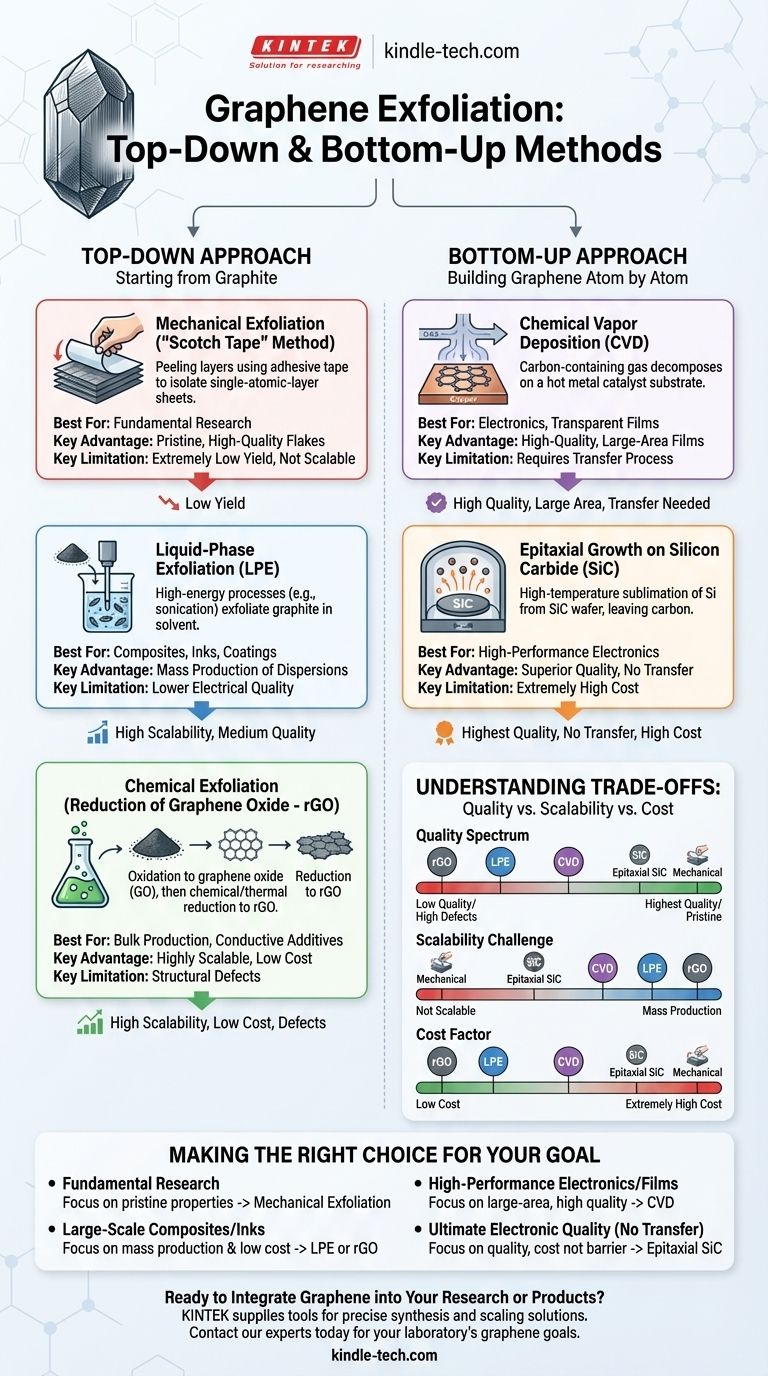
The primary methods for producing graphene are broadly categorized into "top-down" exfoliation from graphite and "bottom-up" synthesis. Top-down methods include mechanical exfoliation, liquid-phase exfoliation (LPE), and the chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO). The main bottom-up approach is chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which builds graphene atom by atom on a substrate.
The "best" method for producing graphene does not exist in a vacuum. The optimal choice is always a trade-off between the desired quality, the required quantity, and the acceptable cost for a specific application.

The "Top-Down" Approach: Starting from Graphite
Top-down methods begin with bulk graphite and separate it into individual or few-layer graphene sheets. These techniques are conceptually simple but vary significantly in their scalability and the quality of the final product.
Mechanical Exfoliation (The "Scotch Tape" Method)
This is the original technique used to first isolate graphene. It involves using adhesive tape to repeatedly peel layers from a piece of highly ordered graphite until a single-atomic-layer sheet is achieved.
While it can produce pristine, defect-free graphene flakes with exceptional electronic properties, the process has extremely low yield. It is not scalable for industrial production and is almost exclusively used for fundamental research.
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE)
LPE is a more scalable top-down approach. Graphite powder is dispersed in a solvent and then subjected to high-energy processes like sonication or high-shear mixing. These forces overcome the van der Waals forces holding the graphite layers together, causing them to exfoliate into graphene flakes suspended in the liquid.
This method is well-suited for mass production of graphene dispersions, which are used in composites, coatings, and inks. However, the resulting flakes are often multi-layered and can have a lower electrical quality compared to other methods.
Chemical Exfoliation (Reduction of Graphene Oxide)
This is another highly scalable chemical route. Bulk graphite is first aggressively oxidized to form graphite oxide, which is easily exfoliated in water to produce graphene oxide (GO). The GO is then "reduced" using chemical or thermal treatments to remove the oxygen functional groups, yielding reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
Like LPE, this process is excellent for bulk production. However, the harsh chemical oxidation and subsequent reduction processes introduce structural defects into the graphene lattice, which can significantly impair its electrical conductivity.
The "Bottom-Up" Approach: Building Graphene Atom by Atom
Bottom-up methods construct graphene from carbon-containing precursor molecules on a substrate. This allows for greater control over the structure and uniformity of the final film.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the most prominent technique for producing high-quality, large-area graphene films. In this process, a carbon-containing gas (like methane) is introduced into a high-temperature furnace containing a metal catalyst substrate, typically copper or nickel. The gas decomposes, and carbon atoms arrange themselves into the hexagonal graphene lattice on the metal surface.
The resulting film can then be transferred to a target substrate (like silicon or plastic), making CVD the leading method for applications in electronics and transparent conductive films.
Epitaxial Growth on Silicon Carbide (SiC)
This method involves heating a silicon carbide wafer to very high temperatures (above 1,100 °C) in a vacuum. The silicon atoms sublime from the surface, leaving behind the carbon atoms, which then rearrange themselves into a graphene layer directly on the SiC substrate.
This produces very high-quality graphene without the need for a transfer step. However, the extremely high cost of the SiC wafers limits its use to specialized, high-performance electronic applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
No single graphene production method is superior in all aspects. The choice is a deliberate compromise based on your primary goal.
The Quality Spectrum
The quality of graphene, measured by factors like crystal size, defect density, and electrical conductivity, varies significantly. Mechanical exfoliation and epitaxial growth on SiC produce the highest-quality material. CVD follows closely, while LPE and rGO produce graphene with more defects and lower electrical performance.
The Scalability Challenge
For applications requiring large quantities (tons) or large surface areas (square meters), scalability is paramount. LPE and rGO are the most scalable for bulk production of powders and dispersions. CVD is the most scalable for producing large-area films. Mechanical exfoliation is fundamentally unscalable.
The Cost Factor
Cost is often the deciding factor. The high cost of SiC wafers makes epitaxial growth prohibitive for most uses. Bulk methods like LPE and rGO are relatively low-cost. CVD represents a middle ground, where the cost is justified by the high quality and large area required for electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct method, you must first define your priority.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine properties: Mechanical exfoliation is the gold standard for producing small, ultra-high-quality flakes.
- If your primary focus is large-scale composites, inks, or conductive additives: Liquid-phase exfoliation or reduced graphene oxide provides the best balance of mass production and low cost.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or transparent films: Chemical vapor deposition is the most practical method for growing large-area, high-quality graphene films.
- If your primary focus is ultimate electronic quality without a transfer step (and cost is not a major barrier): Epitaxial growth on silicon carbide is the superior choice.
By aligning the production method with your end goal, you can effectively harness the unique properties of graphene for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Fundamental Research | Pristine, High-Quality Flakes | Extremely Low Yield, Not Scalable |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE) | Composites, Inks, Coatings | Mass Production of Dispersions | Lower Electrical Quality |
| Chemical Exfoliation (rGO) | Bulk Production, Conductive Additives | Highly Scalable, Low Cost | Structural Defects |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Electronics, Transparent Films | High-Quality, Large-Area Films | Requires Transfer Process |
| Epitaxial Growth (SiC) | High-Performance Electronics | Superior Quality, No Transfer | Extremely High Cost |
Ready to Integrate Graphene into Your Research or Products?
Choosing the right production method is critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert support needed for your graphene applications.
- For Research & Development: We supply tools for precise material synthesis and analysis.
- For Process Scaling: Our solutions help bridge the gap from lab-scale to pilot-scale production.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the optimal equipment and consumables for your laboratory's graphene goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- How many balls are needed for a ball mill? Optimize grinding with the right charge volume.
- How full should a ball mill be? Achieve Peak Grinding Efficiency with the 50% Rule
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge
- How does particle size affect XRF? Achieve Accurate and Repeatable Elemental Analysis
- What is grinder in chemistry? A Guide to Precision Sample Preparation



















