At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is a high-performance ceramic whose applications span from common abrasives to the frontiers of space technology. Its uses include heating elements in industrial furnaces, critical components in semiconductor manufacturing chambers, wear-resistant pump parts, and substrates for modern light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
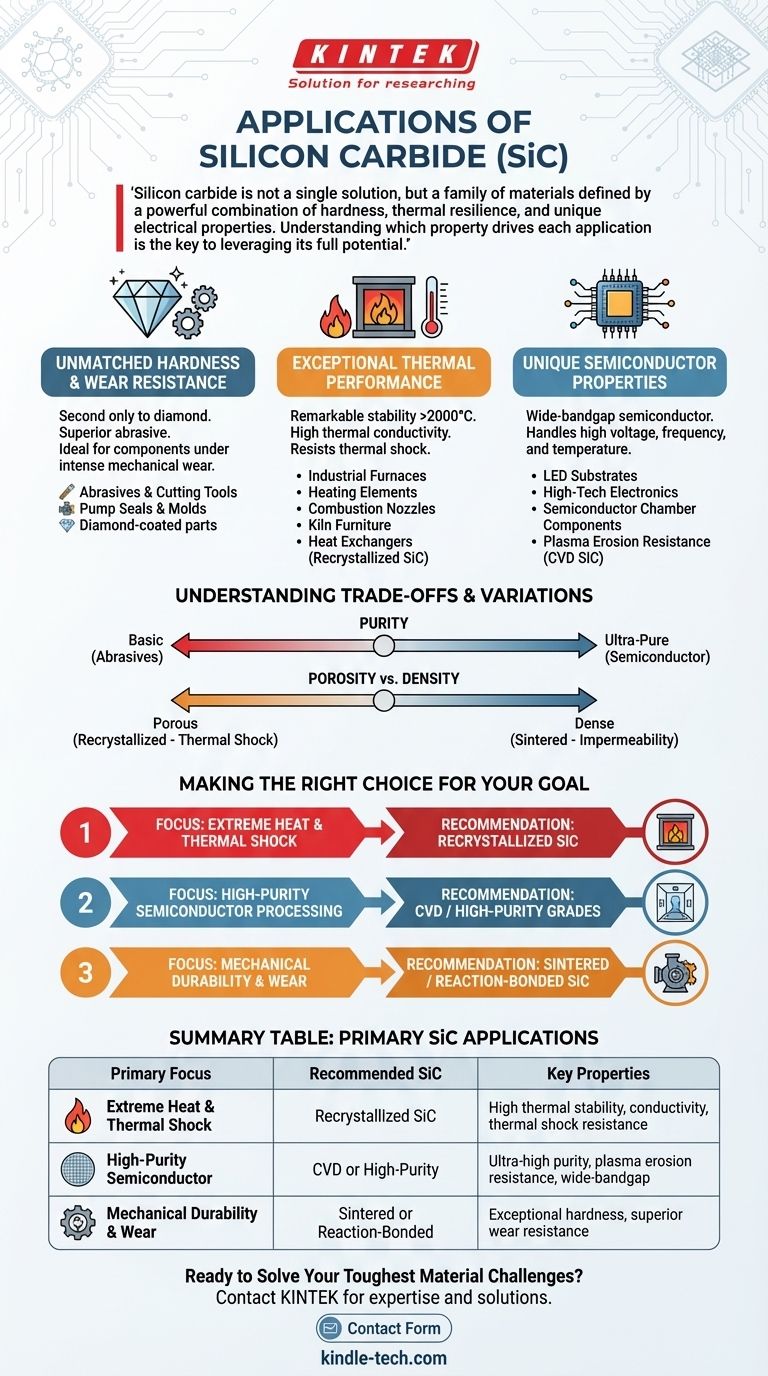
Silicon carbide is not a single solution, but a family of materials defined by a powerful combination of hardness, thermal resilience, and unique electrical properties. Understanding which property drives each application is the key to leveraging its full potential.

The Foundation: Why Silicon Carbide is a "Problem-Solver" Material
Silicon carbide's value comes from a rare blend of characteristics that allow it to perform where many other materials fail. Its applications are a direct result of these fundamental properties.
Unmatched Hardness and Wear Resistance
Silicon carbide is an exceptionally hard synthetic material, second only to diamond in common use. This makes it a superior abrasive and an ideal choice for components subjected to intense mechanical wear.
Historically, this property led to its use in sandpaper and cutting tools. Today, it is used for demanding mechanical parts like pump seals and molds, which are sometimes coated with diamond film to further extend their operational life.
Exceptional Thermal Performance
SiC demonstrates remarkable stability at extreme temperatures, with a refractoriness exceeding 2000°C. Critically, it combines this heat resistance with high thermal conductivity, allowing it to dissipate heat effectively and resist thermal shock.
This makes it indispensable for high-temperature industrial furnaces, where it is used for heating elements, furnace floors, and combustion nozzles. Recrystallized silicon carbide, a pure and porous variant, is particularly valued for kilns and heat exchangers.
Unique Semiconductor Properties
In its highly pure, crystalline form, silicon carbide acts as a wide-bandgap semiconductor. This allows it to handle higher voltages, frequencies, and temperatures than traditional silicon.
This capability is crucial in high-tech fields. It serves as the structural base (substrate) for manufacturing bright and efficient LEDs. Furthermore, its ability to resist erosion from high-energy plasmas makes it a key material for components inside semiconductor processing chambers.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While incredibly capable, "silicon carbide" is not a monolithic term. The manufacturing process and resulting purity dictate its final application and cost, creating a spectrum of grades for different needs.
Purity Dictates Performance
The SiC used for abrasives or basic furnace linings is different from the ultra-pure, defect-free SiC required for semiconductor applications. The latter, often produced via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), is significantly more expensive and complex to manufacture.
Porosity vs. Density
Some applications benefit from the porous structure of recrystallized silicon carbide, which offers excellent thermal shock resistance. In contrast, applications requiring impermeability or maximum plasma resistance will use a dense, fully sintered form. Choosing the wrong grade can lead to premature failure or unnecessary expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of silicon carbide depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat and thermal shock: Seek out recrystallized SiC for components like kiln furniture, heat exchangers, and furnace elements where thermal stability and conductivity are paramount.
- If your primary focus is high-purity semiconductor processing: You will require CVD or equivalent high-purity grades for chamber components and substrates to ensure process integrity and resistance to plasma erosion.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and wear: Use sintered or reaction-bonded SiC for applications like seals, nozzles, and pump components where hardness is the most critical attribute.
Ultimately, silicon carbide excels in environments where conventional materials reach their thermal, mechanical, or electrical limits.
Summary Table:
| Primary Application Focus | Recommended SiC Type | Key Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Heat & Thermal Shock | Recrystallized SiC | High thermal stability & conductivity, thermal shock resistance |
| High-Purity Semiconductor Processing | CVD or High-Purity Grades | Ultra-high purity, plasma erosion resistance, wide-bandgap semiconductor properties |
| Mechanical Durability & Wear Resistance | Sintered or Reaction-Bonded SiC | Exceptional hardness, superior wear resistance |
Ready to Solve Your Toughest Material Challenges?
Whether you need components that withstand extreme temperatures, resist intense wear, or meet the stringent demands of high-purity semiconductor processing, KINTEK has the silicon carbide expertise and lab equipment solutions for you. Our specialists can help you select the right SiC grade for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how KINTEK's high-performance materials and laboratory equipment can enhance your operations and drive innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What is the effect of sintering temperature on density and hardness? Optimize Your Material's Properties
- What does ceramic fiber do? Achieve Superior High-Temperature Insulation and Control
- What is the maximum use temperature for alumina? Unlock High-Thermal Performance for Your Lab
- What is meant by ceramic powder? The Engineered Blueprint for Advanced Ceramics
- What is silicon carbide used for in semiconductor? A Guide to SiC's Dual Role in Power Electronics & Manufacturing
- Why are ceramics more resistant to corrosion? Unlock the Secret to Unmatched Chemical Stability
- Can ceramics withstand high temperatures? Discover Their Exceptional Heat Resistance



















