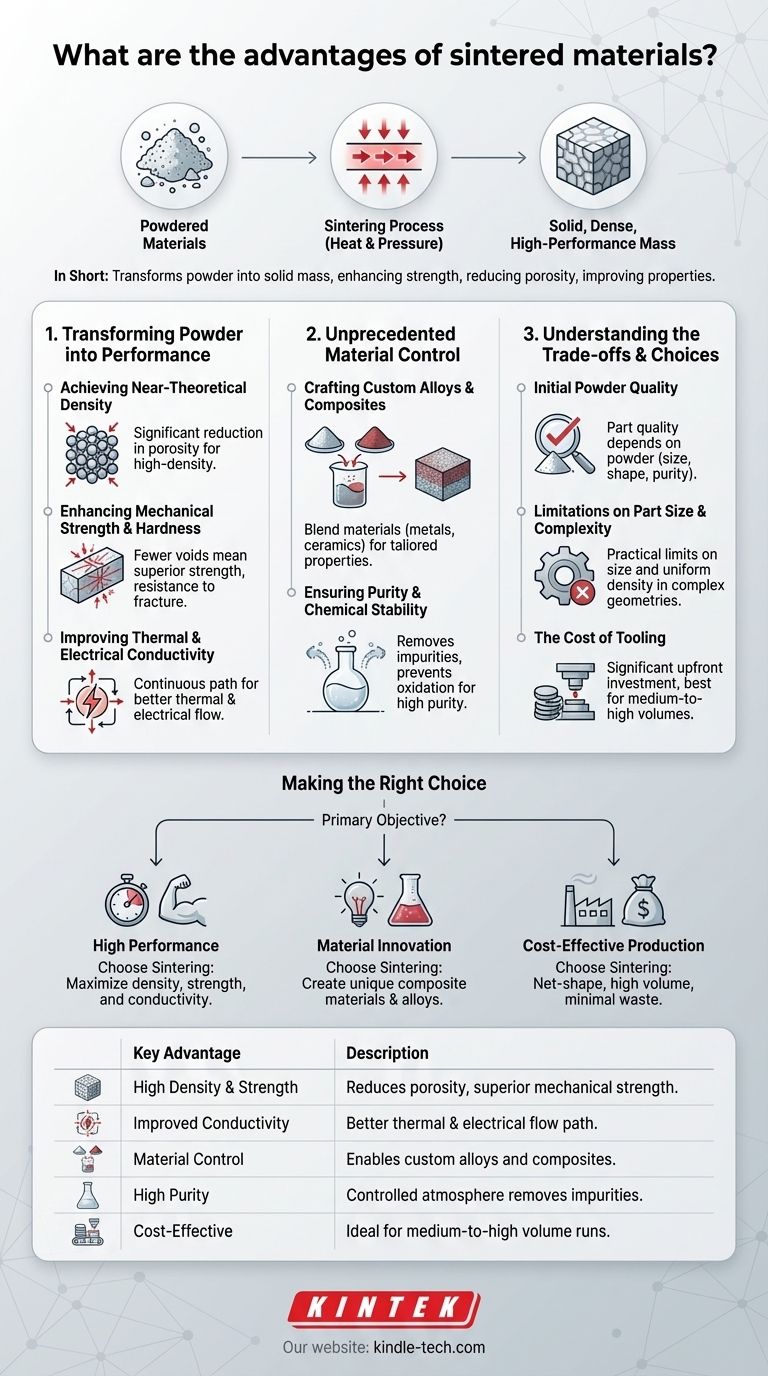
In short, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms powdered materials into a solid mass, providing enhanced strength, reduced porosity, and improved thermal and electrical properties. This is achieved by heating the compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together and form a dense, high-performance final product.
Sintering’s core advantage is not just shaping a part, but fundamentally engineering the material's internal structure. It offers a level of control over density, purity, and composition that is often unattainable with traditional methods like casting or machining.

How Sintering Transforms Powder into Performance
Sintering is a thermal process that bonds particles together, dramatically changing the material's characteristics. This transformation from a loose powder to a solid, functional component is the source of its key advantages.
Achieving Near-Theoretical Density
The most fundamental benefit of sintering is the significant reduction in porosity. As the material is heated, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to bond and pulling them closer together.
This process systematically eliminates the empty spaces between the powder grains, resulting in a high-density final part. This densification is the primary driver for many of the other improvements.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
A direct consequence of higher density is superior mechanical strength. With fewer voids or internal defects to initiate cracks, a sintered part is inherently more robust and resistant to fracture.
The final hardness and strength are also heavily influenced by the initial powder mix, allowing for precise tuning of the material's mechanical properties to suit a specific application.
Improving Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
The voids between particles in an unsintered powder act as insulators, impeding the flow of heat and electricity. By fusing the particles and removing these gaps, sintering creates a more continuous path.
This results in significantly improved thermal and electrical conductivity, a critical advantage for components used in electronics, heat sinks, and other thermal management applications.
The Unique Advantage: Unprecedented Material Control
Beyond simply improving existing properties, sintering opens the door to creating entirely new materials and achieving exceptional levels of purity.
Crafting Custom Alloys and Composites
Sintering allows you to blend powders of different materials—such as metals and ceramics—that could not be combined via melting due to different melting points or immiscibility.
This unique capability enables the creation of custom composites and alloys with tailored properties, such as high hardness combined with self-lubrication, or high strength with a specific thermal expansion rate.
Ensuring Purity and Chemical Stability
When conducted in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum, sintering can actively remove impurities. Volatile materials and trapped gases are drawn out during the heating process.
This process prevents the formation of undesirable oxides and results in a final product with very high purity and chemical stability, which is essential for medical, aerospace, and semiconductor applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Role of Initial Powder Quality
The quality of the final part is entirely dependent on the quality of the initial powder. Particle size, shape, and purity must be tightly controlled, as they directly impact the final density, shrinkage, and mechanical properties.
Limitations on Part Size and Complexity
There are practical limits to the size of parts that can be sintered, often dictated by the capacity of the compaction presses and furnaces. Extremely complex geometries can also present challenges in achieving uniform density throughout the part.
The Cost of Tooling
Creating the dies and tooling used to compact the powder can represent a significant upfront investment. Because of this, sintering is typically most cost-effective for medium-to-high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over many parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if sintering is the correct process, consider your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high performance: Sintering allows you to achieve near-theoretical density and purity, maximizing strength, hardness, and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is material innovation: The process enables the creation of unique composite materials and advanced alloys not possible with other methods.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex parts: Sintering excels at producing net-shape or near-net-shape components in volume, minimizing material waste and secondary machining.
Ultimately, sintering offers a level of microstructural control that empowers you to design the material itself, not just the final part.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Density & Strength | Reduces porosity, resulting in superior mechanical strength and hardness. |
| Improved Conductivity | Creates a continuous path for better thermal and electrical flow. |
| Material Control | Enables creation of custom alloys and composites with tailored properties. |
| High Purity | Controlled atmosphere sintering removes impurities for chemical stability. |
| Cost-Effective Production | Ideal for medium-to-high volume runs, minimizing material waste. |
Ready to engineer high-performance materials for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for sintering and other thermal processes. Whether you are developing new composites or need to ensure material purity, our solutions are designed to meet the precise demands of laboratory research and development.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace facilitate the control of crystal phase composition in NZSSP electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace improve NASICON electrolytes? Optimize Grain Boundary Conductivity
- Why must TiO2 nanotubes undergo calcination? Unlock High Photocatalytic Performance with Precise Thermal Activation
- How do high-temperature industrial furnaces ensure the quality of aluminide diffusion coatings? Precision Thermal Control
- What is thermal sintering? A Guide to Solid-State Powder Processing
- What role does a muffle furnace play in converting loaded activated carbon into an active catalyst? Optimize Your Catalyst Activation
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in YAG synthesis? Master Pure-Phase Crystal Production
- How is a high-temperature box resistance furnace utilized in the preparation of IrO2/Ti electrodes? Expert Guide



















