At its core, dental porcelain is a high-strength ceramic primarily composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz. These naturally occurring minerals are refined, precisely blended, and fired at high temperatures to create a material that is both incredibly durable and remarkably similar in appearance to natural tooth enamel.
Dental porcelain is not one substance but a carefully engineered composite. Its success lies in balancing its core components: kaolin provides the structural foundation, quartz delivers strength, and feldspar creates the glass matrix that gives it a life-like translucency.

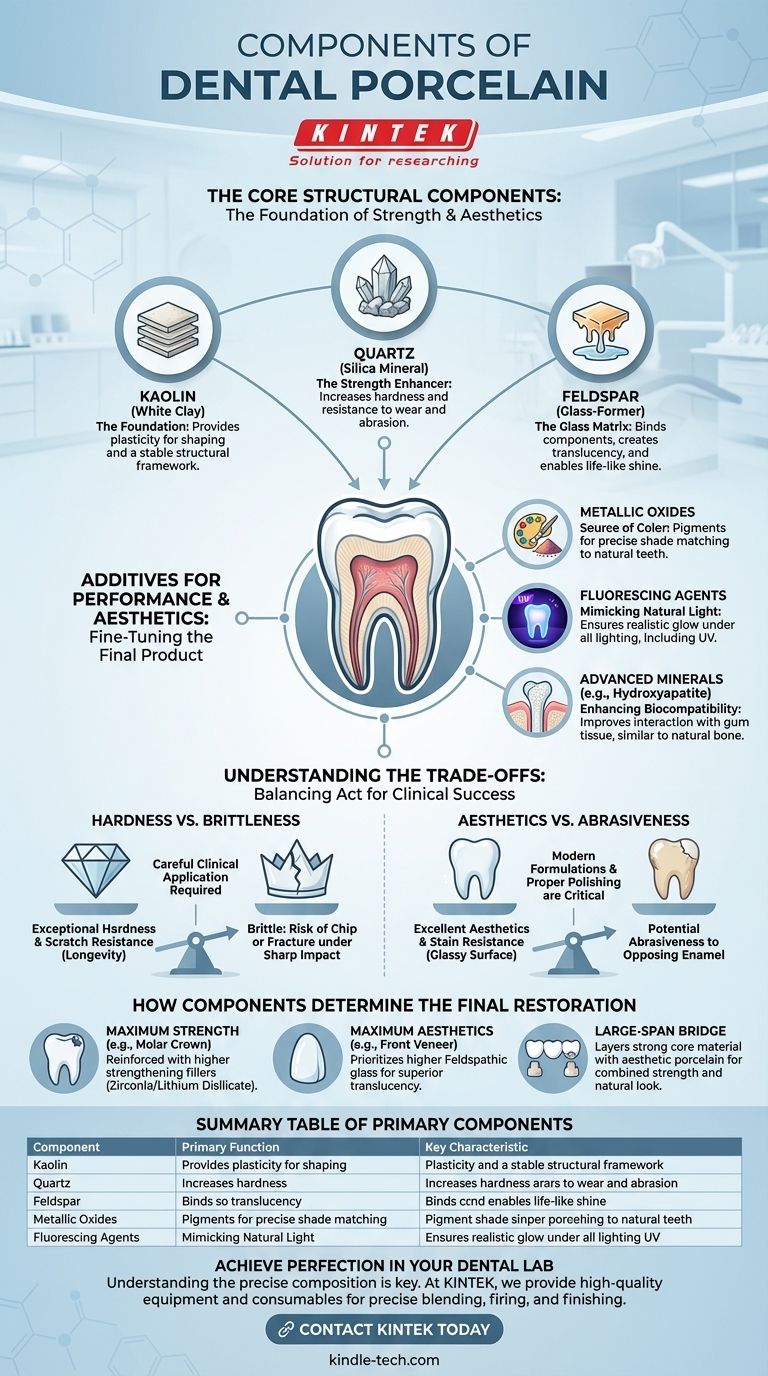
The Core Structural Components
The primary characteristics of any dental porcelain are determined by the ratio of its three main ingredients. Each serves a distinct and critical function in the final product.
Kaolin: The Foundation
Kaolin is a fine, pure white clay. It provides the essential plasticity needed to shape the restoration before it is fired.
During heating, it provides a stable framework, or matrix, that holds the other components in place as they fuse together.
Quartz (Silica): The Strength Enhancer
Quartz is an extremely hard mineral that acts as a strengthening filler within the porcelain mixture.
Its primary role is to increase the material's hardness and resistance to wear and abrasion, ensuring the restoration can withstand the forces of chewing.
Feldspar: The Glass-Forming Matrix
Feldspar is the key to porcelain's aesthetic success. When fired at high temperatures, it melts to form a glass.
This glass matrix flows around and binds the kaolin and quartz particles together. Crucially, it also provides the translucency and shine that allows a porcelain restoration to mimic natural tooth enamel.
Additives for Performance and Aesthetics
Beyond the core three components, manufacturers add small quantities of other substances to fine-tune the porcelain's final properties, from color to biocompatibility.
Metallic Oxides: The Source of Color
The precise shade of a dental restoration is achieved by adding minute amounts of various metallic oxides.
Oxides of iron, titanium, or manganese, among others, are used as pigments to match the restoration to the specific shade of a patient's surrounding teeth.
Fluorescing Agents: Mimicking Natural Light
Natural teeth have a property called fluorescence, meaning they glow slightly under ultraviolet light.
To replicate this subtle effect, special fluorescent minerals are often added. This ensures the restoration looks natural under all lighting conditions, from sunlight to a blacklight.
Advanced Minerals: Enhancing Biocompatibility
Some modern dental ceramics incorporate minerals like hydroxyapatite (HA).
Since HA is the primary mineral component of natural bone and teeth, its inclusion can improve the material's biocompatibility and how it interacts with the surrounding gum tissue.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and the formulation of dental porcelain involves balancing competing properties to achieve the desired clinical result.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
Dental porcelain is exceptionally hard, making it highly resistant to scratching and wear. This is a significant advantage for longevity.
However, this hardness also makes it brittle. A sharp, focused impact can cause it to chip or fracture, a risk that must be managed in its clinical application.
Aesthetics vs. Abrasiveness
The glassy surface of porcelain is responsible for its excellent aesthetics and stain resistance.
In the past, some formulations could be abrasive to the opposing natural teeth. Modern feldspathic porcelains are significantly kinder to opposing enamel, but proper polishing by the dental technician remains critical.
How Components Determine the Final Restoration
The specific blend of these components is adjusted based on the restoration's purpose.
- If the primary focus is maximum strength (e.g., for a molar crown): The formulation will be reinforced with a higher percentage of strengthening fillers, such as zirconia or lithium disilicate, alongside the traditional components.
- If the primary focus is aesthetics (e.g., for a front tooth veneer): The blend will prioritize a higher concentration of feldspathic glass to achieve superior translucency and precise color matching.
- If the primary focus is a large-span bridge: A strong, fracture-resistant core material is used, which is then layered with more aesthetic porcelain to combine mechanical strength with a natural look.
By understanding its core ingredients, you can see how dental porcelain is precisely engineered to meet the demanding requirements of strength, beauty, and biocompatibility.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Kaolin | Provides structural foundation & plasticity | White clay for shaping |
| Quartz | Enhances hardness & wear resistance | Strengthening filler |
| Feldspar | Creates glass matrix for translucency | Provides aesthetic shine |
| Metallic Oxides | Adds color for shade matching | Pigments for aesthetics |
| Fluorescing Agents | Mimics natural tooth glow under UV light | Enhances realism |
Achieve Perfection in Your Dental Lab
Understanding the precise composition of dental porcelain is the first step to creating flawless, long-lasting restorations. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables that dental technicians and laboratories rely on to precisely blend, fire, and finish these advanced materials.
Whether you are crafting durable crowns or aesthetic veneers, our products support the entire process, ensuring consistent results and superior patient outcomes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance the strength, beauty, and efficiency of your dental lab work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance
- What advantages does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace offer for UO2? Precision Fuel Densification
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures











