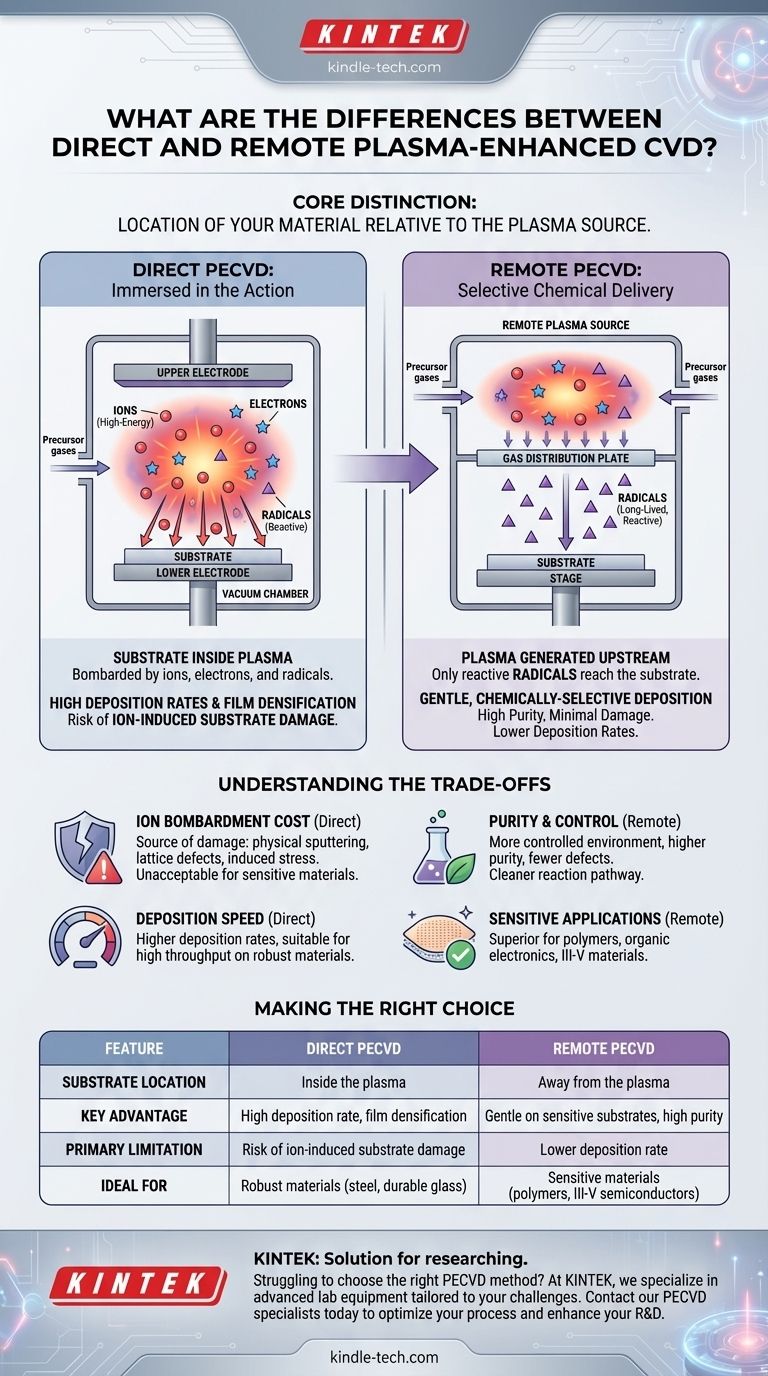
At its core, the difference between direct and remote plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) is the location of your material relative to the plasma source. In direct PECVD, the substrate is placed directly within the plasma, exposing it to a high-energy environment. In remote PECVD, the plasma is generated separately, and only the desired reactive chemical species are transported to the substrate, shielding it from damaging ions.
The decision between direct and remote PECVD is a fundamental trade-off between process intensity and material integrity. Direct PECVD offers higher energy and deposition rates at the cost of potential substrate damage, while remote PECVD prioritizes a gentle, chemically-selective deposition for sensitive applications.
The Role of Plasma in CVD
Before comparing the two methods, it's essential to understand why plasma is used at all.
Why Use Plasma?
Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) relies on high temperatures (often >600°C) to provide the energy needed to break down precursor gases and deposit a film. Plasma-enhanced CVD generates a highly energetic, ionized gas—the plasma—using electromagnetic fields.
This plasma provides an alternative energy pathway for the chemical reactions. By activating the precursor gases in the plasma, the entire process can run at significantly lower temperatures (often <300°C), enabling deposition on materials that cannot withstand high heat, such as polymers or pre-processed semiconductor wafers.
The Components of a Plasma
A plasma isn't a uniform substance. It's a complex soup containing high-energy electrons, positive ions, and chemically reactive but electrically neutral molecules called radicals. Understanding the roles of these components is the key to differentiating direct and remote PECVD.
Direct vs. Remote: A Tale of Two Geometries
The physical arrangement of the reactor fundamentally changes which plasma components interact with your substrate.
Direct PECVD: Immersed in the Action
In a direct PECVD system, the substrate is placed on one of the electrodes used to generate the plasma. It is fully immersed in the plasma glow.
This means the substrate is bombarded by everything: reactive radicals, electrons, and high-energy ions. The ion bombardment can be both a feature and a bug, as it transfers significant kinetic energy to the growing film surface.
Remote PECVD: Selective Chemical Delivery
In a remote PECVD system, the plasma is intentionally generated "upstream" or in a separate chamber, away from the substrate.
The short-lived, high-energy ions and electrons recombine and neutralize before they can travel to the deposition chamber. Only the more stable, long-lived radicals are transported by gas flow to the substrate surface, where they react to form the film. This effectively decouples plasma generation from film deposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Damage vs. Deposition Rate
Your choice of method has direct consequences for your final film quality, your substrate's survival, and your process efficiency.
The High Cost of Ion Bombardment
While the energy from ion bombardment in direct PECVD can sometimes be useful for creating dense films, it is also a primary source of damage. This can manifest as physical sputtering of the substrate, the creation of crystal lattice defects, and induced stress in the final film.
For sensitive electronic materials like III-V semiconductors or flexible organic electronics, this damage is often unacceptable. Remote PECVD almost completely eliminates this risk by keeping energetic ions away from the surface.
The Pursuit of Purity and Control
The high-energy environment of direct PECVD can break precursor molecules into many different fragments. This can lead to the unintended incorporation of impurities (like hydrogen or carbon) into the film, altering its electrical or optical properties.
Because remote PECVD allows for a more controlled chemical environment at the substrate, it generally produces films with higher purity and fewer defects. It provides a "cleaner" chemical reaction pathway.
When Deposition Speed is the Priority
The constant energy flux from ion bombardment in direct PECVD often results in higher deposition rates compared to remote PECVD. For industrial applications where throughput is a key metric and the substrate is robust (e.g., coating steel or durable glass), direct PECVD is often the more economical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method requires you to prioritize your most critical outcome.
- If your primary focus is depositing on sensitive substrates (polymers, organic electronics, III-V materials): Remote PECVD is the superior choice to prevent irreversible ion-induced damage.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible deposition rate on a robust material: Direct PECVD is generally faster and more efficient, provided the resulting film properties meet your needs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing film defects and maximizing chemical purity: Remote PECVD offers unparalleled control by separating the violent plasma generation from the delicate film growth.
- If you are depositing a hard, durable coating and need film densification: The ion bombardment in direct PECVD can be an advantage, helping to compact the growing film.
Ultimately, your choice hinges on a clear understanding of your substrate's limitations and your film's quality requirements.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct PECVD | Remote PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Location | Inside the plasma | Away from the plasma |
| Key Advantage | High deposition rate, film densification | Gentle on sensitive substrates, high purity |
| Primary Limitation | Risk of ion-induced substrate damage | Lower deposition rate |
| Ideal For | Robust materials (e.g., steel, durable glass) | Sensitive materials (e.g., polymers, III-V semiconductors) |
Struggling to choose the right PECVD method for your specific materials and film quality requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique challenges. Whether you're working with delicate polymers requiring the gentle touch of remote PECVD or need the high throughput of direct PECVD for industrial applications, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to optimize your deposition process, protect your substrates, and achieve superior film quality.
Contact our PECVD specialists today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition



















