pellet. Following a precise procedure is critical for obtaining reliable data.
Step 1: Meticulous Preparation
Before you begin, all components of the die set must be perfectly clean and dry. Clean the die, anvils, and plunger with a solvent like chloroform and dry them thoroughly to remove any contaminants.
To ensure dryness, it is best practice to gently heat the die set components before use. This removes any adsorbed moisture, which is a major source of interference.
Step 2: The Sample and KBr Mixture
The ideal concentration of sample in KBr is very low, typically 0.2% to 1%. Because the pellet is much thicker than a typical liquid sample cell, a high concentration will absorb too much light, resulting in a noisy or unusable spectrum.
Crucially, you should grind the sample material into a very fine powder, but do not grind the KBr powder. Grinding KBr aggressively can cause it to absorb moisture from the air. Instead, gently mix the pre-ground sample into the KBr powder.
Step 3: Pressing the Pellet
Place the KBr/sample mixture into the die. Typical conditions involve using a 13 mm die with a 10-ton pressing load or a smaller 7 mm die with as little as 2 tons of load.
The pressure causes the KBr to cold-flow and fuse, trapping the sample particles within a solid, transparent disc. The thickness of the final pellet depends on the amount of powder used and the force applied.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Problem of Moisture
Moisture is the primary enemy of good KBr pellets. Water has strong absorption bands in the infrared spectrum and will obscure your sample's data. Always use dry, spectroscopy-grade KBr and keep all equipment free of moisture.
Incorrect Sample Concentration
Using too much sample is a frequent mistake. A high concentration leads to total absorption of the IR beam or significant scattering, which creates a very noisy spectrum with poorly defined peaks. It's better to start with too little sample than too much.
Opaque or Cloudy Pellets
A pellet that is not transparent is a sign of a problem. This is often caused by inadequate mixing, particles that are too large, or trapped moisture. Ensure your sample is ground to a fine, consistent powder and is thoroughly dispersed in the KBr.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your preparation technique should be guided by your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is obtaining a clear, low-noise spectrum: Prioritize keeping all components—KBr, sample, and die set—perfectly dry and use a low sample concentration (under 1%).
- If your primary focus is analyzing a very small amount of sample: Use a smaller die set, such as 2 mm or 4 mm, to create a usable pellet without requiring a large quantity of material.
- If your primary focus is preventing sample degradation: Mix the sample and KBr gently rather than grinding them together, as the pressure from grinding can sometimes alter the sample's crystalline structure.
Ultimately, a well-prepared KBr pellet is the foundation for obtaining reliable and high-quality infrared data from solid samples.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Solid sample analysis via FTIR spectroscopy |
| Key Component | Potassium Bromide (KBr), transparent to IR light |
| Typical Sample Concentration | 0.2% to 1% |
| Common Die Size / Load | 13 mm die / 10-ton load; 7 mm die / 2-ton load |
| Critical Factor for Success | Ensuring all materials and equipment are perfectly dry |
Achieve Superior FTIR Results with KINTEK
Mastering the KBr pellet technique is crucial for accurate solid sample analysis. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable pellet dies and spectroscopy-grade KBr, designed to help you avoid common pitfalls like moisture contamination and achieve clear, reliable spectra.
Let our expertise support your laboratory's success. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect solution for your FTIR sample preparation needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- What are the disadvantages of press working? High Costs and Design Limits for Mass Production
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- How do you make biomass pellets at home? A Step-by-Step Guide to DIY Fuel Production
- How do I choose a hydraulic press? Match Tonnage, Size & Features to Your Needs
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in LGPS electrolyte fabrication? Master Cold-Pressing for SSBs
- What are the advantages of press forging over hammer forging? Achieve Superior Internal Integrity
- How many types of hydraulic presses are there? A Guide to Frame Designs for Your Application



















