In short, a temperature control system is used anywhere that maintaining a specific temperature is critical. This includes common applications like residential HVAC and refrigeration, as well as highly specialized industrial processes, food production, and scientific equipment. Their primary function is to regulate heating or cooling elements to hold a precise temperature, improve energy efficiency, and ensure safety and consistency.
The true purpose of a temperature control system is not just to set a temperature, but to achieve and maintain equilibrium. It is the technology that ensures stability, efficiency, and predictability in processes ranging from heating a home to manufacturing life-saving medicines.

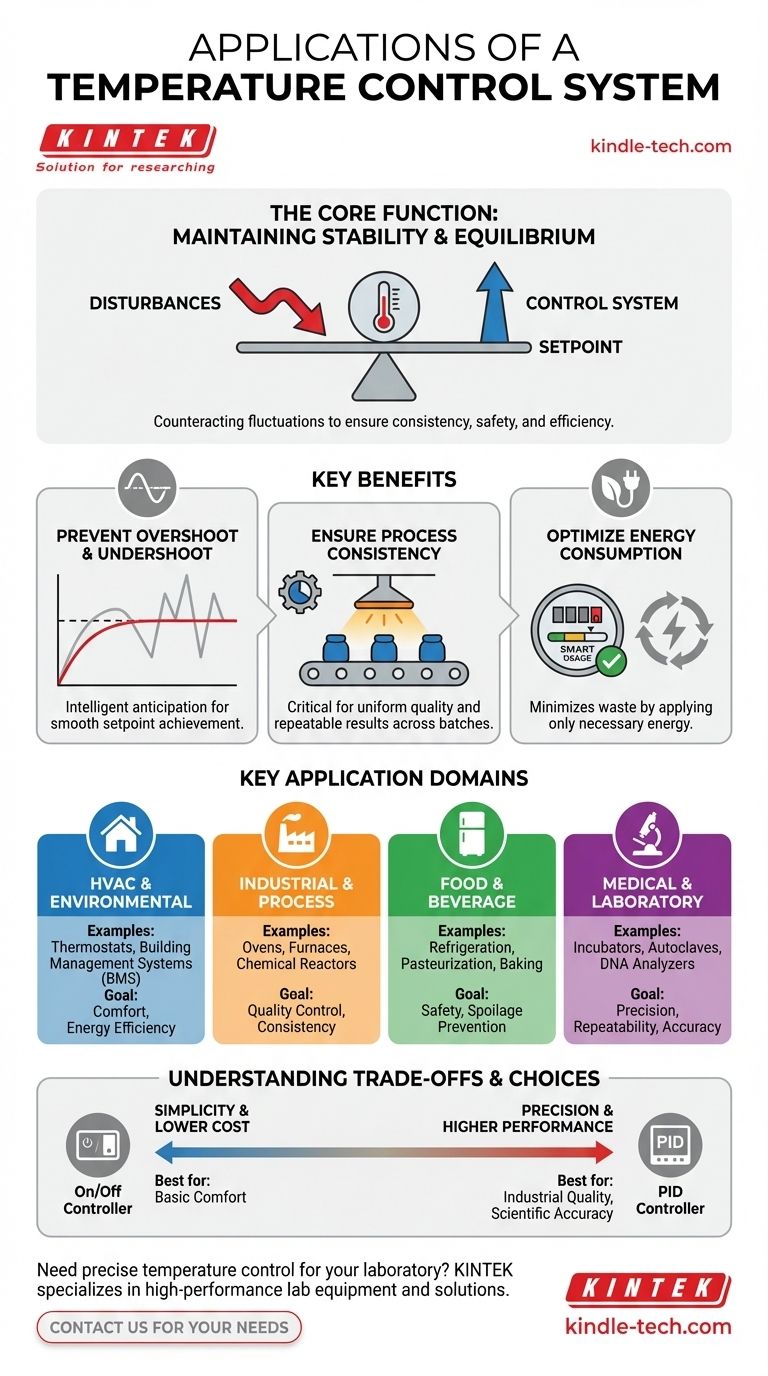
The Core Function: Maintaining Stability
At its heart, a temperature controller's job is to counteract external and internal disturbances that would otherwise cause a system's temperature to fluctuate. It creates a stable thermal environment.
Preventing Overshoot and Undershoot
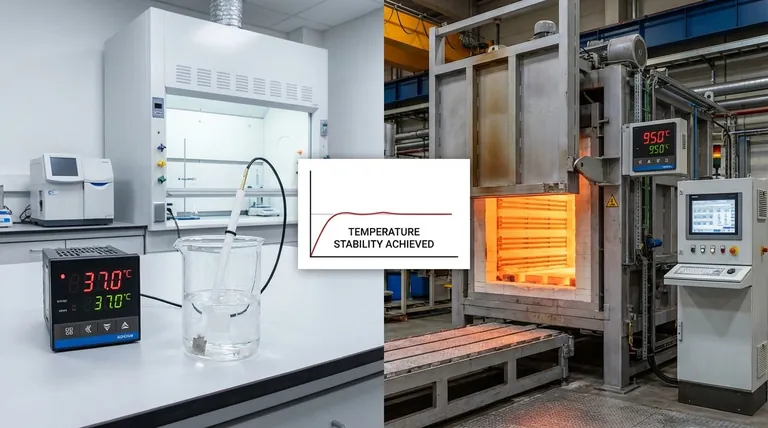
A key goal is to avoid overshooting (getting too hot) or undershooting (getting too cold) the desired temperature, known as the setpoint. A naive system might heat at full power until it hits the target, but residual heat will cause it to overshoot significantly.
Modern controllers anticipate this, reducing power as they approach the setpoint to land on the target temperature smoothly and precisely.
Ensuring Process Consistency
In manufacturing, science, and food production, even minor temperature variations can ruin a product. A temperature controller ensures that every batch of a product is created under the exact same thermal conditions.
This consistency is critical for quality control, whether it's baking bread, curing composites, or growing cell cultures in a laboratory incubator.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
By intelligently modulating heating or cooling output instead of simply running at 100% or 0%, a control system minimizes energy waste.
It applies only the necessary amount of energy required to maintain the setpoint, preventing the expensive cycles of over-cooling and re-heating common in simpler systems.
Key Application Domains
While the principles are universal, the applications are incredibly diverse. Temperature control is a foundational technology in nearly every modern industry.
HVAC and Environmental Control
This is the most familiar application. Thermostats in homes and complex Building Management Systems (BMS) in commercial towers all use temperature control to maintain occupant comfort and optimize energy usage for heating and cooling.
Industrial and Process Control
In factories, temperature controllers are essential for ovens, furnaces, and chemical reactors. They enable precise control over processes like plastic molding, metal tempering, and chemical synthesis, where exact temperatures dictate the final product's properties.
Food and Beverage
From large-scale commercial refrigeration that prevents spoilage to ovens and pasteurization vats that require exact temperatures for safety and quality, the food industry relies heavily on these systems. They ensure food is safe to eat and has a consistent taste and texture.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Scientific and medical devices demand the highest level of precision. Laboratory incubators, autoclaves (sterilizers), and DNA analysis machines must hold temperatures within a fraction of a degree to produce valid and repeatable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Implementing a temperature control system involves balancing precision, cost, and complexity. The "best" system is entirely dependent on the application's requirements.
Simplicity vs. Precision
A simple on/off controller (like an old home thermostat) is cheap and easy to implement but often results in significant temperature swings.
A more advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller is far more precise and stable but requires careful "tuning" and a deeper understanding of the system's thermal properties to function optimally.
Cost of Implementation
Higher precision comes at a price. Achieving tight temperature control requires more sensitive sensors, faster and more intelligent controllers, and often more sophisticated heating or cooling elements. The cost must be justified by the need for quality, safety, or efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of a temperature control strategy depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is basic comfort in a home or small office: A modern programmable thermostat with simple proportional control offers an excellent balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is industrial quality or scientific accuracy: A precisely tuned PID controller is the only way to guarantee the stability and repeatability required for high-stakes processes.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency at scale: An advanced system with PID logic and smart analytics will provide the greatest long-term return on investment by minimizing energy waste.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is about choosing the right tool to create the exact thermal environment your process demands.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Key Examples | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC & Environmental | Home thermostats, Building Management Systems | Comfort, Energy Efficiency |
| Industrial & Process | Ovens, Furnaces, Chemical Reactors | Quality Control, Consistency |
| Food & Beverage | Refrigeration, Pasteurization, Baking | Safety, Consistency, Spoilage Prevention |
| Medical & Laboratory | Incubators, Autoclaves, DNA Analyzers | Precision, Repeatability, Accuracy |
Need precise temperature control for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, ensuring the stability and accuracy your research demands. Whether you require a reliable incubator, a precise oven, or a custom temperature control solution, our expertise helps you achieve consistent, repeatable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What is the proper post-treatment procedure for a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Long-Term Accuracy & Protect Your Investment
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum sheet electrodes? Unlock Superior Electrochemical Performance
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the key performance characteristics and applications of platinum sheets? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications
















