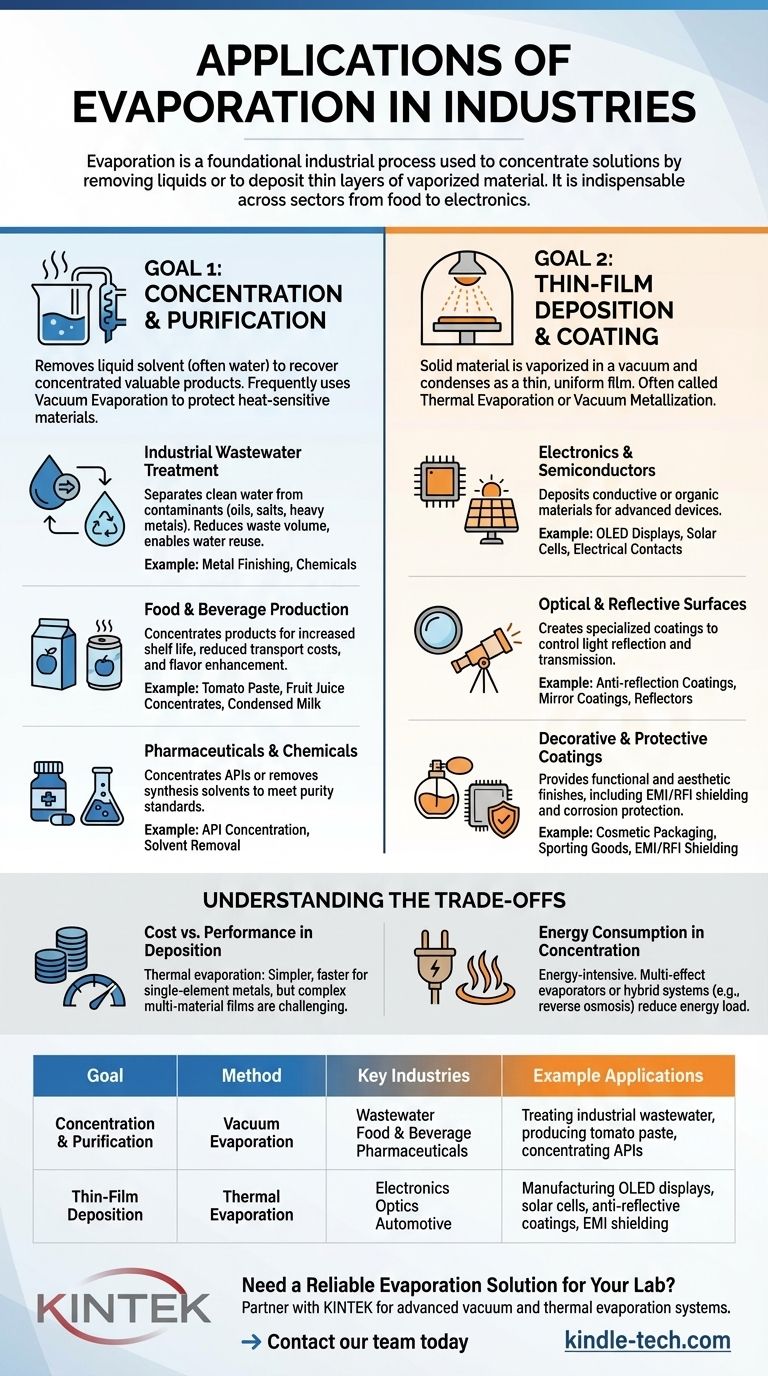
In short, evaporation is a foundational industrial process used for two primary purposes: concentrating a solution by removing a liquid, or depositing a thin layer of vaporized material onto a surface. This makes it indispensable in sectors ranging from food and beverage and wastewater treatment to the manufacturing of advanced electronics and solar cells.
Evaporation is not a single technology but a versatile principle applied in two distinct ways. It is used either to purify and concentrate liquids by removing a solvent, or to create high-performance coatings and thin films by depositing a vaporized solid. The specific application dictates the method used.

The Two Pillars of Industrial Evaporation
The diverse applications of evaporation can be understood by separating them into two main strategic goals: concentration and deposition.
Goal 1: Concentration and Purification
In these applications, the liquid solvent (often water) is removed, and the remaining concentrated product is the valuable component. Vacuum evaporation is frequently used here because lowering the pressure also lowers the boiling point, protecting heat-sensitive materials.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Vacuum evaporation is a powerful tool for treating industrial wastewater. It separates clean, distilled water from dissolved contaminants like oils, salts, and heavy metals.
This process significantly reduces the volume of hazardous waste for disposal and allows for the reuse of the recovered water, creating a more sustainable and cost-effective operation in industries like metal finishing and chemicals.
Food and Beverage Production
Evaporation is critical for concentrating products to increase shelf life, reduce packaging and transportation costs, and enhance flavor.
Common examples include the production of tomato paste, fruit juice concentrates, and condensed milk. The process removes water content without degrading the quality of the food product.
Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, evaporation is used to concentrate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or to remove solvents used during synthesis and crystallization processes. This ensures the final product meets strict purity and concentration standards.
Goal 2: Thin-Film Deposition and Coating
For this goal, a solid material is heated in a vacuum until it vaporizes and then condenses as a thin, uniform film onto a substrate. This process is often called thermal evaporation or vacuum metallization.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Thermal evaporation is essential for building modern electronic devices. It is used to deposit the thin layers of conductive or organic materials needed for products like OLED displays and solar cells.
It is also a standard method for creating the electrical contacts on microchips and other components by depositing single metals like aluminum or silver with high precision.
Optical and Reflective Surfaces
This technique is used to form highly specialized coatings that control the way light is reflected or transmitted. Applications include anti-reflection coatings on lenses, mirror coatings for telescopes, and light reflectors for the automotive, medical, and aerospace industries.
Decorative and Protective Coatings
Evaporation provides both functional and aesthetic finishes. It's used for the metallic sheen on cosmetic packaging and sporting goods, as well as for creating EMI/RFI shielding on electronic housings to prevent interference.
Furthermore, it can be used to deposit permeation barrier films on flexible food packaging or to apply corrosion-protective coatings on various components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, evaporation techniques come with specific considerations that are critical for industrial-scale implementation.
Cost vs. Performance in Deposition
Thermal evaporation is often simpler and faster than other deposition methods like sputtering, especially for single-element metals.
However, achieving complex multi-material films (alloys or compounds) can be challenging, as it requires precise, independent temperature control for each source material. The quality and adhesion of the film can also be lower than with higher-energy deposition processes.
Energy Consumption in Concentration
Evaporation is an energy-intensive process, as it requires heat to vaporize a liquid (the latent heat of vaporization). The high energy cost can be a significant operational expense.
To mitigate this, industrial systems often use multi-effect evaporators that reuse heat or are paired with more energy-efficient pre-concentration technologies, such as reverse osmosis, to reduce the total load on the evaporator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct evaporation strategy depends entirely on your end goal, whether it's achieving purity, creating a function, or managing waste.
- If your primary focus is liquid concentration and purification: Vacuum evaporation is the ideal method for efficiently removing solvents from heat-sensitive products or wastewater streams.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity thin films: Thermal evaporation is the industry standard for depositing materials like metals and organics for electronic, optical, and decorative applications.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective large-scale treatment: A hybrid approach, such as combining reverse osmosis with a final evaporation step, will almost always yield the most economical results.
Ultimately, leveraging evaporation effectively means matching the specific technique—be it for removal or deposition—to the precise material and economic demands of your industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Method | Key Industries | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration & Purification | Vacuum Evaporation | Wastewater, Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals | Treating industrial wastewater, producing tomato paste, concentrating APIs |
| Thin-Film Deposition | Thermal Evaporation | Electronics, Optics, Automotive | Manufacturing OLED displays, solar cells, anti-reflective coatings, EMI shielding |
Need a Reliable Evaporation Solution for Your Lab?
Whether your goal is precise liquid concentration for purification or high-quality thin-film deposition for R&D, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment is engineered for performance and reliability. Our vacuum and thermal evaporation systems help researchers in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and electronics achieve accurate and repeatable results.
Partner with KINTEK to enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Our experts will help you select the ideal system to meet your specific material and economic demands.
➡️ Contact our team today to discuss your application and receive a personalized solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















