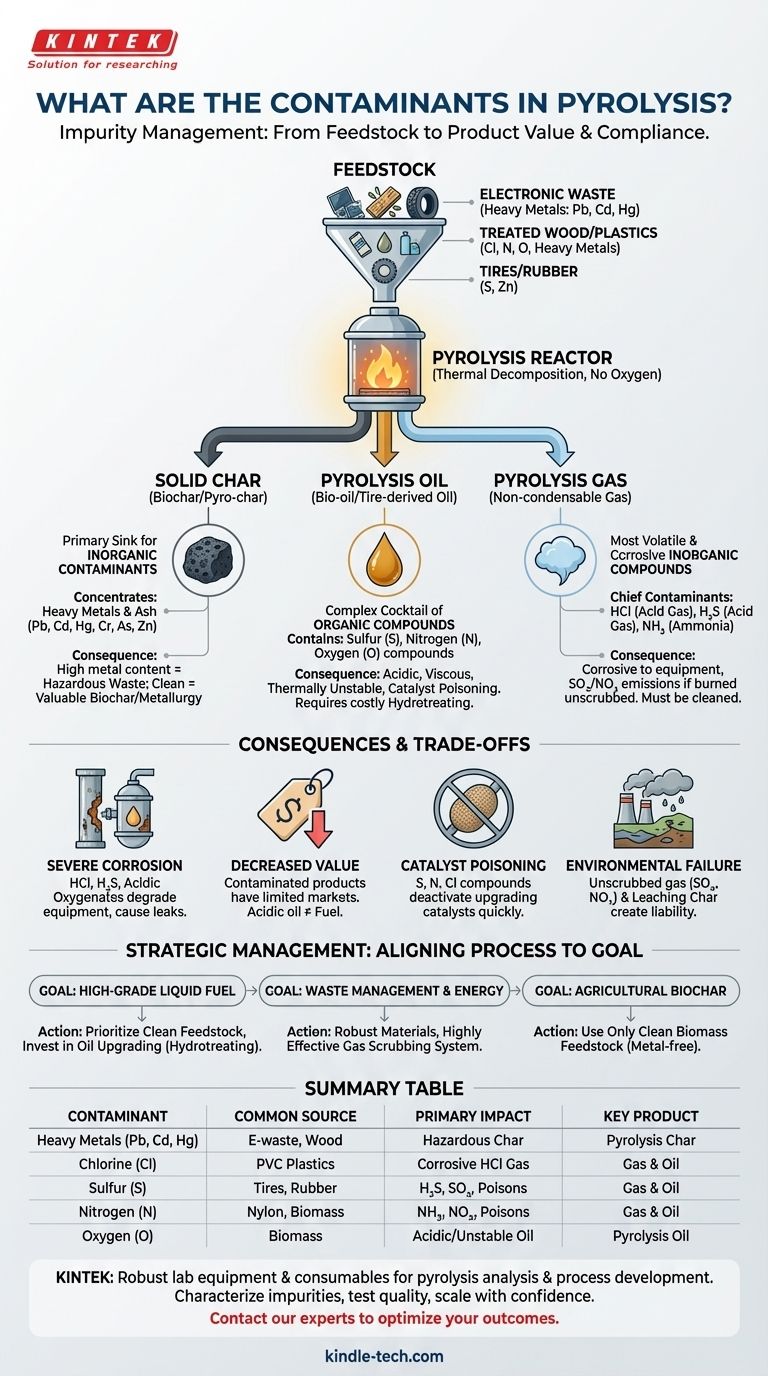
The primary contaminants in pyrolysis are a direct reflection of the initial feedstock and can be broadly categorized into inorganic compounds like heavy metals and organic compounds containing sulfur, nitrogen, and halogens. These impurities are not created by the process itself but are released and transformed from the materials being broken down, distributing themselves across the final products: pyrolysis oil, char, and gas.
The central challenge of pyrolysis is not just thermal decomposition; it is managing the inherent contaminants from the feedstock. The economic viability and environmental compliance of any pyrolysis operation depend entirely on understanding and controlling these impurities from the start.

The Source: Contamination Begins with the Feedstock
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. It doesn't destroy elements, it merely re-arranges them. Therefore, whatever you put into the reactor will come out in a different form across the three product streams.
Inorganic Contaminants: Ash and Heavy Metals
The non-combustible, mineral-based components of the feedstock are collectively known as ash.
These materials do not vaporize during pyrolysis and become concentrated in the solid pyrolysis char (also called biochar or pyro-char).
This category includes benign minerals like silica and alumina but also hazardous heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium, and arsenic, which are often present in electronic waste, treated wood, or certain types of plastics. Zinc is also a major contaminant from tire pyrolysis.
Organic "Heteroatom" Contaminants
These are non-carbon elements chemically bonded within the organic molecules of the feedstock. They are highly problematic because they create corrosive and toxic compounds in the oil and gas phases.
The three most significant heteroatoms are:
- Chlorine: Primarily from plastics like Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). During pyrolysis, it forms highly corrosive hydrochloric acid (HCl) gas and chlorinated organic compounds in the oil.
- Sulfur: Originates from vulcanized rubber in tires and some types of biomass or coal. It primarily converts to hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) in the gas phase and sulfur-containing organic molecules in the oil.
- Nitrogen: Found in plastics like polyurethane and nylon, as well as in the proteins and enzymes within all biomass. It forms compounds like ammonia (NH₃) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the gas phase and nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds (e.g., pyridines) in the oil.
Oxygenated Compounds and Water
While not always viewed as a "contaminant" in the same way as heavy metals, oxygen is a critical impurity, especially in bio-oil derived from biomass.
High oxygen content leads to the formation of carboxylic acids, phenols, and ketones. This makes the bio-oil acidic (low pH), corrosive, and thermally unstable, preventing it from being used as a drop-in fuel without significant upgrading.
Water is also present, either from moisture in the feedstock or as a reaction product, which lowers the energy value of the pyrolysis oil.
Distribution of Contaminants by Product
Contaminants do not distribute evenly. Understanding where they accumulate is crucial for designing purification systems.
In Pyrolysis Oil
The liquid product, often called bio-oil or tire-derived oil, is a complex cocktail. Its primary contaminants are sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen-containing organic compounds. These make the oil viscous, acidic, and unstable, requiring a costly upgrading process called hydrotreating to remove them before it can be co-processed in a traditional refinery.
In Pyrolysis Char
The solid char is the primary sink for inorganic contaminants. All the heavy metals and mineral ash from the feedstock will be concentrated here. This is the single biggest factor determining the char's end-use. High metal content renders it a hazardous waste, while a clean, metal-free char can be a valuable product for agriculture (biochar) or metallurgy.
In Pyrolysis Gas
The non-condensable gas product is where the most volatile and corrosive inorganic compounds end up. The chief contaminants are the acid gases HCl (from chlorine) and H₂S (from sulfur). Ammonia (NH₃) is also a common issue. These gases must be "scrubbed" or cleaned before the gas can be safely burned in an engine or turbine to generate power.
Understanding the Consequences and Trade-offs
Ignoring contaminants leads to operational failure, environmental penalties, and poor economic outcomes.
Severe Equipment Corrosion
The presence of HCl, H₂S, and acidic oxygenates creates a highly corrosive environment inside the reactor and downstream piping, especially when water is present. This can lead to rapid equipment degradation, leaks, and costly shutdowns.
Decreased Product Value and Usability
Contaminated products have severely limited markets. An acidic, unstable oil cannot be used as fuel. A char laden with heavy metals cannot be used on soil. Uncleaned gas will destroy an engine. The value of the outputs is directly tied to their purity.
Catalyst Poisoning during Upgrading
Many processes to upgrade pyrolysis oil to usable fuels rely on catalysts. Sulfur, nitrogen, and chlorine compounds are potent catalyst poisons, deactivating them quickly and adding significant operational expense.
Environmental Compliance Failures
Burning unscrubbed pyrolysis gas can lead to emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), key components of acid rain. Leaching of heavy metals from improperly stored char can contaminate soil and groundwater, leading to significant liability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for dealing with contaminants must align with your primary objective for the pyrolysis unit.
- If your primary focus is producing high-grade liquid fuel: You must prioritize extremely clean, sorted feedstock with minimal PVC, sulfur, and nitrogen, and invest heavily in oil upgrading technologies like hydrotreating.
- If your primary focus is waste management and energy recovery: You must invest in robust, corrosion-resistant reactor materials and a highly effective gas scrubbing system to meet emissions regulations, accepting that your oil and char products may be of lower quality.
- If your primary focus is creating agricultural biochar: Your entire process must be dedicated to using clean, uncontaminated biomass feedstock to ensure the final char is free from heavy metals and other toxins.
Ultimately, proactively managing feedstock contaminants is the defining factor in a successful pyrolysis venture.
Summary Table:
| Contaminant Type | Common Sources | Primary Impact | Key Product Affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals (Pb, Cd, Hg) | Electronic waste, treated wood | Renders char hazardous; soil/water pollution | Pyrolysis Char |
| Chlorine (Cl) | PVC plastics | Forms corrosive HCl gas; catalyst poisoning | Pyrolysis Gas & Oil |
| Sulfur (S) | Tires, rubber | Forms H₂S gas; SOx emissions; catalyst poisoning | Pyrolysis Gas & Oil |
| Nitrogen (N) | Nylon, polyurethane, biomass | Forms NH₃, HCN; NOx emissions; catalyst poisoning | Pyrolysis Gas & Oil |
| Oxygen (O) | Biomass | Makes oil acidic, unstable, and corrosive | Pyrolysis Oil |
Ready to build a successful, compliant pyrolysis operation?
Managing contaminants is critical to your project's efficiency, product value, and environmental compliance. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis analysis and process development. Whether you need to characterize feedstock impurities, test product quality, or scale your process, our solutions help you mitigate risks and optimize outcomes.
Let's ensure your pyrolysis venture is built on a foundation of clarity and control. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Spacer Cam Profile and Various Spacer Types
People Also Ask
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions

















