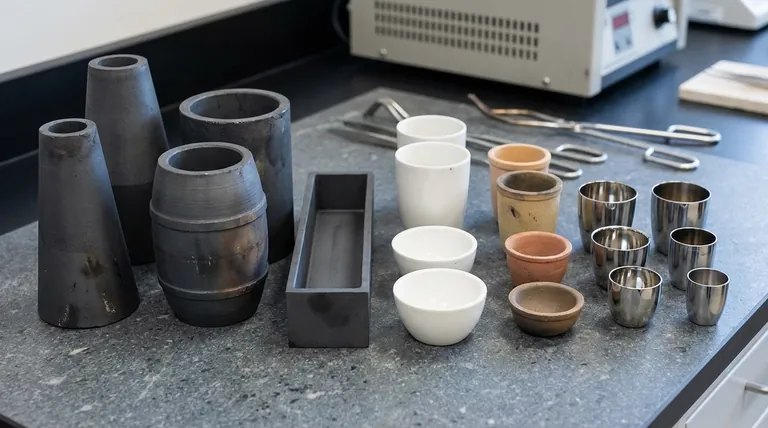
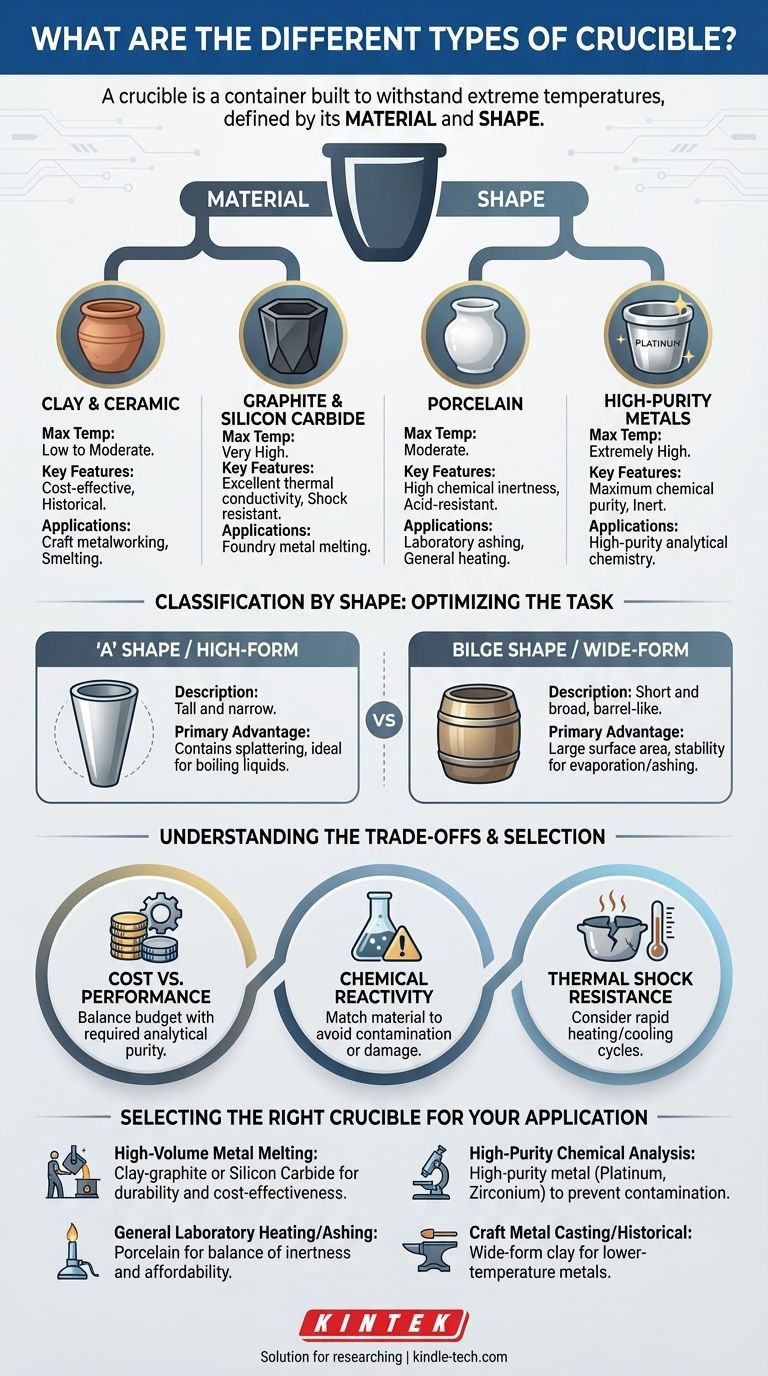
At its core, a crucible is a container built to withstand extreme temperatures, and its "type" is defined by two key characteristics: the material it is made from and its physical shape. Crucibles are categorized based on materials like clay, graphite, silicon carbide, porcelain, and high-purity metals like platinum, which are chosen for their heat resistance and chemical inertness. Their shape, from tall and narrow to wide and shallow, is designed to optimize heating and handling for specific tasks.
Choosing the right crucible is a critical decision based on two factors: the material, which must withstand your maximum temperature and resist chemical reaction with the contents, and the shape, which must be compatible with your furnace and process.

Classification by Material: The Core Decision
The material of a crucible is its most important attribute. It dictates the maximum temperature it can handle, its resistance to chemical attack, and its ability to survive rapid temperature changes (thermal shock).
Clay and Ceramic Crucibles
These are among the earliest and most fundamental types of crucibles, historically used for smelting metals like copper. They are typically made from clay mixed with other refractory materials.
While less common now in high-performance settings, they are cost-effective for lower-temperature applications and craft metalworking.
Graphite and Silicon Carbide Crucibles
These are the workhorses of the modern foundry. They are often made from a composite of clay and graphite or, for more demanding applications, silicon carbide.
Their primary advantage is excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for fast and even heating of the contents. They also have superior resistance to thermal shock, making them durable for repeated cycles of heating and cooling when melting ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Porcelain Crucibles
Porcelain crucibles are a staple in chemistry laboratories. While they cannot handle the extreme temperatures of a foundry, they are highly resistant to chemical attack from acids and corrosive substances.
They are primarily used for tasks like ashing a sample—burning off all organic material to determine the weight of the non-combustible inorganic residue—and for general-purpose heating of chemical compounds.
High-Purity Metal Crucibles
For applications where even the slightest contamination can ruin an analysis, metal crucibles are required. Materials include platinum, zirconium, and specialized alloys like platinum-rhodium.
These are used in analytical chemistry for sample preparation techniques like high-temperature fusions. Their defining features are an extremely high melting point and exceptional chemical inertness, ensuring that the crucible itself does not react with and contaminate the sample.
Classification by Shape: Optimizing the Task
A crucible's shape is not arbitrary; it is designed to suit a specific type of furnace, heating method, or handling requirement.
'A' Shape vs. Bilge Shape
These terms are common in foundry settings. The 'A' shape is a standard tapered, conical design. The bilge shape is wider in the middle, resembling a barrel.
While their surface finishes may differ, the choice between them often comes down to matching the internal shape of the furnace and the type of tongs used to lift and pour.
High-Form vs. Wide-Form
This terminology is more common in laboratory settings. High-form crucibles are tall and narrow, ideal for containing materials that might splatter or boil over during heating.
Wide-form (or squat) crucibles are short and broad. This shape provides a large surface area, making it perfect for processes like evaporation or ashing, where maximum exposure to air is beneficial. They also offer greater stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single crucible is perfect for every job. Selecting one involves balancing performance, cost, and the specific demands of your process.
Cost vs. Performance
This is the most significant trade-off. A platinum crucible offers unmatched performance for analytical purity but costs thousands of dollars. A clay-graphite crucible is a consumable item that costs orders of magnitude less but is unsuitable for high-purity analysis.
Chemical Reactivity
You must match the crucible material to the substance being heated. For example, melting certain metals in a platinum crucible can cause them to form an alloy, permanently damaging the expensive crucible. A material that is inert for one process may be highly reactive in another.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Ceramic and porcelain crucibles can crack if heated or cooled too quickly. Graphite and silicon carbide are far more robust in this regard, which is why they are favored in foundries where rapid cycling is common.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Your final choice should be guided by your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume metal melting (e.g., foundry work): A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best combination of durability, thermal performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical analysis: A high-purity metal crucible, such as platinum or zirconium, is essential to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory heating or ashing samples: A standard porcelain crucible provides a good balance of chemical inertness and affordability for moderate temperatures.
- If your primary focus is craft metal casting or historical smelting: A simple, wide-form clay crucible is both historically appropriate and effective for lower-temperature metals like aluminum, bronze, or copper.
By aligning the crucible's material and shape with your specific temperature, chemical, and process requirements, you ensure the safety and success of your work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay/Ceramic | Low to Moderate | Cost-effective, historical use | Craft metalworking, smelting |
| Graphite/Silicon Carbide | Very High | Excellent thermal conductivity, shock resistant | Foundry metal melting |
| Porcelain | Moderate | High chemical inertness, acid-resistant | Laboratory ashing, general heating |
| Platinum/High-Purity Metals | Extremely High | Maximum chemical purity, inert | High-purity analytical chemistry |
| Shape | Description | Primary Advantage | |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | |
| 'A' Shape / High-Form | Tall and narrow | Contains splattering, ideal for boiling liquids | |
| Bilge Shape / Wide-Form | Short and broad, barrel-like | Large surface area, stability for evaporation/ashing |
Need Help Selecting the Perfect Crucible?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the safety and success of your work. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering a wide range of crucibles for every application—from high-volume foundry melting to ultra-pure analytical chemistry.
Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between material, shape, and cost to find the ideal solution for your specific temperature, chemical, and process requirements.
Ensure optimal performance and durability in your lab or foundry. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What functions do steel crucibles and protective atmospheres serve? Ensure Purity in Mg-Ag Alloy Melting
- Why are nickel crucibles preferred for Li2OHBr preparation? Ensuring High Purity in Molten Electrolytes
- What are the applications of a crucible furnace? Versatile Melting for Small Batches
- What temperature does crucible melt? Choose the Right Material for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the maximum temperature for clay crucibles? Find the Right Crucible for Your Melting Needs
- What are the two types of crucibles and their uses? Choose the Right Crucible for Your Application
- Can you use the same crucible for different metals? Why dedicated crucibles are essential for metal purity and safety.
- What is the function of a graphite crucible in the FFC process? Key to High-Entropy Alloy Production



















