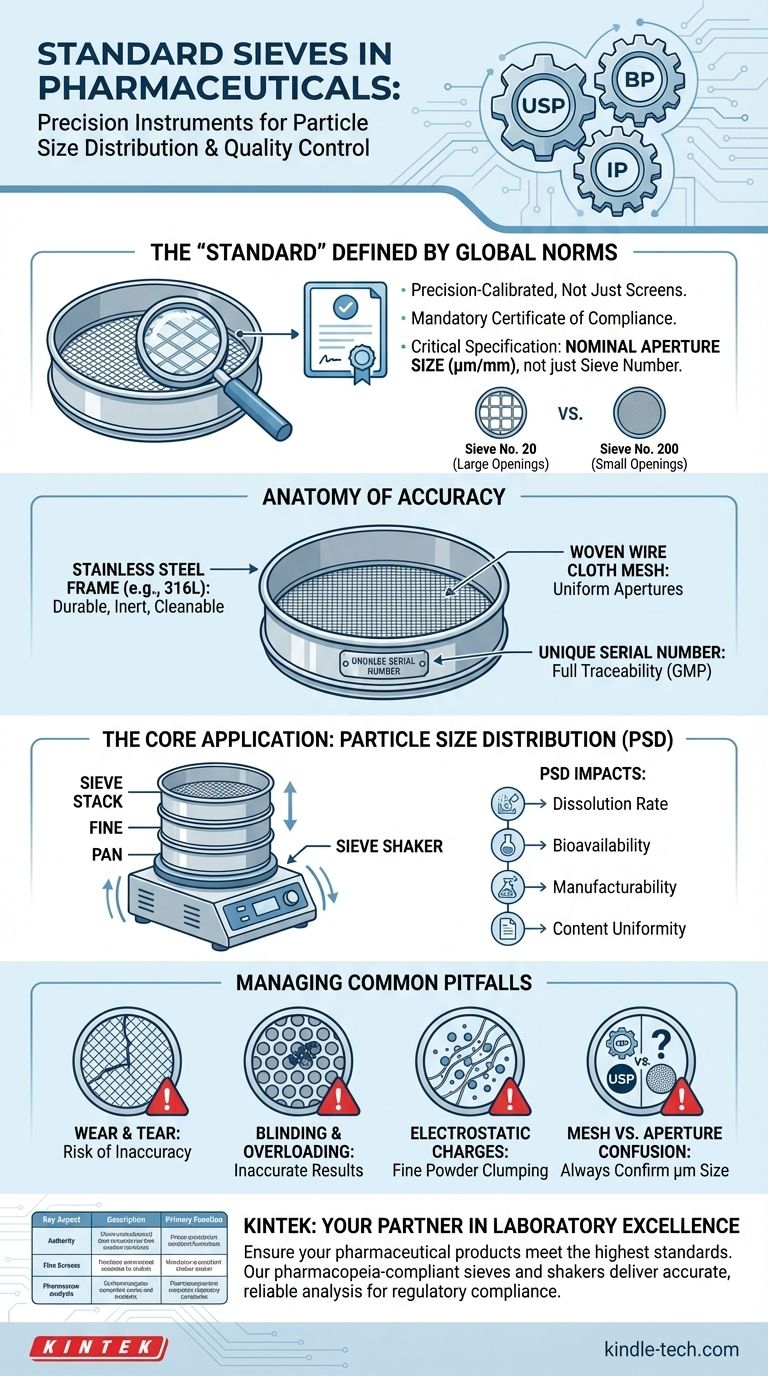
In pharmaceuticals, standard sieves are precision-calibrated instruments, not just simple screens, used to measure the particle size distribution of powders and granules. They are defined by international standards, such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), British Pharmacopoeia (BP), and Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP), which specify the exact dimensions of the wire mesh, including the nominal aperture size.
The core purpose of a standard sieve is to ensure product consistency and quality. By precisely sorting particles by size, these tools play a critical role in determining a drug's dissolution rate, bioavailability, and manufacturability, making them fundamental to both regulatory compliance and effective formulation.

The Foundation: What Defines a "Standard" Sieve?
A sieve used in a non-regulated environment might just be a screen for separation. In the pharmaceutical world, a "standard" sieve is a calibrated piece of testing equipment subject to strict controls.
Beyond a Simple Screen: The Role of Calibration
A standard sieve comes with a certificate of compliance. This document verifies that the mesh openings conform to the tight tolerances required by pharmacopeial standards. Regular inspection and recalibration are mandatory to ensure the sieve remains accurate over time.
Key Standards: USP, BP, and IP
Global pharmacopeias provide the legal and scientific benchmarks for pharmaceutical quality. They publish tables that correlate sieve numbers with specific nominal aperture sizes. While there is significant overlap, the specifications between standards like USP/ASTM and BP/ISO can differ slightly, making it critical to use the sieve specified in the relevant product monograph.
Deciphering Sieve Numbers (Mesh Count)
The sieve number (or mesh count) refers to the number of openings per linear inch of the mesh. A higher sieve number indicates more wires per inch and therefore smaller openings. For example, a No. 20 sieve has much larger openings than a No. 200 sieve.
The Critical Specification: Aperture Size
While the sieve number is a useful shorthand, the most important parameter is the nominal aperture size. This is the actual dimension of the opening, measured in micrometers (µm) or millimeters (mm). Always refer to the aperture size for precise work, as this is the true measure of the particle size it will retain.
Anatomy of a Pharmaceutical Sieve
Every part of a standard sieve is designed for accuracy, durability, and cleanliness.
The Sieve Mesh: Woven Wire Cloth
The screening surface is almost always made of woven wire cloth. The precision of the weave is what ensures uniform aperture sizes across the entire surface of the sieve.
Materials of Construction: Stainless Steel Dominance
Sieves are typically constructed from high-quality stainless steel (e.g., 316L). This material is chosen because it is chemically inert, resistant to corrosion, durable, and easy to clean and sterilize, preventing cross-contamination between different drug products.
The Frame and Serial Number
The mesh is mounted under tension in a rigid circular frame. Each sieve is engraved with a unique serial number. This number is essential for traceability, linking the physical sieve to its calibration certificates and usage logs in a GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) environment.
The Core Application: Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
The primary use of sieves is to determine the Particle Size Distribution (PSD) of a material, which has a direct impact on the drug's performance.
Why PSD Matters for Drugs
Particle size influences almost every aspect of a solid dosage form. Finer particles generally dissolve faster, which can increase bioavailability. Consistent PSD is also crucial for content uniformity in tablets and for ensuring good flowability and compressibility during manufacturing.
The Sieve Shaker: Ensuring Reproducible Results
To get reliable and repeatable results, sieves are agitated using a mechanical sieve shaker. These devices impart a consistent tapping and/or orbital motion, ensuring all particles have an opportunity to pass through the apertures without the variability of manual shaking.
Building a Sieve Stack
For PSD analysis, a "stack" of sieves is arranged with the largest aperture sieve on top and progressively smaller ones below. A solid collection pan sits at the bottom. The sample is placed on the top sieve, the stack is shaken for a set time, and the weight of material retained on each sieve is measured to calculate the distribution.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While essential, sieve analysis is a physical method with potential sources of error that must be managed.
Wear and Tear: The Risk of Inaccuracy
With use, sieve mesh can stretch, warp, or get damaged. A single dented wire can alter the aperture size and compromise results. This is why routine visual inspection and periodic recalibration are critical quality control procedures.
The Problem of Blinding and Overloading
Blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh apertures, blocking them. Overloading a sieve with too much sample prevents particles from having a chance to pass through. Both lead to an inaccurate overestimation of coarse particles.
Electrostatic Charges with Fine Powders
Very fine, dry powders can develop electrostatic charges, causing them to cling to the sieve wires and frame. This can skew the results by preventing the particles from passing through the appropriate apertures.
Mesh Number vs. Nominal Aperture: A Common Confusion
Never assume that a sieve number (e.g., No. 40) from one standard (ASTM) has the exact same aperture size as the same number from another standard (ISO). Always confirm the nominal aperture size in µm as specified by the pharmacopeia you are following.
Selecting the Right Sieve for Your Task
Your choice of sieves should be driven by the specific goal of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is regulatory QC testing: Use the exact sieve numbers specified in the official pharmacopeial monograph for the drug substance or product.
- If your primary focus is formulation or process development: Select a broader range of sieves (e.g., 5-8 sieves) to build a detailed distribution curve that reveals how changes in a process affect the final PSD.
- If your primary focus is raw material inspection: Use a two-sieve test (a coarse and a fine sieve) to quickly verify that an incoming material meets its fineness specification and is free from contamination.
By understanding that standard sieves are precision instruments, you can effectively use them to control processes and guarantee the quality and efficacy of the final pharmaceutical product.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measure particle size distribution (PSD) of powders and granules. |
| Key Standards | USP (United States Pharmacopeia), BP (British Pharmacopoeia), IP (Indian Pharmacopoeia). |
| Critical Specification | Nominal aperture size (in µm or mm), not just the sieve/mesh number. |
| Common Material | Stainless steel (e.g., 316L) for durability, cleanliness, and corrosion resistance. |
| Core Importance | Ensures consistent drug dissolution, bioavailability, and manufacturability. |
Ensure your pharmaceutical products meet the highest standards of quality and consistency.
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying precision laboratory equipment and consumables. Our range of pharmacopeia-compliant standard sieves and sieve shakers are designed to deliver the accurate, reliable particle size analysis you need for regulatory compliance and effective formulation.
Let KINTEK be your trusted partner in laboratory excellence. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the sieve sizes for particle size distribution? A Guide to ASTM and ISO Standards
- How accurate are test sieves? Understand the Variables That Impact Your Particle Analysis
- What is the primary purpose of using laboratory standard sieves? Optimize Composting Pre-treatment for Pig Manure
- How accurate is a sieve analysis? Achieve Reliable Particle Size Distribution Data
- How to choose sieve size? Build the Perfect Sieve Stack for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the preferred size in sieving method? Optimize Your Particle Analysis Accuracy
- What is the use of sieve in laboratory? Measure Particle Size Distribution for Quality Control
- What is the standard for sieve analysis? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Compliance



















