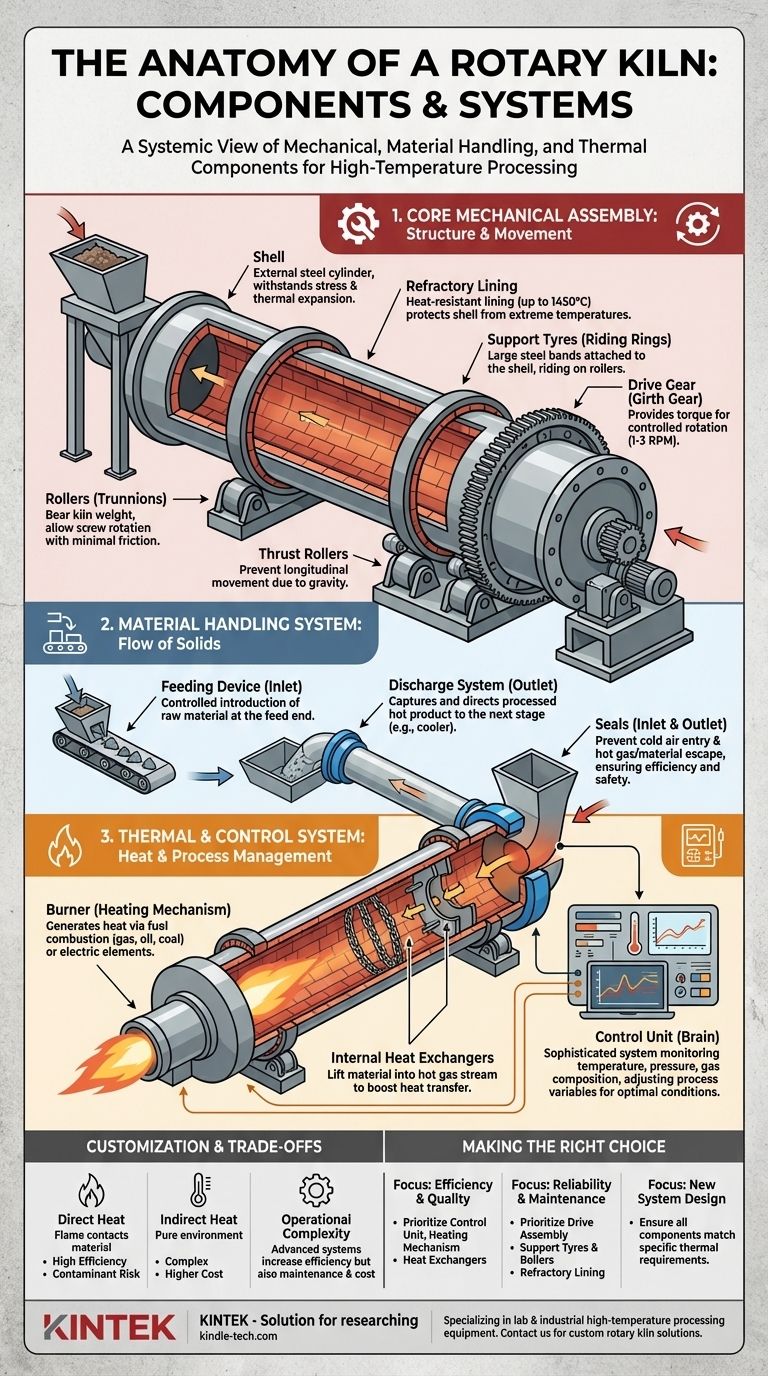
At its core, a rotary kiln is comprised of several key mechanical components. These include the main cylindrical shell, a protective refractory lining, support tyres (or riding rings) and rollers that allow it to rotate, and a drive gear that provides the rotational force. These parts work in concert to transport and process materials at extremely high temperatures.
A rotary kiln is not merely a collection of mechanical parts, but a complete thermal processing system. Understanding it requires looking beyond the rotating cylinder to the integrated systems for material handling, heating, and process control that enable its function.

Deconstructing the Rotary Kiln: A Systemic View
To truly understand a rotary kiln, it is best to analyze it as three interconnected systems that work together: the core mechanical assembly that rotates, the material handling system that moves product through it, and the thermal system that controls the process.
The Core Mechanical Assembly
This is the central rotating structure and the components that enable its movement.
The Shell
The shell is the external steel cylinder of the kiln. It provides the primary structure and is engineered to withstand the immense mechanical stress of rotation and thermal expansion.
The Refractory Lining
Inside the shell is a lining made of heat-resistant bricks or castable material. This refractory lining protects the steel shell from the extreme internal process temperatures, which can exceed 1450°C (2640°F) in applications like cement production.
Support Tyres & Rollers (Riding Rings & Trunnions)
Large steel bands called support tyres are attached to the outside of the shell. These tyres ride on a set of heavy-duty rollers (or trunnion wheels), which bear the entire weight of the kiln and allow it to rotate with minimal friction.
The Drive Assembly
The drive assembly consists of a motor and a large ring gear (the girth gear) that encircles the kiln shell. This system provides the torque necessary to turn the massive cylinder at a slow, controlled speed, typically between 1 to 3 revolutions per minute.
Thrust Rollers
Because a kiln is installed at a slight angle, gravity constantly pulls it downhill. Thrust rollers are positioned to push against the side of a support tyre, preventing this longitudinal movement and keeping the kiln in its proper place.
The Material Handling System
This system manages the flow of solids into, through, and out of the kiln.
The Feeding Device
Raw material is introduced at the upper, or "feed," end of the inclined kiln. This can range from a simple chute to a more complex screw feeder, ensuring a consistent and controlled rate of material input.
The Discharge System
Processed material exits at the lower, or "discharge," end. A discharge breeching or housing captures the hot product and directs it to the next stage, which is often a cooler.
Seals
Seals are critical components at both the feed and discharge ends. They prevent cold air from leaking into the kiln and hot gases or material from escaping, ensuring both process efficiency and operational safety.
The Thermal and Control System
This is the "brain" and "heart" of the operation, managing the heat and process variables.
The Heating Mechanism
Heat is typically generated by a large burner mounted at the discharge end, firing a flame of gas, oil, or pulverized coal directly into the kiln. Some specialized kilns use electric heating elements arranged around the shell for precise, uniform temperature control.
Internal Heat Exchangers
To improve efficiency, many kilns feature internal components like metal chains or ceramic fins. These heat exchangers lift material into the hot gas stream, dramatically increasing the rate of heat transfer.
The Control Unit
Modern kilns are governed by a sophisticated control unit. This system uses sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, and gas composition, then uses actuators and intelligent instruments to adjust the fuel rate, rotation speed, and feed rate to maintain optimal conditions.
Understanding Customization and Trade-offs
A rotary kiln is never a one-size-fits-all solution; its components are highly customized for the specific material and thermal process.
Material-Specific Design
The choice of refractory material, the design of internal heat exchangers, and even the kiln's dimensions are dictated by the process. For example, a kiln for drying will operate at much lower temperatures and have different needs than one used for the high-temperature calcination of limestone.
Direct vs. Indirect Heat
Direct-fired kilns, where the flame and combustion gases contact the material, are highly efficient but can introduce contaminants. Indirectly heated or electric kilns offer a pure processing environment but are often more complex and costly to operate.
Operational Complexity
Adding complex internal heat exchangers or advanced control systems can boost thermal efficiency and product quality. However, this also increases maintenance requirements and the initial capital cost of the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the function of each component allows you to focus on what matters most for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and product quality: Pay closest attention to the control unit, the type of heating mechanism, and the design of the internal heat exchangers.
- If your primary focus is reliability and maintenance: Your key components are the drive assembly, support tyres and rollers, and the durability of the refractory lining.
- If your primary focus is designing or procuring a new system: The critical task is to ensure all components, from the feed system to the seals, are specified to match the exact thermal requirements of your material.
Ultimately, mastering a rotary kiln comes from understanding that it operates as a single, dynamic system where every component has a critical role in the final outcome.
Summary Table:
| System | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanical Assembly | Shell, Refractory Lining, Support Tyres, Rollers, Drive Gear, Thrust Rollers | Provides structural integrity and enables controlled rotation |
| Material Handling System | Feeding Device, Discharge System, Seals | Manages the flow of materials into, through, and out of the kiln |
| Thermal and Control System | Burner/Heating Mechanism, Internal Heat Exchangers, Control Unit | Generates and regulates heat, monitors process variables for optimal performance |
Need a reliable rotary kiln or expert advice on high-temperature processing equipment? KINTEK specializes in lab and industrial equipment, including custom rotary kilns designed for your specific material and thermal requirements. Whether you're focused on process efficiency, product quality, or system reliability, our solutions are tailored to meet your needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting biochar production? Key Variables to Engineer Biochar for Your Application
- What happens to plastic after pyrolysis? Discover How to Turn Waste into Fuel and Chemicals
- How does a continuous furnace work? Unlock High-Volume, Consistent Thermal Processing
- Is pyrolysis of plastic safe? Understanding the Critical Risks and Engineering Controls
- What is biomass and explain the process of biomass pyrolysis? A Guide to Converting Waste into Valuable Resources
- What is the purpose of a rotary furnace? Achieve Unmatched Heating Uniformity for Powders & Parts
- What are the components of a pyrolysis plant? Unlock the 4 Key Systems for Waste-to-Energy
- What is the operating temperature of pyrolysis? Master the Key to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Production



















