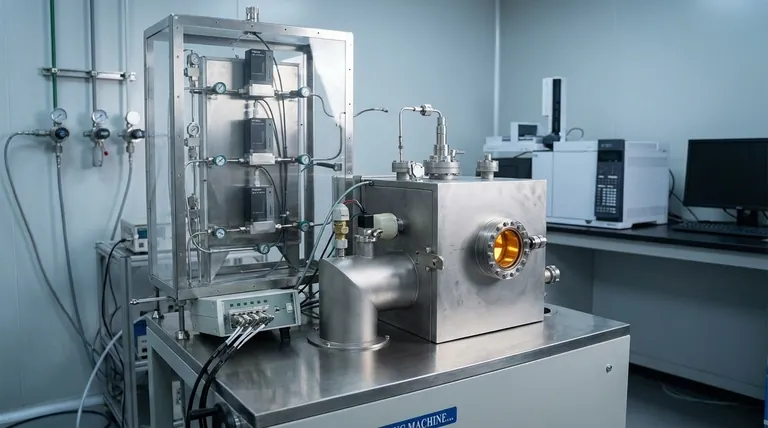
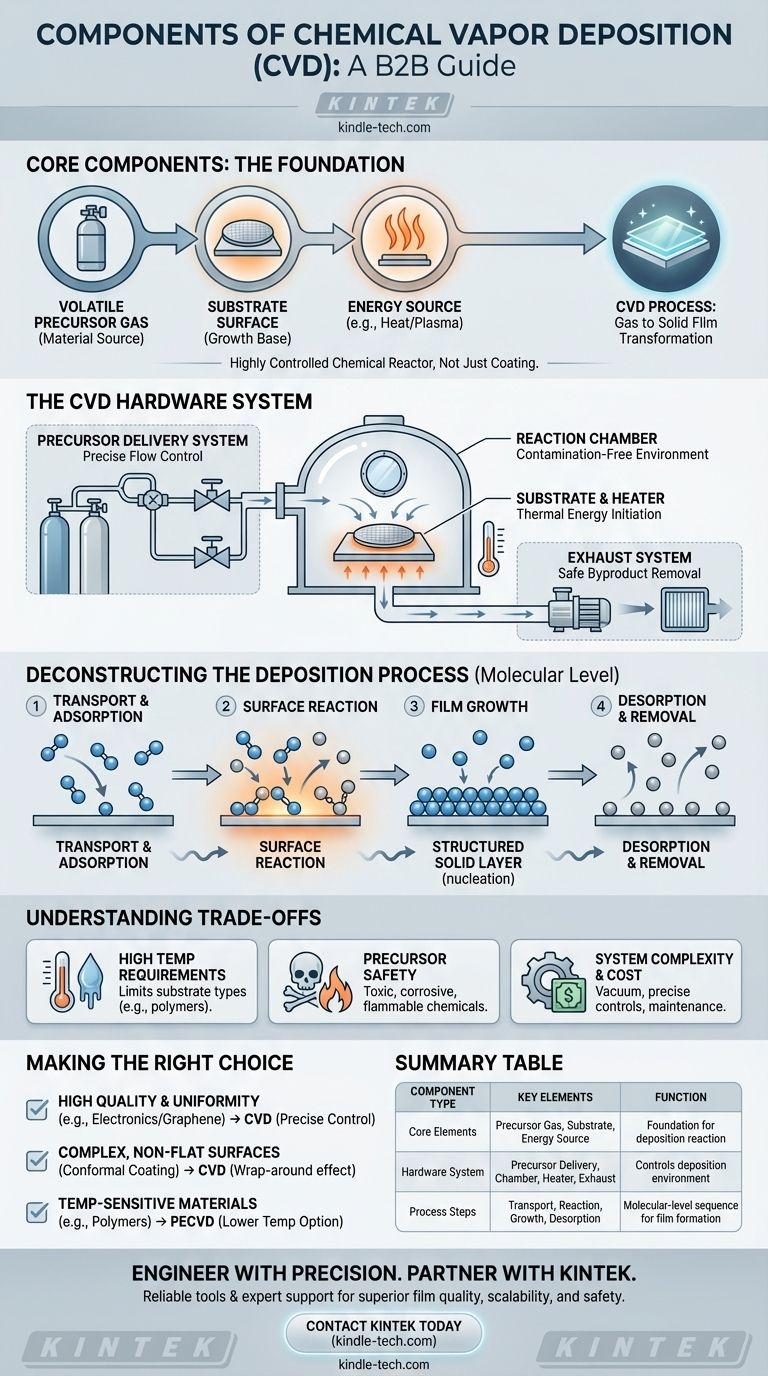
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process built on three fundamental components: a volatile precursor gas containing the material to be deposited, a substrate surface where the film will grow, and an energy source (typically heat) to drive the chemical reaction. These elements work together within a reaction chamber to transform the gas into a solid, high-quality thin film on the substrate's surface.
The essential insight is that CVD is not merely a coating machine, but a highly controlled chemical reactor. Its "components" include both the physical hardware and the sequential process steps that transform gaseous chemicals into a solid, precisely engineered material layer.

The Core Elements of a CVD System
A functional CVD system is an assembly of several critical hardware components, each with a distinct role in controlling the deposition environment.
The Precursor Delivery System
This component is responsible for storing and accurately delivering one or more volatile precursor gases into the reaction chamber. The ability to precisely control the flow rate of these gases is critical for determining the final composition and growth rate of the film.
The Reaction Chamber
This is the heart of the system. It's a sealed chamber, often operating under vacuum, that contains the substrate and provides a stable environment for the chemical reaction to occur without contamination from the outside atmosphere.
The Substrate and Heater
The substrate is the material or workpiece onto which the thin film is deposited. It is placed on a holder that can be heated to very specific temperatures, providing the thermal energy needed to initiate the chemical reaction on its surface.
The Energy Source
While high temperature is the most common energy source for driving the reaction (thermal CVD), it's not the only one. Advanced systems like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) use plasma to energize the precursor gases, allowing the process to run at much lower temperatures.
The Exhaust System
Once the precursor gases react and deposit material, there are gaseous byproducts left over. The exhaust system safely removes these byproducts from the reaction chamber, typically treating them before they are released.
Deconstructing the Deposition Process
Beyond the physical hardware, the CVD "process" itself consists of a sequence of well-defined steps that occur at the molecular level.
Step 1: Transport and Adsorption
Reactant gases are transported into the chamber and flow over the substrate. Molecules of the precursor gas then stick to the heated surface in a process called adsorption.
Step 2: Surface Reaction
With energy from the heated substrate, the adsorbed precursor molecules undergo a chemical change. They may decompose or react with other gases, releasing the atoms that will form the film and creating other gaseous byproducts.
Step 3: Film Growth
The newly freed atoms diffuse across the substrate surface, find energetically favorable locations (growth sites), and begin to form a solid layer. This process of nucleation and growth builds the thin film, layer by layer.
Step 4: Desorption and Removal
The gaseous byproducts from the chemical reaction detach from the substrate surface (desorption) and are transported away by the gas flow, eventually being removed by the exhaust system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not without its challenges. Objectively evaluating its limitations is key to using it effectively.
High Temperature Requirements
Traditional thermal CVD often requires very high temperatures to decompose the precursor gases. This can damage or fundamentally alter certain substrates, limiting the types of materials that can be coated.
Precursor Chemistry and Safety
CVD relies on volatile chemical precursors. These compounds can be expensive, toxic, corrosive, or flammable, requiring complex and robust safety protocols for handling and storage.
System Complexity and Cost
The need for vacuum chambers, precise gas flow controllers, high-temperature heating, and exhaust treatment makes CVD systems complex and costly to acquire and maintain compared to simpler methods like spray pyrolysis or plating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components allows you to tailor the CVD process to specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, uniform films for electronics (like graphene): CVD is the leading approach because its precise control over gas flow and temperature yields films with a low defect count.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces: CVD's "wrap-around" properties are a major advantage, as the gas precursor can reach and coat all exposed areas conformally.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials (like polymers): You must explore lower-temperature variations like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) to avoid damaging the substrate.
By mastering these fundamental components, you can leverage Chemical Vapor Deposition to engineer materials with precision at the atomic scale.
Summary Table:
| Component Type | Key Elements | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core Elements | Precursor Gas, Substrate, Energy Source | Foundation for the deposition reaction |
| Hardware System | Precursor Delivery, Reaction Chamber, Heater, Exhaust | Controls the deposition environment |
| Process Steps | Transport/Adsorption, Surface Reaction, Film Growth, Desorption | Molecular-level sequence for film formation |
Ready to Engineer High-Quality Thin Films with Precision?
Understanding the components of CVD is the first step. Implementing them effectively requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs.
We provide the reliable tools and expert support to help your laboratory:
- Achieve superior film uniformity and quality.
- Scale your research from development to production.
- Ensure safety and efficiency in your deposition processes.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how our solutions can optimize your CVD workflow and help you master material engineering at the atomic scale.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures



















