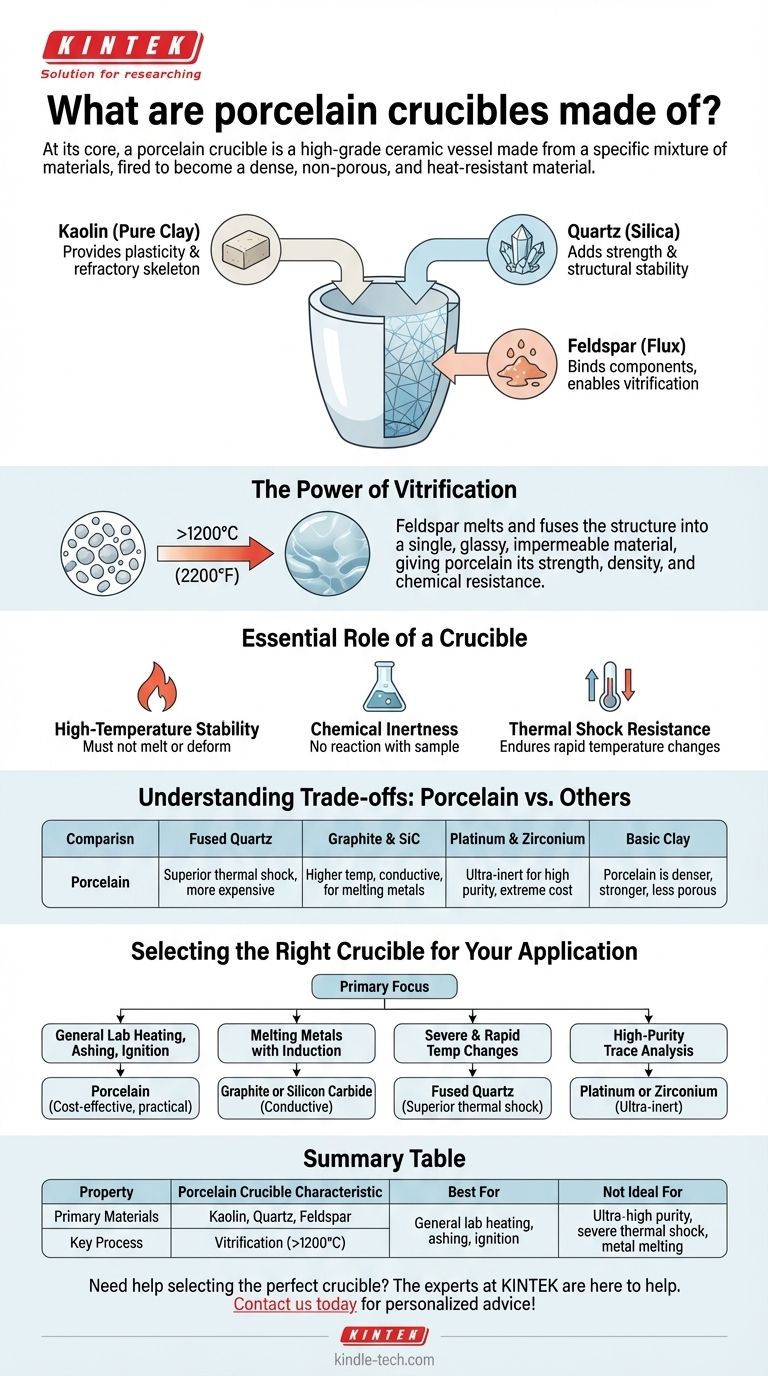
At its core, a porcelain crucible is a high-grade ceramic vessel made from a specific mixture of materials, primarily kaolin (a pure clay), quartz (silica), and feldspar. These components are fired at extremely high temperatures until they fuse, or vitrify, into a dense, non-porous, and heat-resistant material. This composition gives porcelain its signature strength and stability for laboratory and industrial heating applications.
Choosing the right crucible is not just about withstanding heat. Porcelain's value lies in its unique balance of thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and affordability, making it a foundational tool for a wide range of general-purpose applications where ultra-high purity is not the absolute priority.

The Essential Role of a Crucible
Before examining porcelain specifically, it's crucial to understand what any crucible must accomplish. Its performance is defined by a few key requirements that dictate the material choice.
High-Temperature Stability
The most fundamental job of a crucible is to contain a substance while being heated without melting, deforming, or breaking. The material's melting point must be significantly higher than the intended working temperature.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible should not react with the sample it holds. Any chemical reaction can contaminate the sample, leading to inaccurate analytical results or ruining an industrial process. This is especially critical in analytical chemistry.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Crucibles must often endure rapid changes in temperature, such as being moved from a furnace to a cool surface. A material with poor thermal shock resistance will crack under this stress.
Deconstructing Porcelain: Composition and Properties
Porcelain is not a single element but a precisely formulated ceramic. Its properties are a direct result of its constituent parts and the manufacturing process.
The Primary Ingredients
A typical porcelain body is a mixture of three main components:
- Kaolin: A pure, white clay that provides plasticity for forming the crucible's shape and acts as a refractory skeleton during firing.
- Quartz (Silica): This mineral adds strength and structural stability to the final product, ensuring it holds its form at high temperatures.
- Feldspar: This acts as a "flux," melting at a lower temperature during firing. It flows into the gaps between the kaolin and quartz particles, binding them together and creating a vitrified, non-porous surface.
The Power of Vitrification
When these ingredients are fired above 1200°C (2200°F), the feldspar melts and fuses the entire structure into a single, glassy, and impermeable material. This process, known as vitrification, is what gives porcelain its strength, density, and resistance to chemical attack.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Porcelain vs. Other Materials
Porcelain is a versatile workhorse, but it is not the ideal choice for every task. Understanding its limitations in comparison to other materials is key to proper selection.
vs. Fused Quartz
Fused quartz crucibles offer superior thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for applications with extremely rapid heating and cooling cycles. However, they are significantly more expensive than porcelain.
vs. Graphite and Silicon Carbide
These are conductive materials often used in furnaces for melting metals or in semiconductor manufacturing. They can withstand much higher temperatures than porcelain and are chosen when electrical conductivity or extreme heat is required. Porcelain, being a ceramic, is an excellent electrical insulator.
vs. Platinum and Zirconium
For high-purity trace element analysis, even porcelain can leach minor contaminants into a sample. Platinum and zirconium are exceptionally inert and are the standard for tasks demanding the highest level of accuracy. Their extreme cost, however, makes them impractical for general use.
vs. Basic Clay
Compared to a simple, unrefined clay crucible, porcelain is far denser, stronger, and less porous. This makes it more durable and much less likely to absorb or react with the sample material.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Your choice of crucible should be dictated entirely by the demands of your specific task and budget.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory heating, ashing, or ignition of samples: Porcelain is often the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is melting metals with induction heating: You require a conductive material like graphite or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is applications with severe and rapid temperature changes: Fused quartz is the superior, albeit more expensive, option.
- If your primary focus is high-purity trace analysis where contamination is unacceptable: You must invest in an ultra-inert material like platinum or zirconium.
Understanding these material distinctions is the key to ensuring the accuracy and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Property | Porcelain Crucible Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Primary Materials | Kaolin (clay), Quartz (silica), Feldspar (flux) |
| Key Process | Vitrification (firing >1200°C / 2200°F) |
| Best For | General lab heating, ashing, ignition (cost-effective) |
| Not Ideal For | Ultra-high purity analysis, severe thermal shock, metal melting |
Need help selecting the perfect crucible for your lab's specific heating, ashing, or ignition applications? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment, including a wide range of crucibles, to ensure the accuracy and efficiency of your work. Contact us today for personalized advice and solutions tailored to your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production



















