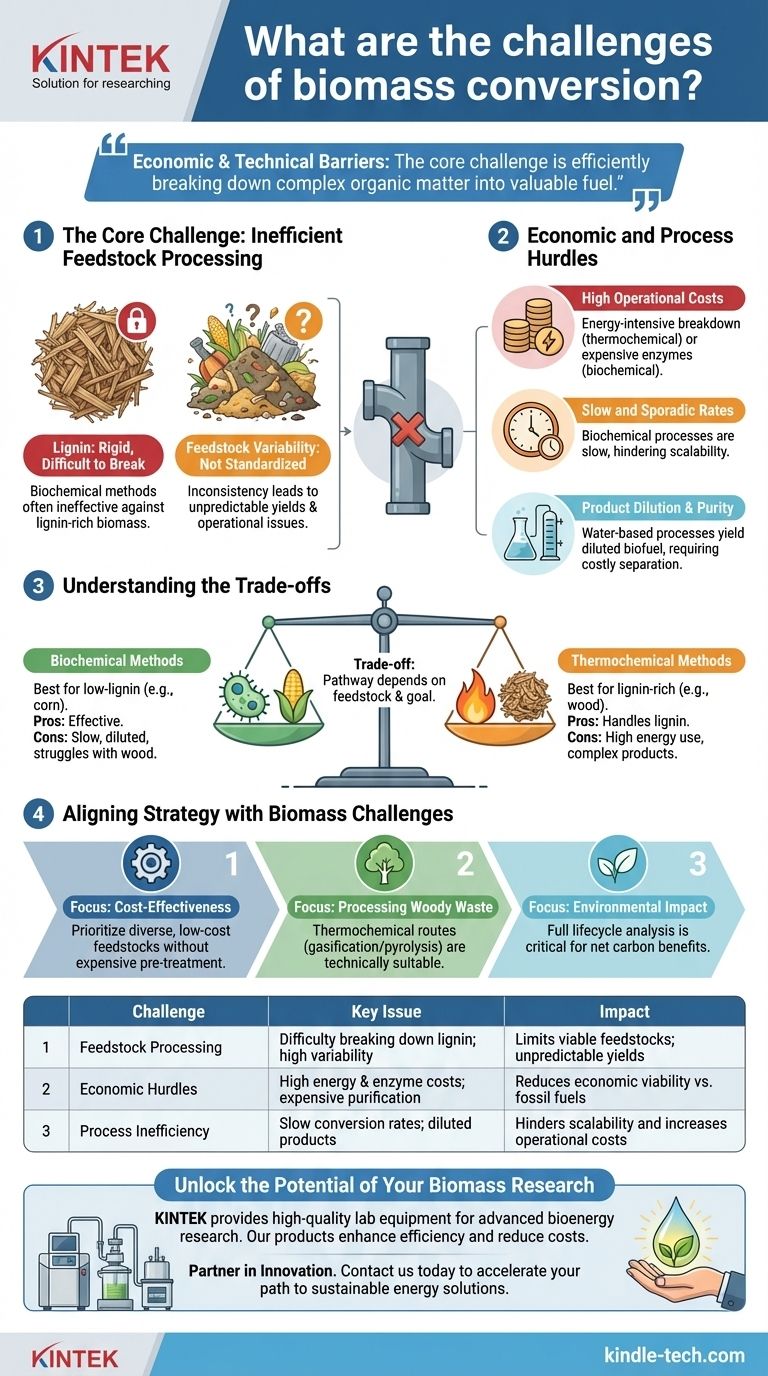
The primary challenges of biomass conversion center on high costs, the difficulty of processing resilient plant materials like lignin, and process inefficiencies. These hurdles often manifest as slow conversion rates and final products that are diluted and require further energy-intensive purification.
While biomass is a promising renewable resource, its path to widespread adoption is fundamentally blocked by economic and technical barriers. The core challenge is not a lack of potential, but the difficulty in efficiently and affordably breaking down complex organic matter into valuable fuel or chemicals.

The Core Challenge: Inefficient Feedstock Processing
The greatest single obstacle in biomass conversion is the nature of the raw material itself. Unlike uniform chemical feedstocks, biomass is highly variable and structurally complex.
The Lignin Problem
Lignin is the rigid, organic polymer that gives wood and bark its structure. It is notoriously difficult to break down.
Biochemical methods, which use enzymes or microbes, are often ineffective against lignin-rich biomass. This severely limits the range of viable feedstocks for these processes.
Feedstock Variability
Biomass is not a standardized commodity. Its moisture content, density, and chemical composition can vary dramatically depending on the source, season, and handling.
This inconsistency makes it difficult to design and operate a conversion facility that performs reliably, leading to unpredictable yields and operational headaches.
Economic and Process Hurdles
Beyond the feedstock itself, the conversion processes introduce their own set of economic and technical difficulties that must be overcome.
High Operational Costs
Breaking down tough plant matter is an energy-intensive and therefore cost-intensive endeavor.
Whether using high heat and pressure (thermochemical methods) or expensive, specialized enzymes (biochemical methods), the upfront energy and material costs are significant barriers to economic viability.
Slow and Sporadic Conversion Rates
Biochemical processes that rely on microbial fermentation are often relatively slow and sporadic.
This lack of speed and consistency makes it difficult to scale production and compete with the rapid, continuous output of traditional fossil fuel refining.
Product Dilution and Purity
Many biochemical conversion processes occur in water. The resulting biofuel, such as ethanol, becomes heavily diluted.
Separating the final product from this large volume of water requires significant energy for distillation, adding another layer of cost and inefficiency to the overall process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the challenges are significant, it's important to recognize that they are not universal. The specific hurdles depend heavily on the chosen conversion pathway.
Biochemical Methods
These methods (e.g., fermentation) excel with feedstocks low in lignin, like corn or sugar cane.
However, as noted, they face major challenges with cost, speed, product dilution, and their inability to process woody biomass effectively.
Thermochemical Methods
These methods (e.g., gasification, pyrolysis) use heat to break down biomass. They are far more effective at handling lignin-rich materials like wood chips or agricultural residue.
The primary trade-off is their high energy consumption and the potential to produce complex mixtures of products that require extensive and costly refinement.
Aligning Strategy with Biomass Challenges
Successfully implementing a biomass strategy requires acknowledging these challenges and selecting a pathway that aligns with your specific goals and available resources.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness: You must prioritize technologies that can process diverse, low-cost feedstocks without expensive pre-treatment or catalysts.
- If your primary focus is processing woody waste: Thermochemical routes like gasification or pyrolysis are technically more suitable, as biochemical methods will struggle with the high lignin content.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: A full lifecycle analysis is critical to ensure the energy spent on transportation and conversion does not negate the carbon benefits of using biomass.
Successfully navigating these economic and technical hurdles is the key to unlocking the full potential of biomass as a cornerstone of a sustainable energy future.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Processing | Difficulty breaking down lignin; high variability | Limits viable feedstocks; unpredictable yields |
| Economic Hurdles | High energy & enzyme costs; expensive purification | Reduces economic viability vs. fossil fuels |
| Process Inefficiency | Slow conversion rates; diluted products | Hinders scalability and increases operational costs |
Unlock the Potential of Your Biomass Research
Navigating the complexities of biomass conversion requires robust and reliable laboratory equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for advanced bioenergy and biochemical research.
Whether you are developing new thermochemical processes like pyrolysis or optimizing biochemical methods, our products are designed to enhance efficiency, improve yield, and reduce operational costs.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you overcome the challenges of biomass conversion and accelerate your path to sustainable energy solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are drawbacks of XRF technique? Key Limitations and Trade-offs to Consider
- What frequency is used in RF sputtering? The Critical Role of 13.56 MHz
- What is HIP hot isostatic pressing used for? Achieve Maximum Density & Reliability
- What is the process of thin film production? A Guide to Atomic-Level Material Engineering
- What is the process of sputtering in a vacuum? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of samples for XRF? Master Solid, Powder, and Liquid Preparation
- Can you provide a typical example of the calcination process? Discover the Limestone to Lime Transformation
- How many times can metal be heat treated? The True Limit Isn't a Number







