The primary advantages of the Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) method center on its ability to dramatically improve a material's physical properties. PVD coatings impart superior hardness, exceptional wear and corrosion resistance, and a high-quality aesthetic finish. This is all accomplished through a low-temperature process that deposits an extremely thin, durable film without altering the critical dimensions of the underlying part.
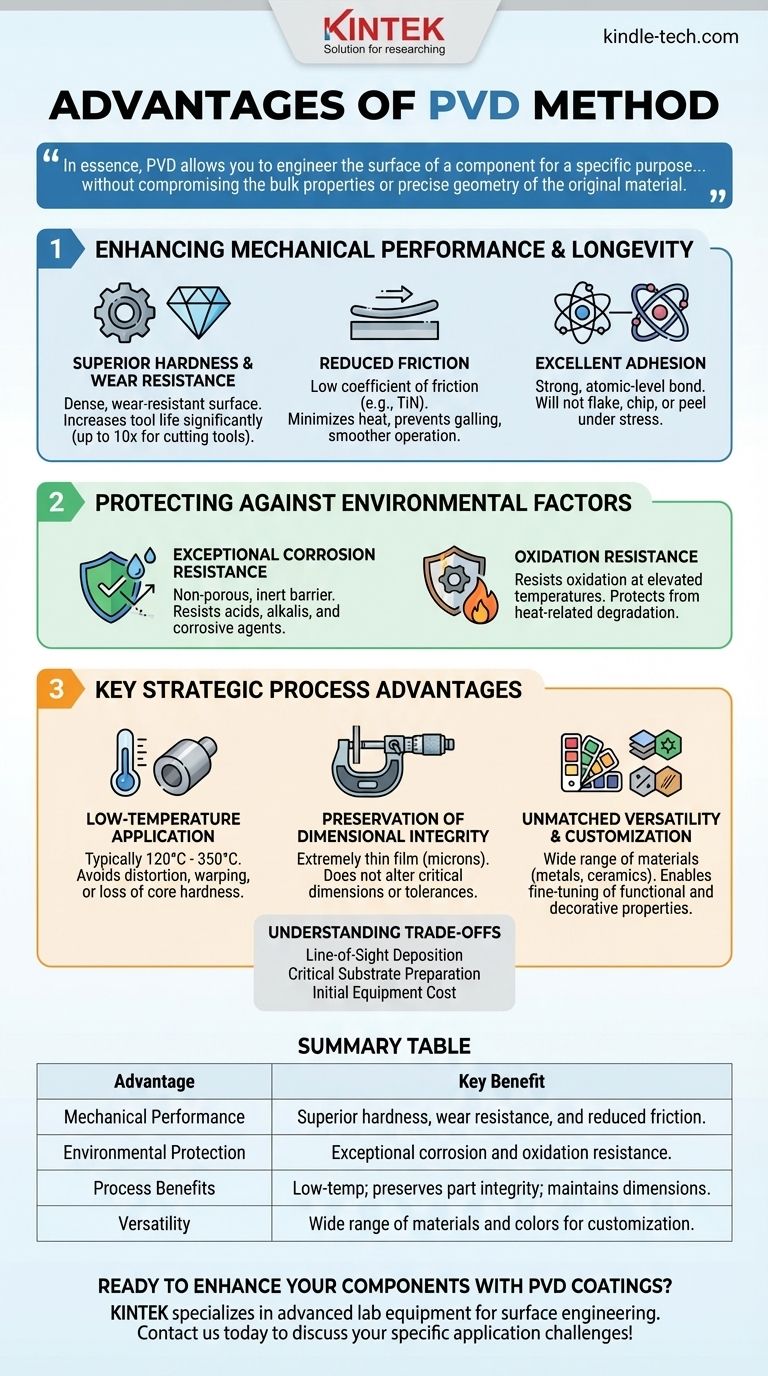
In essence, PVD allows you to engineer the surface of a component for a specific purpose—be it extreme durability, low friction, or a premium appearance—without compromising the bulk properties or precise geometry of the original material.

Enhancing Mechanical Performance and Longevity
The most common reason for specifying a PVD coating is to increase the functional lifespan and performance of a component, especially one subjected to mechanical stress.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard, often measuring multiple times harder than chrome. This creates a dense, wear-resistant surface that protects the substrate from abrasion, erosion, and microscopic wear.
For applications like cutting tools, this can increase tool life by as much as ten times, leading to significant gains in manufacturing productivity and efficiency.
Reduced Friction
Many PVD coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), possess a low coefficient of friction. This "lubricious" quality is critical for moving parts and cutting applications.
By reducing friction, the coating minimizes heat generation, prevents material galling, and allows for smoother operation with less energy consumption.
Excellent Adhesion
The PVD process creates a strong, atomic-level bond between the coating and the substrate. Unlike simple plating, the coating becomes an integral part of the component's surface.
This ensures the protective layer will not flake, chip, or peel, even under high stress, vibration, or thermal cycling.
Protecting Against Environmental Factors
PVD coatings form a chemically inert barrier that isolates the substrate material from its environment, preventing degradation.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
The thin film deposited during the PVD process is non-porous and highly resistant to attack from acids, alkalis, and other corrosive agents. This is a key advantage for medical devices, automotive components, and parts used in harsh industrial settings.
Oxidation Resistance
Specialized PVD coatings are designed to resist oxidation at elevated temperatures. This protects the component from heat-related degradation and maintains its performance integrity in high-temperature applications.
Key Strategic Advantages of the PVD Process
Beyond the properties of the final coating, the PVD process itself offers unique benefits that make it the ideal choice for high-precision manufacturing.
Low-Temperature Application
PVD is a low-temperature process, typically operating between 120°C and 350°C. This is well below the tempering or annealing temperatures of most steels and other metals.
This means it can be applied to finished, heat-treated parts without causing distortion, warping, or a loss of core hardness—a critical advantage over high-temperature methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Preservation of Dimensional Integrity
Because the applied coating is extremely thin (typically just a few microns), PVD does not materially alter the dimensions of a component.
This precision is essential for parts with tight tolerances, such as threaded fasteners, injection mold components, and precision medical instruments. The process accurately follows even polished or textured surfaces.
Unmatched Versatility and Customization
The PVD process is highly versatile. It allows for the deposition of a wide array of materials, including metals, alloys, and ceramics, in various structures such as monolayers, multilayers, or even nanostructures.
This versatility provides a broad palette of colors for decorative applications and enables the fine-tuning of functional properties like hardness, lubricity, and chemical resistance to meet specific performance goals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD is a powerful technology, it's important to recognize its limitations to determine if it's the right solution for your needs.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process. The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the part, making it difficult to coat complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes uniformly.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The success of a PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate surface. Any contaminants, such as oils or oxides, will compromise adhesion and lead to coating failure. This requires a rigorous, multi-stage cleaning process before coating.
Initial Equipment Cost
PVD requires a high-vacuum environment and sophisticated equipment. The initial capital investment can be substantial, which can make it less cost-effective for very low-volume or non-critical applications compared to simpler finishing processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PVD should be a decision driven by your primary performance or aesthetic goals.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of cutting tools or high-wear components: PVD's combination of extreme hardness, low friction, and superior wear resistance is its most powerful advantage.
- If your primary focus is protecting precision parts without altering their dimensions: The low-temperature nature of PVD is the key benefit, as it prevents material distortion and maintains critical tolerances.
- If your primary focus is creating a premium, durable decorative finish: PVD offers a wide range of brilliant colors on a hard, scratch-resistant surface that far outlasts traditional plating or paints.
Ultimately, PVD provides a robust method for engineering a component's surface, adding significant value and performance without compromising the integrity of the underlying material.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Performance | Superior hardness, wear resistance, and reduced friction for longer component life. |
| Environmental Protection | Exceptional corrosion and oxidation resistance for harsh environments. |
| Process Benefits | Low-temperature application preserves part integrity; thin, durable coatings maintain dimensions. |
| Versatility | Wide range of materials and colors for functional or decorative customization. |
Ready to enhance your components with PVD coatings?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our solutions help you achieve superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finishes without compromising part integrity.
Contact us today to discuss how PVD can solve your specific application challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection



















